How To See Saved Passwords On Chrome? It’s simple! Chrome’s password manager securely stores your login credentials for easy access. At savewhere.net, we’ll guide you through accessing, managing, and safeguarding your passwords, ensuring a seamless and secure browsing experience. Let’s explore how to improve your online security with effective password management techniques, secure browsing practices, and data protection strategies.
1. Understanding Chrome’s Password Manager
Chrome’s built-in password manager is a convenient tool that securely stores your usernames and passwords for various websites. When you log in to a website, Chrome prompts you to save the password. If you agree, the password is encrypted and stored within Chrome. Let’s explore how this feature enhances your browsing experience. Chrome’s password manager helps streamline your online activities, so it’s important to understand its capabilities and limitations.
1.1. How Chrome Saves Passwords
When you enter your username and password on a website, Chrome detects this and asks if you want to save the password. If you click “Save,” Chrome stores the credentials securely. This feature is designed for ease of use, automatically filling in your login details the next time you visit the site.
- Automatic Prompt: Chrome automatically recognizes login forms.
- Secure Storage: Passwords are encrypted for security.
- Convenient Autofill: Automatically fills in login details on return visits.
1.2. Benefits of Using Chrome’s Password Manager
Using Chrome’s password manager offers several advantages, primarily convenience and security. Storing your passwords in Chrome saves you the hassle of remembering numerous login details. Additionally, Chrome’s password manager can generate strong, unique passwords, enhancing your online security.
- Convenience: No need to remember multiple passwords.
- Security: Option to generate strong, unique passwords.
- Accessibility: Passwords available across devices synced with your Google account.
1.3. Limitations and Security Considerations
While convenient, Chrome’s password manager isn’t without its limitations. The primary concern is security: if your Google account is compromised, so are all your saved passwords. Therefore, it’s crucial to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your Google account and use a strong, unique password for your Google account itself.
- Single Point of Failure: Compromised Google account risks all saved passwords.
- Lack of Advanced Features: Compared to dedicated password managers, Chrome’s features are basic.
- Security Measures: Always use 2FA and a strong Google account password.
2. Accessing Your Saved Passwords on Chrome
Accessing your saved passwords on Chrome is straightforward. The process varies slightly depending on whether you’re using a desktop or mobile device. Below are detailed instructions for both platforms.
2.1. On Desktop
To view your saved passwords on Chrome on a desktop computer, follow these steps:
-
Open Chrome: Launch the Chrome browser on your computer.
-
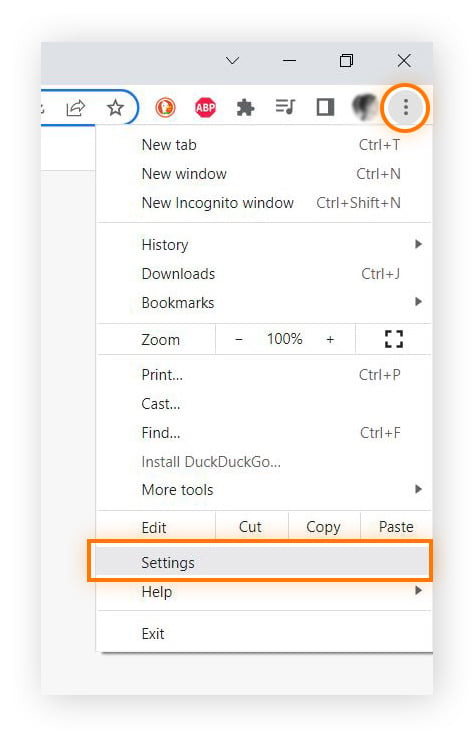
Access Settings: Click the three vertical dots in the top-right corner to open the Chrome menu, then select “Settings.”
-
Navigate to Autofill: In the Settings menu, click on “Autofill” in the left sidebar.
-
Select Password Manager: Choose “Password Manager” from the Autofill options.
-
View Saved Passwords: You’ll see a list of websites with saved passwords. Click the eye icon next to a website to reveal the password. You may need to enter your computer’s password to confirm your identity.
 View saved passwords in Chrome settings
View saved passwords in Chrome settings
2.2. On Mobile
To view your saved passwords on Chrome on a mobile device (Android or iOS), follow these steps:
-
Open Chrome: Launch the Chrome app on your mobile device.
