Planning for retirement can feel like navigating a maze, but understanding How Much Do I Need To Save To Retire is the first step towards financial security. At savewhere.net, we offer clear, actionable strategies to help you determine your retirement savings target and achieve your financial goals, ensuring a stress-free and enjoyable retirement, and financial freedom.
1. What’s the Magic Number: How Much Should I Save for Retirement?
The golden question: just how much should you stash away for those golden years? Determining the ideal retirement savings amount isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. The answer to the question “how much do I need to save to retire” depends on factors like your desired lifestyle, anticipated expenses, and expected retirement age. Let’s break it down:
-
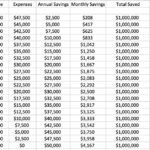
The Rule of Thumb: A common guideline suggests saving 25 times your estimated annual retirement expenses. For example, if you anticipate needing $60,000 per year in retirement, you’d aim for a nest egg of $1.5 million.
-
The 4% Rule: This principle suggests you can withdraw 4% of your retirement savings each year without running out of money. It’s a useful benchmark, but it’s not foolproof. You can adjust it based on your risk tolerance.
-
Personalized Calculation: To get a more accurate picture, consider these factors:
- Current Age: This will change the time you have left to save.
- Desired Retirement Age: When you want to retire plays a big role in how much you need to save.
- Current Savings: What you have already saved will impact the amount needed.
- Estimated Retirement Expenses: Figure out what your expenses will be in retirement.
- Expected Investment Returns: How your investments perform will affect your savings.
- Other Sources of Income: Consider Social Security, pensions, or other income.
Remember, it’s better to overestimate than underestimate.
2. Digging Deeper: Factors That Influence Your Retirement Savings Target
The number you need isn’t pulled from thin air. Several factors dramatically influence how much you should squirrel away:
- Lifestyle Expectations: Do you dream of traveling the world or prefer staying close to home? Luxurious lifestyles require heftier savings.
- Healthcare Costs: Healthcare expenses tend to increase as we age. Factor in potential medical bills and insurance premiums.
- Inflation: The cost of goods and services will rise over time. Account for inflation when estimating your future expenses. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics provides valuable data on inflation trends, which can help you make informed projections.
- Longevity: People are living longer. This means your retirement savings need to stretch further.
- Taxes: Don’t forget about taxes. Depending on your retirement income sources, you may owe income taxes, property taxes, and other levies.
- Unexpected Expenses: Life throws curveballs. Car repairs, home renovations, or unforeseen medical emergencies can put a dent in your retirement savings.
- Debt: Entering retirement with debt can significantly impact your financial security. Prioritize paying off high-interest debt before you retire.
- Social Security Benefits: While Social Security can provide a safety net, it’s unlikely to cover all your retirement expenses. Estimate your Social Security benefits using the Social Security Administration’s calculator.
- Pension Plans: If you have a pension plan, factor in the expected payments when calculating your retirement savings needs.
- Part-Time Work: Plan to work part-time in retirement? This supplemental income can reduce the amount you need to withdraw from your savings.
3. The 70% Rule: A Simpler Approach to Retirement Planning
Not keen on crunching a ton of numbers? The 70% rule offers a more straightforward approach. The 70% rule suggests that you’ll need about 70% of your pre-retirement income to maintain your current lifestyle in retirement. The basic idea behind the 70% rule is that you won’t need 100% of your current income because some expenses, like commuting costs and retirement savings contributions, will disappear.
- How it Works: Estimate your current annual income and multiply it by 70%. This is the income you’ll need to generate from your retirement savings and other sources.
- Example: If you currently earn $80,000 per year, you’d aim for $56,000 per year in retirement income.
- Pros: Simple to calculate and easy to understand.
- Cons: It may not be accurate for everyone, especially those with unique financial circumstances or ambitious retirement goals.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: Calculating Your Retirement Number
Ready to put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard)? Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating your retirement number:
- Estimate Your Annual Retirement Expenses: Start by listing all your anticipated expenses in retirement, including housing, food, transportation, healthcare, travel, and entertainment.
- Factor in Inflation: Adjust your estimated expenses for inflation. Use a conservative inflation rate, such as 3%, to project future costs.
- Calculate Your Retirement Income Needs: Multiply your inflation-adjusted annual expenses by the number of years you expect to be retired.
- Subtract Other Sources of Income: Deduct any income you expect to receive from Social Security, pensions, or part-time work.
- Calculate Your Retirement Savings Goal: The remaining amount is the total you’ll need to save for retirement.
