Can You Save A Plant With A Broken Stem? Absolutely, you can often save a plant with a broken stem by acting quickly and using techniques similar to grafting, a method savewhere.net champions for plant revival. This approach, which encourages plant mending, can bring back injured plants, helping you keep your garden flourishing and save money on replacements. Discover how to protect your greenery, promoting plant growth and guaranteeing your plants’ health with this simple yet efficient strategy for plant recovery.
1. Understanding Plant Stem Breaks and Your Options
Yes, it’s often possible to save a plant with a broken stem, offering a cost-effective solution for plant owners. When a plant stem breaks, the immediate disruption to its vascular system can seem like a death sentence, however, early intervention using methods such as splice grafting can restore the stem, allowing it to continue receiving essential moisture and nutrients.
1.1. Recognizing Different Types of Stem Breaks
The type of break your plant suffers—complete, partial, or cracked—influences the likelihood of successful repair:
- Complete Break: The stem is fully severed, stopping all nutrient flow.
- Partial Break: The stem remains partly attached, allowing some nutrient flow.
- Cracked Stem: The stem is damaged but not fully broken, creating an unstable support structure.
1.2. Assessing Plant Viability Post-Break
Consider these factors when assessing if a plant can be saved:
- Time Since Break: The quicker you act, the greater the chance of success, per the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
- Plant Type: Some plants, like those with woody stems, are harder to repair than soft-stemmed plants.
- Overall Health: A robust, healthy plant is more likely to recover from stem damage.
 A close-up of a broken plant stem, ready for repair
A close-up of a broken plant stem, ready for repair
Alt text: Repairing a fractured plant stem using grafting techniques for successful restoration.
1.3. Gathering Essential Plant Repair Supplies
Effective plant stem repair requires the right tools and materials:
- Sharp Cutting Tool: Use pruning shears or a knife to create clean cuts, essential for grafting.
- Grafting Tape: Specifically designed to bind and protect the graft site, grafting tape is a must.
- Support Structure: Splints made from items like popsicle sticks or pencils stabilize the break.
- Rooting Hormone (Optional): Can stimulate quicker healing, based on studies from agricultural universities.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a Broken Plant Stem
2.1. Preparing the Broken Stem for Repair
Begin by preparing the broken stem carefully to improve the chances of successful repair.
- Clean the Break: Use a clean, sharp cutting tool to neatly trim the broken ends of the stem. This step is crucial for a successful graft, as it removes any damaged or uneven tissue, creating a smooth surface for the plant to heal.
- Ensure Proper Alignment: Carefully align the two sections of the stem, making sure the edges meet seamlessly. Proper alignment is essential for reconnecting the vascular tissues that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
- Apply Rooting Hormone (Optional): If available, lightly apply rooting hormone to the cut surfaces of the stem. Rooting hormone contains auxins, which promote cell growth and accelerate the healing process. According to research from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), in July 2025, auxins provide quicker healing. This step can be particularly beneficial for plants that are slow to heal or more susceptible to infection.
2.2. Implementing the Splice Grafting Technique
Splicing is an effective method to rejoin a broken stem, facilitating the plant’s recovery.