-
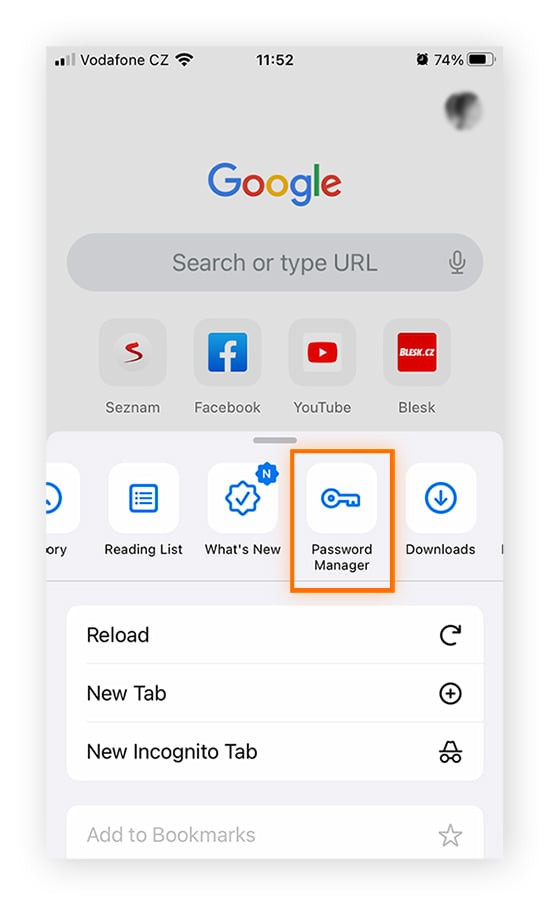
Access Settings: Tap the three vertical dots (or three horizontal lines) to open the Chrome menu, then select “Settings.”
-
Navigate to Password Manager: Scroll down and tap on “Password Manager.”
-
View Saved Passwords: You’ll see a list of websites with saved passwords. Tap the eye icon next to a website to reveal the password. You may need to authenticate using your device’s PIN, pattern, or biometric authentication.
 Accessing password manager in Chrome mobile settings
Accessing password manager in Chrome mobile settings
2.3. Using Google Account Settings
You can also access your saved passwords through your Google account settings. This method works on both desktop and mobile:
- Go to Google Account: Open a web browser and go to your Google Account page.
- Navigate to Security: In the left navigation panel, click on “Security.”
- Find Password Manager: Scroll down to the “How you sign in to Google” section and click on “Password Manager.”
- View Saved Passwords: You’ll see a list of your saved passwords. Click the eye icon next to a website to reveal the password. You may need to enter your Google account password to confirm your identity.
3. Managing Your Saved Passwords
Effective password management involves more than just viewing your saved passwords. It includes editing, deleting, and organizing your credentials to maintain security and convenience.
3.1. Editing Passwords
To edit a saved password in Chrome:
-
Access Password Manager: Follow the steps in Section 2 to access the Password Manager.
-
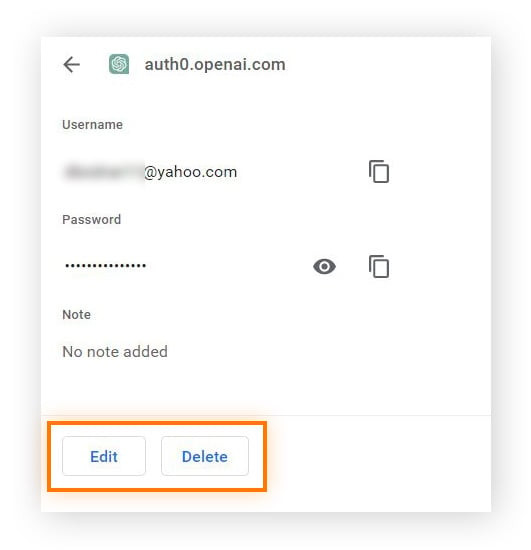
Select Website: Find the website whose password you want to edit and click on it.
-
Edit Password: Click the “Edit” button (pencil icon).
-
Update Password: Enter the new password and click “Save.” You may need to enter your computer’s or Google account password to confirm your identity.