Let’s illustrate with an example:
- Estimated Annual Expenses: $50,000
- Inflation Rate: 3%
- Years in Retirement: 30
- Social Security Benefits: $20,000 per year
Calculation:
- Inflation-Adjusted Annual Expenses: $50,000 * (1 + 0.03)^30 = $121,363
- Total Retirement Income Needs: $121,363 * 30 = $3,640,890
- Social Security Benefits: $20,000 * 30 = $600,000
- Retirement Savings Goal: $3,640,890 – $600,000 = $3,040,890
In this scenario, you’d need to save approximately $3 million to retire comfortably.
5. Supercharge Your Savings: Strategies to Reach Your Retirement Goals
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Compounding-Interest-Chart-Update-2023-02-07-f73f1a4923444283a7b3b0d728591484.png)
Saving for retirement isn’t a sprint. It’s a marathon. Here are some strategies to help you stay on track:
- Start Early: The earlier you start saving, the more time your money has to grow.
- Automate Your Savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your retirement savings account each month.
- Take Advantage of Employer Matching: If your employer offers a 401(k) match, contribute enough to get the full match. It’s free money.
- Increase Your Contribution Rate: Gradually increase your contribution rate over time. Even a small increase can make a big difference.
- Diversify Your Investments: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate.
- Rebalance Your Portfolio: Periodically rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation.
- Minimize Fees: High fees can eat into your investment returns. Opt for low-cost investment options, such as index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- Avoid Debt: Minimize debt, especially high-interest debt, such as credit card debt.
- Consider a Roth IRA: A Roth IRA offers tax advantages that can boost your retirement savings.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
- Cut Back on Expenses: Identify areas where you can cut back on spending and redirect those savings to your retirement account.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your retirement plan and adjust it as needed to stay on track.
6. Retirement Savings Vehicles: Choosing the Right Account
Selecting the right retirement savings account is crucial for maximizing your savings potential. Here are some popular options:
- 401(k): A 401(k) is a retirement savings plan sponsored by your employer. It allows you to contribute a portion of your salary on a pre-tax basis, reducing your taxable income. Many employers offer matching contributions, which can significantly boost your savings.
- IRA (Individual Retirement Account): An IRA is a retirement savings account that you can open on your own. There are two main types of IRAs: Traditional and Roth. Traditional IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions, while Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Roth IRA: A Roth IRA is funded with after-tax dollars, but your earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals in retirement are also tax-free. This can be a great option if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
- SEP IRA: A SEP IRA is a retirement savings account for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It allows you to contribute a percentage of your self-employment income on a pre-tax basis.
- SIMPLE IRA: A SIMPLE IRA is another retirement savings account for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It offers a simplified contribution structure compared to a SEP IRA.
- Taxable Brokerage Account: A taxable brokerage account allows you to invest in stocks, bonds, and other assets. While it doesn’t offer the same tax advantages as retirement accounts, it can be a useful supplement to your retirement savings.
7. Catch-Up Contributions: Making Up for Lost Time
Falling behind on your retirement savings? Don’t despair. Catch-up contributions can help you make up for lost time. If you’re age 50 or older, you’re eligible to make catch-up contributions to your 401(k) or IRA.
- 401(k) Catch-Up Contributions: In 2023, the catch-up contribution limit for 401(k)s is $7,500. This means you can contribute an additional $7,500 to your 401(k) on top of the regular contribution limit of $22,500.
- IRA Catch-Up Contributions: In 2023, the catch-up contribution limit for IRAs is $1,000. This means you can contribute an additional $1,000 to your IRA on top of the regular contribution limit of $6,500.
Catch-up contributions can significantly boost your retirement savings, especially if you’re nearing retirement age.
8. Retirement Planning Tools and Resources: Leveraging Technology for Success
Numerous tools and resources can help you plan for retirement:
- Retirement Calculators: Online retirement calculators can help you estimate your retirement savings needs and track your progress.
- Financial Planning Software: Financial planning software can help you create a comprehensive retirement plan and manage your investments.
- Financial Advisors: A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and help you make informed decisions about your retirement savings.
- Websites and Blogs: Numerous websites and blogs offer valuable information and advice on retirement planning.
Here at savewhere.net, we have an arsenal of tools that will help you estimate your expenses and savings for the future.
9. Common Retirement Planning Mistakes: Avoiding Pitfalls
Steer clear of these common retirement planning mistakes:
- Procrastinating: Delaying retirement planning can significantly reduce your savings potential.
- Underestimating Expenses: Failing to accurately estimate your retirement expenses can lead to financial shortfalls.
- Investing Too Conservatively: Investing too conservatively can limit your investment returns and make it difficult to reach your retirement goals.