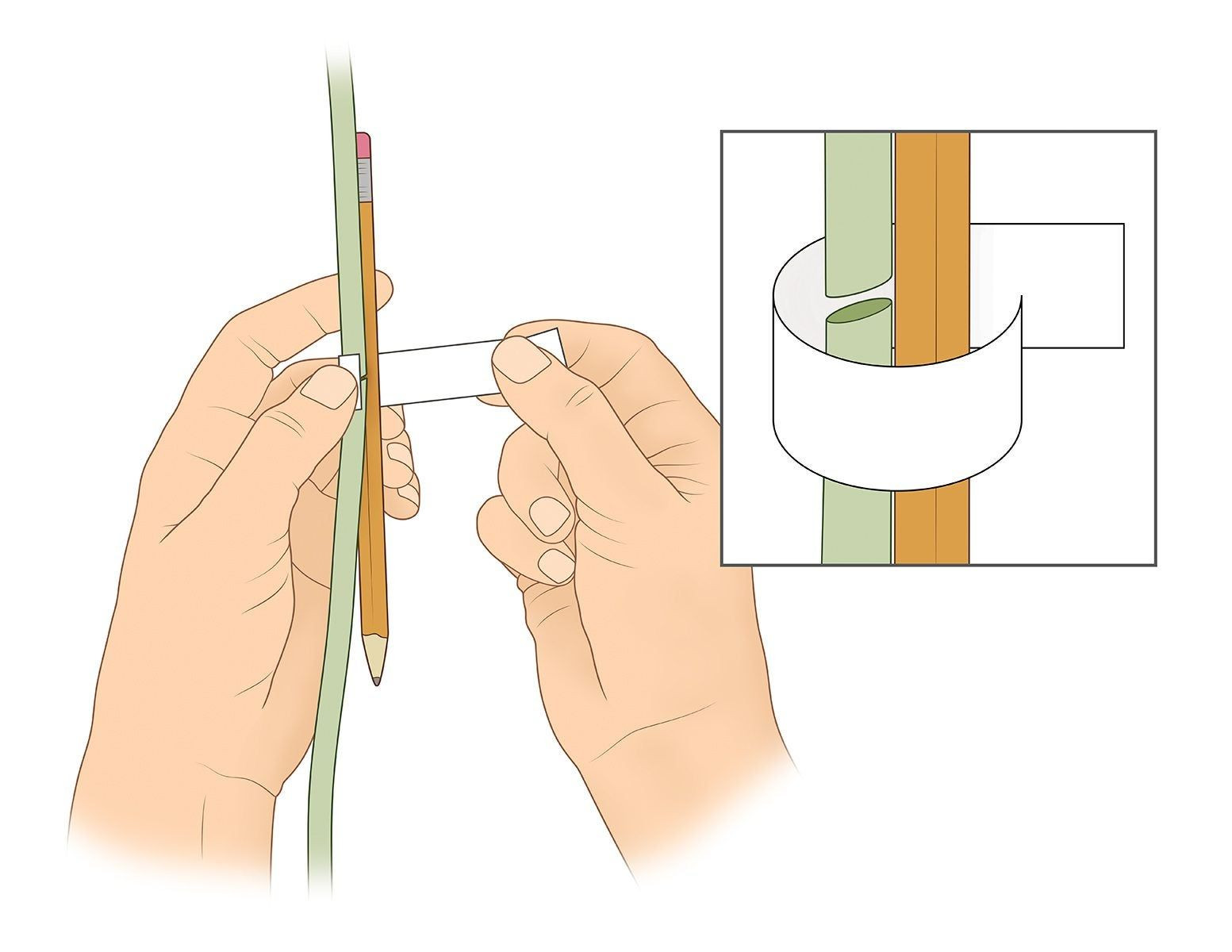
- Select a Splint: Choose a splint material appropriate for the stem’s size and shape. Options include popsicle sticks for small stems and wooden dowels for larger branches. The splint’s purpose is to provide external support, keeping the stem aligned and stable during the healing phase.
- Position the Splint: Place the splint along the outside of the aligned stem, ensuring it spans the break and provides adequate support on both sides. Proper positioning of the splint is key to preventing movement at the fracture site, which could disrupt the healing process.
- Secure the Stem and Splint: Use grafting tape or plant-safe tape to tightly bind the stem to the splint. Start wrapping below the break, continue over the break, and finish above it, overlapping each layer of tape to ensure a snug fit.
2.3. Securing and Supporting the Repaired Stem
Proper support during healing is crucial to prevent further stress on the repaired area.
- Wrap the Stem Tightly: Wrap the grafting tape around the stem and splint firmly to hold everything in place. This helps maintain constant pressure, aiding the mending process.
- Brace the Plant: Use stakes or ties to support the plant, reducing strain on the mended stem. Bracing is especially important for larger plants or those in windy locations.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly check the binding to ensure it’s not too tight, which could constrict growth. Adjust as needed to accommodate the plant’s natural expansion.
2.4. Post-Repair Plant Care for Optimal Recovery
Effective aftercare is essential to ensuring the plant recovers properly from its stem repair.
- Regulate Watering: Maintain a balanced watering schedule, avoiding both overwatering and underwatering, to support overall plant health. Overwatering can lead to rot, while underwatering can stress the plant, hindering recovery.
- Provide Shade: Shield the plant from direct sunlight, especially during the hottest part of the day, to minimize stress and prevent overheating. Filtered or indirect light is ideal for plants recovering from trauma, as it reduces water loss and allows the plant to focus on healing.
