Borneo, a name that conjures images of lush rainforests, exotic wildlife, and vibrant cultures, is the third-largest island in the world. But Where Is Borneo Located exactly? Nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, Borneo is a geographical treasure, surrounded by a tapestry of seas and neighboring islands. Understanding its precise location is the first step to appreciating its unique ecological and cultural significance. This article will delve into the geographical coordinates of Borneo, explore its surrounding waters and neighboring lands, and highlight why its location is so crucial to its identity.
Geographical Location of Borneo
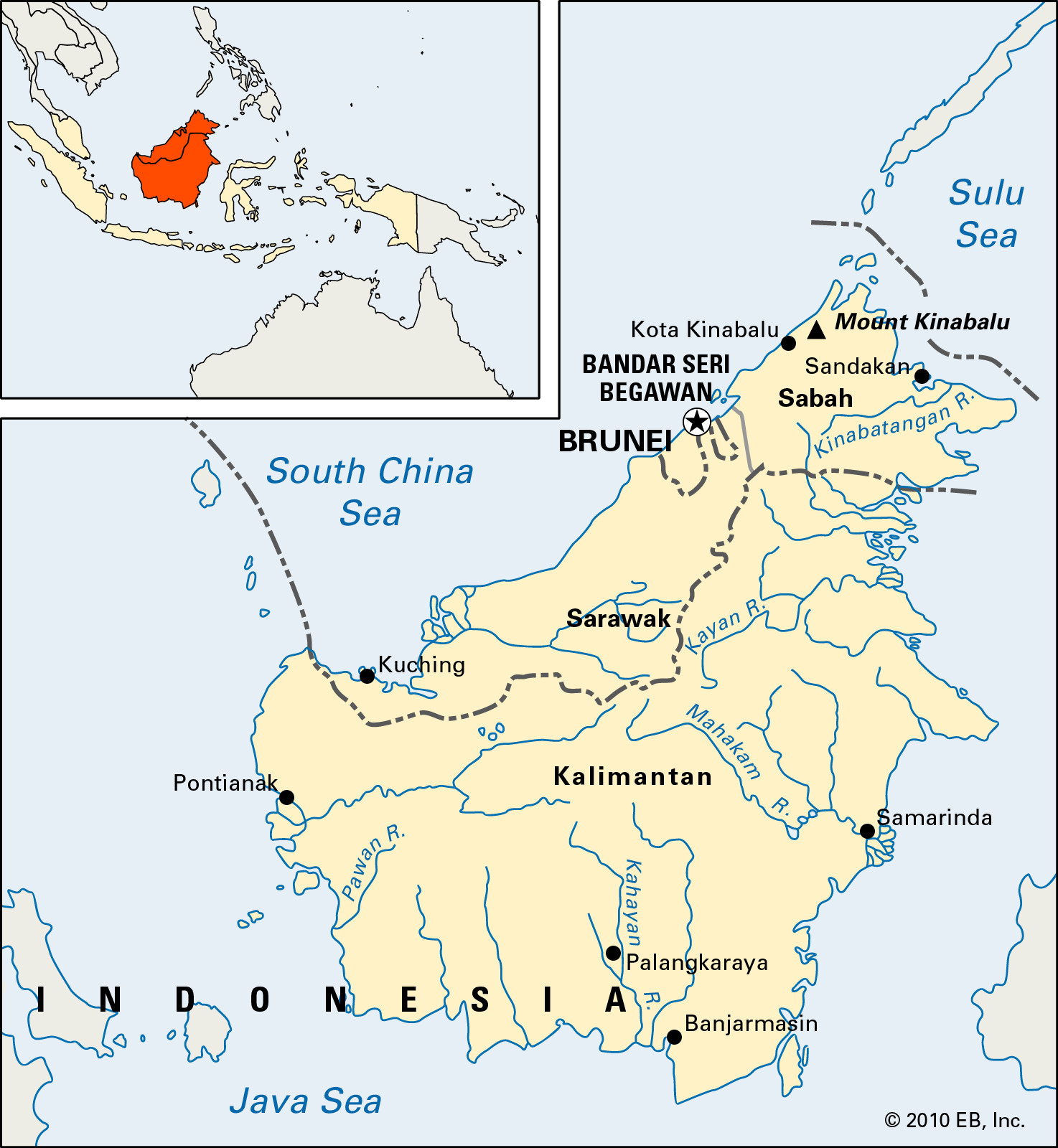
Borneo is strategically positioned in the southwestern part of the Pacific Ocean. More specifically, it sits within the Malay Archipelago, the world’s largest archipelago, and is part of the Greater Sunda Islands. To pinpoint Borneo’s location in relation to mainland Asia, it lies southeast of the Malay Peninsula.
The island is bordered by several important bodies of water that define its maritime context:
- To the northwest lies the South China Sea, a critical waterway for global trade and biodiversity.
- The northeast is flanked by the Sulu Sea, known for its stunning coral reefs and diverse marine life.
- To the east, the Celebes Sea (also known as the Sulawesi Sea) separates Borneo from the island of Celebes (Sulawesi).
- Finally, the Java Sea forms Borneo’s southern boundary, lying between Borneo and the densely populated island of Java.
The Makassar Strait, situated to the east and southeast, acts as a significant passage separating Borneo from Celebes (Sulawesi). To the west, a series of shallower seas and straits create a maritime bridge between Borneo and the island of Sumatra.
Borneo’s Political Divisions: A Tri-Nation Island
Adding another layer of complexity to Borneo’s location is its unique political landscape. Unlike many islands belonging to a single nation, Borneo is shared by three different countries:
- Indonesia: The largest portion of the island belongs to Indonesia, and this region is known as Kalimantan. Kalimantan is further divided into five provinces: Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, South Kalimantan, and West Kalimantan.