- Withdrawing Too Early: Withdrawing from your retirement accounts before retirement can trigger penalties and reduce your savings.
- Ignoring Inflation: Failing to account for inflation can erode the purchasing power of your retirement savings.
- Not Diversifying: Not diversifying your investments can increase your risk and reduce your potential returns.
- Ignoring Taxes: Failing to consider taxes can reduce your retirement income.
- Not Seeking Professional Advice: Not seeking professional advice can lead to poor financial decisions.
10. Retirement Abroad: Considering International Options
Dreaming of retiring in a tropical paradise? Retiring abroad can be an attractive option for those seeking a lower cost of living or a different lifestyle. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the financial implications.
- Cost of Living: Research the cost of living in your desired retirement destination. Some countries offer a significantly lower cost of living than the United States.
- Healthcare: Investigate the healthcare system in your chosen country. Ensure you have access to quality healthcare at an affordable price.
- Taxes: Understand the tax implications of retiring abroad. You may be subject to taxes in both the United States and your retirement destination.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Be aware of currency exchange rates. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact your retirement income.
- Cultural Differences: Consider the cultural differences in your chosen country. Ensure you’re comfortable adapting to a new culture.
11. The Role of Social Security in Retirement Planning
Social Security is a crucial component of retirement planning for many Americans. It provides a safety net of income that can help cover basic living expenses in retirement.
- Eligibility: To be eligible for Social Security benefits, you must have worked and paid Social Security taxes for at least 10 years (40 credits).
- Benefit Amount: The amount of your Social Security benefits depends on your earnings history, your age at retirement, and other factors.
- Retirement Age: You can start receiving Social Security benefits as early as age 62, but your benefits will be reduced if you retire before your full retirement age (FRA). The FRA is 67 for those born in 1960 or later.
- Delaying Benefits: You can increase your Social Security benefits by delaying retirement until age 70. For each year you delay, your benefits will increase by 8%.
- Spousal Benefits: If you’re married, you may be eligible for spousal benefits based on your spouse’s earnings history.
- Survivor Benefits: If your spouse dies, you may be eligible for survivor benefits based on their earnings history.
12. Managing Risk in Retirement: Protecting Your Nest Egg
Managing risk is crucial in retirement. Protecting your nest egg from market volatility and unexpected expenses is vital for ensuring financial security.
- Asset Allocation: Maintain a diversified asset allocation that aligns with your risk tolerance and time horizon.
- Withdrawal Rate: Be mindful of your withdrawal rate. Withdrawing too much too soon can deplete your savings.
- Healthcare Costs: Plan for healthcare costs. Consider purchasing long-term care insurance to protect against the cost of long-term care.
- Inflation: Protect your savings from inflation by investing in assets that tend to outpace inflation, such as stocks and real estate.
- Emergency Fund: Maintain an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Insurance: Ensure you have adequate insurance coverage, including health insurance, homeowners insurance, and life insurance.
13. Estate Planning: Leaving a Legacy
Estate planning is an essential part of retirement planning. It involves creating a plan for how your assets will be distributed after your death.
- Will: A will is a legal document that specifies how your assets will be distributed after your death.
- Trust: A trust is a legal arrangement that allows you to transfer assets to a trustee, who manages the assets for the benefit of your beneficiaries.
- Power of Attorney: A power of attorney is a legal document that authorizes someone to act on your behalf if you become incapacitated.
- Healthcare Directive: A healthcare directive is a legal document that specifies your wishes regarding medical treatment if you become unable to make decisions for yourself.
- Beneficiary Designations: Ensure your beneficiary designations are up to date on all your retirement accounts and insurance policies.
14. Early Retirement: Is It Possible?
Dreaming of retiring early? Early retirement is possible, but it requires careful planning and significant savings.
- Savings Rate: To retire early, you’ll need to save a higher percentage of your income than someone who retires at a traditional retirement age.
- Expenses: You’ll need to carefully estimate your expenses and ensure your savings can cover them for a longer period.
- Healthcare: Healthcare costs can be a significant expense for early retirees.
- Taxes: You’ll need to consider the tax implications of withdrawing from your retirement accounts early.
- Part-Time Work: Consider working part-time in retirement to supplement your income.
15. Maintaining Financial Flexibility in Retirement
Maintaining financial flexibility is crucial in retirement. Life can throw curveballs, and having the ability to adapt to changing circumstances is essential.
- Emergency Fund: Maintain an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Liquid Assets: Keep a portion of your savings in liquid assets, such as cash or short-term investments, that you can access easily.
- Line of Credit: Consider establishing a line of credit that you can tap into if needed.