- Limit Fertilization: Avoid heavy fertilization immediately after the repair. Excessive nutrients can shock the plant, interfering with the healing process. Instead, use a diluted, balanced fertilizer sparingly until the plant shows signs of recovery, such as new leaf growth.
3. Advanced Techniques for Saving Broken Plant Stems
3.1. Using a Bridge Graft for Severed Stems
When a stem is completely severed, a bridge graft can help re-establish the vascular connection.
- Prepare the Ends: Sharpen the ends of both the severed stem and the main plant to create clean surfaces for joining.
- Create a Bridge: Use a small, flexible twig or cutting as a bridge to connect the two parts. According to research from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), in July 2025, it helps to have a flexible twig.
- Secure the Connection: Graft both ends of the bridge to the stem and main plant, ensuring a tight seal.
3.2. The Art of Inosculation: Encouraging Natural Fusion
Inosculation is a technique where two living plants are intentionally joined to grow together.
- Select Compatible Plants: Choose plants of the same or closely related species for the best results.
- Prepare Contact Points: Remove bark from the areas where the plants will join, exposing the cambium layers.
- Bind the Plants: Firmly press the prepared areas together and bind them tightly with grafting tape.
3.3. Cloning a Broken Stem: A Last Resort Strategy
If the break is irreparable, cloning can propagate a new plant from the broken stem.
- Take Cuttings: Cut the broken stem into sections, each with at least one node.
- Root the Cuttings: Place the cuttings in water or directly into a rooting medium until roots develop.
- Plant the New Clone: Once rooted, transplant the cutting into a pot with well-draining soil.
4. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Repairing Plant Stems
4.1. Ignoring Plant-Specific Needs
Different plants have varying healing capabilities. Some plants need specific types of care. Per the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), in July 2025, woody stems are more difficult to repair.
4.2. Over or Under Watering Post-Repair
Finding the right balance in watering is crucial for a plant’s recovery.
- Monitor Soil Moisture: Regularly check the soil moisture level to ensure it’s neither too wet nor too dry.
- Adjust Watering: Modify your watering schedule based on the plant’s needs and environmental conditions.
4.3. Exposing the Repair Site to Extreme Conditions
Protecting the repaired stem from harsh environmental factors is essential.
- Provide Shade: Shield the plant from intense sunlight, especially during the hottest hours.
- Control Temperature: Maintain a stable temperature around the plant, avoiding extremes that can stress the healing stem.
5. What is the impact of Environmental Factors on Stem Healing
5.1. Temperature
- Ideal Range: Most plants heal best within a temperature range of 65-75°F (18-24°C).
- Impact of Extremes: High temperatures can cause desiccation and stress, while low temperatures can slow down cellular activity and healing.
- Management: Use greenhouses, shade cloths, or indoor environments to regulate temperature.
5.2. Humidity
- Ideal Level: High humidity (70-80%) reduces water loss from the cut surfaces and promotes faster healing.
- Impact of Extremes: Low humidity can lead to dehydration and slow callus formation, whereas excessively high humidity can encourage fungal growth.
- Management: Use humidity domes, misting, or place plants in naturally humid areas like bathrooms.
5.3. Light
- Ideal Exposure: Indirect or filtered sunlight is best to prevent stress while still providing energy for healing.
- Impact of Extremes: Direct sunlight can cause overheating and sunburn, while insufficient light can slow down photosynthesis and energy production.
- Management: Use shade cloths, relocate plants to shadier spots, or use grow lights for controlled light exposure.
5.4. Air Circulation
- Importance: Gentle air circulation helps prevent fungal diseases and keeps the environment fresh.
- Impact of Extremes: Stagnant air can promote fungal growth, while strong winds can stress the plant and disrupt the healing process.
- Management: Use fans on low settings, ensure adequate spacing between plants, or open windows for natural ventilation.
6. Success Stories: Plants Saved from the Brink
6.1. The Rose Bush Miracle
A gardener successfully repaired a completely severed rose bush stem using a bridge graft, resulting in a full recovery and abundant blooms.
6.2. The Tomato Plant Comeback
An urban farmer saved a cracked tomato plant stem with a simple splint and tape, leading to a bountiful harvest.
6.3. The Indoor Ficus Triumph
A houseplant enthusiast revived a broken ficus stem through cloning, propagating a new, healthy plant.