- Malaysia: Two Malaysian states, Sabah and Sarawak, are situated on the northwest coast and northern tip of Borneo. These states are often collectively referred to as East Malaysia.
- Brunei: Nestled between Sarawak and Sabah is the independent sultanate of Brunei, a small but oil-rich nation.
This tri-national division makes Borneo’s geographical location not just a point on a map, but a place where different cultures, histories, and political systems intersect.
Key Geographical Features of Borneo
Borneo’s location near the Equator profoundly influences its climate and environment. Straddling the Equator, Borneo experiences an equatorial climate – hot and humid year-round. This tropical location is a major factor contributing to its dense rainforests, which are among the oldest and most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
The island’s terrain is largely mountainous, featuring a central spine of ranges extending southwest from Mount Kinabalu in the northeast. Mount Kinabalu, the highest peak in Borneo and Malaysia, reaches an elevation of 13,455 feet (4,101 meters). Despite the mountains, Borneo also has extensive lowland areas, particularly in Kalimantan and Sarawak, which are often swampy near the coasts.
Rivers are vital to Borneo’s geography and its inhabitants. Numerous navigable rivers, such as the Kapuas and Mahakam, serve as crucial transportation and trade routes. These rivers have historically been the lifelines for communities within Borneo’s interior.
The island’s equatorial location results in a distinct division into two seasons: the wet monsoon period (landas) from October to March and a drier period (tedoh) for the rest of the year. The average annual rainfall is abundant, contributing to the island’s lush vegetation.
Borneo’s rainforests are famed for their extraordinary biodiversity. They are home to a vast array of flora and fauna, including unique species like the orangutan, proboscis monkey, and the Rafflesia arnoldii, the world’s largest flower.
Conclusion: Borneo’s Location – A Crossroads of Nature and Culture
In conclusion, Borneo is located in Southeast Asia, within the Malay Archipelago and the Greater Sunda Islands, southeast of the Malay Peninsula. It is surrounded by the South China Sea, Sulu Sea, Celebes Sea, and Java Sea. This strategically important location is shared by Indonesia (Kalimantan), Malaysia (Sabah and Sarawak), and Brunei.
Borneo’s location is not just a matter of coordinates; it’s fundamental to understanding its climate, biodiversity, and cultural tapestry. Its equatorial position fosters its rainforests and diverse wildlife, while its tri-national division makes it a fascinating crossroads of different societies. Exploring where Borneo is located reveals the gateway to a world of natural wonders and cultural richness, inviting further exploration and discovery.
[
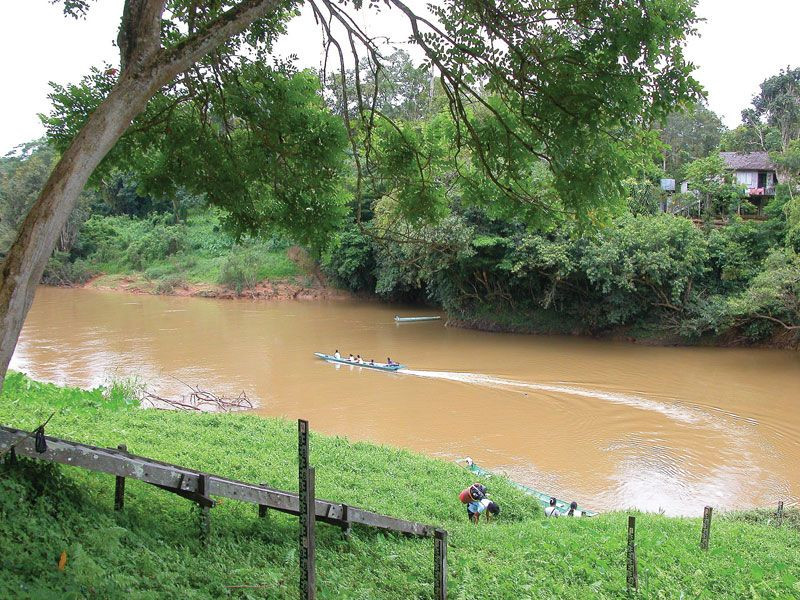
 Sarawak: river
Sarawak: river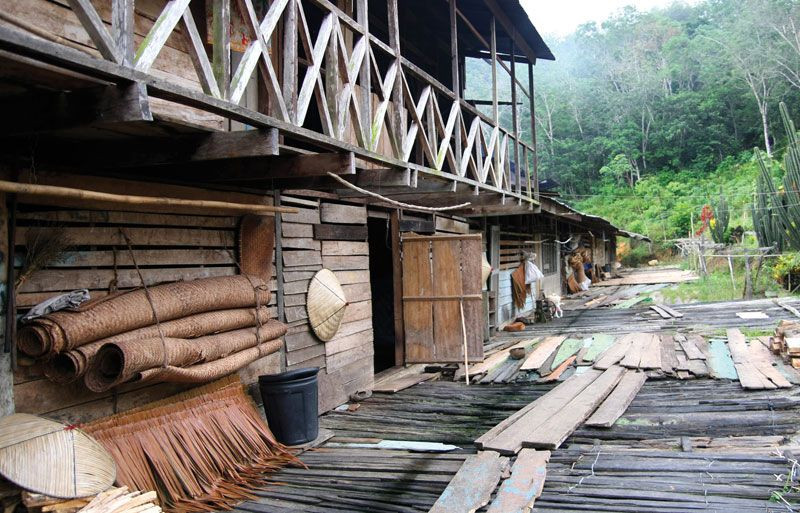 longhouse
longhouse