- Part-Time Work: Be open to working part-time in retirement to supplement your income.
- Downsizing: Consider downsizing your home to reduce your expenses.
- Budgeting: Stick to a budget to track your income and expenses and ensure you’re not overspending.
16. Seeking Professional Financial Advice
Navigating the complexities of retirement planning can be daunting. Seeking professional financial advice can provide personalized guidance and help you make informed decisions.
- Financial Advisor: A financial advisor can help you create a comprehensive retirement plan, manage your investments, and navigate the tax implications of retirement.
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP): A CFP is a financial advisor who has met specific education and experience requirements and has passed a rigorous examination.
- Fee-Only Advisor: A fee-only advisor is a financial advisor who is compensated solely by fees paid by their clients, rather than commissions from selling financial products.
- Fiduciary: A fiduciary is a financial advisor who is legally obligated to act in their clients’ best interests.
17. Utilizing SaveWhere.net to Maximize Retirement Savings
At savewhere.net, we provide a wealth of resources to help you maximize your retirement savings.
- Budgeting Tools: Use our budgeting tools to track your income and expenses and identify areas where you can save money.
- Savings Calculators: Use our savings calculators to estimate how much you need to save for retirement and track your progress.
- Investment Guides: Access our investment guides to learn about different investment options and strategies.
- Financial Articles: Read our financial articles for tips and advice on retirement planning, saving money, and managing your finances.
- Community Forum: Join our community forum to connect with other savers and share tips and advice.
Take action today and start planning for a secure and fulfilling retirement!
18. Real-Life Examples: Retirement Savings Success Stories
Inspiration can come from seeing how others have successfully navigated their retirement savings journey. Here are a few real-life examples to motivate you:
- The Frugal Couple: A couple in their late 50s, earning a combined income of $120,000, committed to saving 25% of their income for retirement. Through diligent budgeting and smart investing, they reached their retirement goal of $1.5 million in just 15 years.
- The Early Starter: A young professional who started saving for retirement in their early 20s, contributing just 10% of their income to a 401(k). Thanks to the power of compounding, they were able to retire comfortably in their early 60s.
- The Catch-Up Contributor: A woman in her early 50s realized she was behind on her retirement savings. She started making catch-up contributions to her 401(k) and was able to significantly boost her savings in just a few years.
These stories demonstrate that with discipline, planning, and the right strategies, anyone can achieve their retirement savings goals.
19. Retirement Savings: Staying Motivated and Disciplined
The road to retirement can be long, so it’s important to stay motivated and disciplined along the way. Here are some tips to help you stay on track:
- Set Clear Goals: Define your retirement goals and write them down.
- Track Your Progress: Regularly track your progress and celebrate your milestones.
- Visualize Your Future: Imagine yourself enjoying your retirement. This can help you stay motivated.
- Find a Support System: Connect with other savers and share tips and advice.
- Reward Yourself: Treat yourself to something special when you reach a savings milestone.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on the latest retirement planning news and advice.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Retirement Savings
Here are some frequently asked questions about retirement savings:
- How much do I need to save to retire?
- The amount you need to save depends on your desired lifestyle, anticipated expenses, and expected retirement age. A common guideline suggests saving 25 times your estimated annual retirement expenses.
- What is the 4% rule?
- The 4% rule suggests you can withdraw 4% of your retirement savings each year without running out of money.
- What are the different types of retirement savings accounts?
- Popular options include 401(k)s, IRAs, Roth IRAs, SEP IRAs, and SIMPLE IRAs.
- What are catch-up contributions?
- Catch-up contributions allow individuals age 50 or older to contribute additional amounts to their 401(k) or IRA.
- How can I stay motivated to save for retirement?
- Set clear goals, track your progress, visualize your future, find a support system, and reward yourself.
- What are some common retirement planning mistakes?
- Procrastinating, underestimating expenses, investing too conservatively, withdrawing too early, and ignoring inflation.
- Should I seek professional financial advice?
- Seeking professional financial advice can provide personalized guidance and help you make informed decisions.
- What role does Social Security play in retirement planning?
- Social Security provides a safety net of income that can help cover basic living expenses in retirement.
- How can I manage risk in retirement?
- Maintain a diversified asset allocation, be mindful of your withdrawal rate, plan for healthcare costs, and protect your savings from inflation.
- What is estate planning?
- Estate planning involves creating a plan for how your assets will be distributed after your death.
Call to Action
Ready to take control of your financial future? Visit savewhere.net today to discover valuable tips, explore money-saving deals, and connect with a supportive community. Start building your dream retirement now! Address: 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States. Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000.