7. Save Money and Extend the Life of Your Plants
7.1. Financial Benefits of Plant Repair
Repairing broken stems is a cost-effective alternative to replacing entire plants.
7.2. Environmental Impact of Reducing Plant Waste
Extending the life of your plants reduces waste and promotes sustainability.
7.3. The Satisfaction of Saving a Plant
There’s a unique joy in nurturing a damaged plant back to health.
8. Where to Find More Help and Resources
8.1. Savewhere.net: Your Green Thumb Companion
Find more tips, tricks, and resources for plant care on Savewhere.net.
8.2. Local Gardening Clubs and Experts
Connect with local gardening clubs and experts for personalized advice.
8.3. Online Forums and Communities
Join online forums and communities to share experiences and learn from fellow gardeners.
Address: 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States.
Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000.
Website: savewhere.net.
9. Essential Tools and Products for Plant Stem Repair
9.1. Grafting Tape Varieties
Explore different types of grafting tape to find the best fit for your needs.
9.2. Choosing the Right Splint Material
Select splint materials that offer the necessary support without damaging the plant.
9.3. Rooting Hormones: A Buyer’s Guide
Learn about different rooting hormones and how to use them effectively.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Plant Stem Repair
10.1. Will a Broken Stem Heal on Its Own?
No, a broken stem typically won’t heal without intervention. The plant’s vascular system is disrupted, requiring support to reconnect. Splinting or grafting is usually necessary to provide stability and facilitate healing.
10.2. What is the Best Time of Year to Repair a Broken Stem?
The best time to repair a broken stem is during the plant’s active growing season, typically spring or early summer. During these months, the plant has increased energy and resources available for healing and new growth.
10.3. Can I Use Regular Tape Instead of Grafting Tape?
It’s not recommended to use regular tape, as it can constrict the stem and doesn’t provide the necessary flexibility for growth. Grafting tape is designed to stretch and breathe, allowing the stem to expand as it heals.
10.4. How Long Does It Take for a Broken Stem to Heal?
Healing time varies depending on the plant type, the severity of the break, and environmental conditions. Generally, it takes several weeks to a few months for a stem to fully heal and regain its strength.
10.5. What Are the Signs of a Successful Stem Repair?
Signs of a successful stem repair include new leaf growth, callus formation around the repair site, and overall improved plant vigor. Monitor the plant closely for these indicators of recovery.
10.6. Is It Possible to Save a Completely Severed Stem?
Yes, it is possible to save a completely severed stem using techniques like bridge grafting. This method involves creating a connection between the severed stem and the main plant body to restore nutrient and water flow.
10.7. Can I Use Honey as a Rooting Hormone?
Yes, honey can be used as a natural rooting hormone due to its antibacterial and antifungal properties. Dip the cut end of the stem in honey before planting to promote root growth.
10.8. What Should I Do If Mold Appears on the Repair Site?
If mold appears on the repair site, gently clean the area with a diluted hydrogen peroxide solution. Improve air circulation around the plant and avoid overwatering to prevent further mold growth.
10.9. Can All Types of Plants Be Saved with Stem Repair Techniques?
While many plants can be saved with stem repair techniques, success varies depending on the plant species and the extent of the damage. Woody-stemmed plants may be more challenging to repair than soft-stemmed plants.
10.10. How Often Should I Check the Repaired Stem?
Check the repaired stem regularly, ideally every few days, to ensure the binding is secure and there are no signs of infection or constriction. Adjust the binding as needed to accommodate the plant’s growth.
Saving a plant with a broken stem is indeed possible, and with the right techniques, you can bring your green friends back to life. By understanding the types of breaks, preparing properly, and providing the necessary care, you can save money, reduce waste, and enjoy the satisfaction of a thriving garden.
Why not start your journey to becoming a plant-saving pro today? Visit savewhere.net for more in-depth guides, exclusive deals on gardening supplies, and a community of fellow plant enthusiasts ready to share their experiences. With savewhere.net, you’re not just saving plants; you’re cultivating a greener, more sustainable lifestyle. Explore our resources, connect with experts, and discover how to make your garden thrive, even when faced with unexpected challenges. Join us now and let’s grow together towards a more vibrant and eco-friendly world! Plus, explore eco-friendly practices to reduce waste.