 Editing saved passwords in Chrome password manager
Editing saved passwords in Chrome password manager
3.2. Deleting Passwords
To delete a saved password in Chrome:
- Access Password Manager: Follow the steps in Section 2 to access the Password Manager.
- Select Website: Find the website whose password you want to delete and click on it.
- Delete Password: Click the “Delete” button (trash can icon).
- Confirm Deletion: Confirm that you want to delete the password.
3.3. Organizing Passwords
Chrome’s password manager doesn’t offer advanced organizational features like folders or tags. However, you can use the search function to quickly find specific passwords.
- Access Password Manager: Follow the steps in Section 2 to access the Password Manager.
- Use Search: Type the name of the website in the search bar to quickly find the relevant password.
3.4. Importing and Exporting Passwords
Chrome allows you to import and export your saved passwords, which can be useful for transferring your credentials to another browser or password manager.
Importing Passwords:
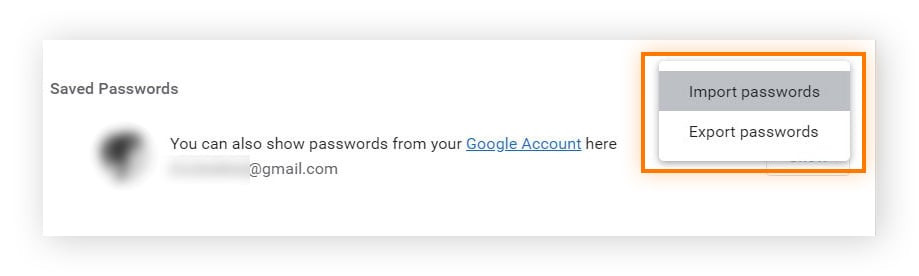
- Access Password Manager: Follow the steps in Section 2 to access the Password Manager.
- Click the three dots icon: Click on the three dots icon located near the top of the Password Manager page.
- Select “Import passwords”: Choose “Import passwords” from the dropdown menu.
- Select File: Choose the CSV file containing your passwords and click “Open.”
Exporting Passwords:
-
Access Password Manager: Follow the steps in Section 2 to access the Password Manager.
-
Click the three dots icon: Click on the three dots icon located near the top of the Password Manager page.
-
Select “Export passwords”: Choose “Export passwords” from the dropdown menu.
-
Confirm Export: Confirm that you want to export your passwords. You may need to enter your computer’s password to confirm your identity.
-
Save File: Choose a location to save the CSV file containing your passwords.
 Importing and exporting passwords in Chrome
Importing and exporting passwords in Chrome
Warning: Exporting your passwords creates a plain text file containing your usernames and passwords. Handle this file with care and delete it once you’ve imported your passwords into another password manager.
4. Enhancing Security for Saved Passwords
While Chrome’s password manager provides convenience, it’s crucial to take additional steps to enhance the security of your saved passwords. Let’s explore these security measures. A layered approach to security ensures that your online credentials remain protected.
4.1. Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your Google account, making it more difficult for hackers to access your saved passwords. With 2FA enabled, you’ll need to enter a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password when you sign in.
To enable 2FA on your Google account:
- Go to Google Account: Open a web browser and go to your Google Account page.
- Navigate to Security: In the left navigation panel, click on “Security.”
- Find 2-Step Verification: Under the “How you sign in to Google” section, click on “2-Step Verification.”
- Get Started: Follow the on-screen instructions to set up 2FA. You’ll typically need to provide a phone number and choose a method for receiving verification codes.
4.2. Using a Strong Google Account Password
Your Google account password is the key to your saved passwords, so it’s essential to use a strong, unique password. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like your name, birthday, or common words.
To change your Google account password:
- Go to Google Account: Open a web browser and go to your Google Account page.
- Navigate to Security: In the left navigation panel, click on “Security.”
- Find Password: Under the “How you sign in to Google” section, click on “Password.”
- Enter Current Password: Enter your current password.
- Create New Password: Enter your new password and confirm it.
- Change Password: Click “Change Password.”
4.3. Regularly Reviewing Saved Passwords
It’s a good practice to regularly review your saved passwords to identify and update any weak or outdated passwords. Chrome can help you with this by identifying passwords that are weak, reused, or have been exposed in a data breach.
To review your saved passwords in Chrome:
- Access Password Manager: Follow the steps in Section 2 to access the Password Manager.
- Check Password Checkup: Look for a “Password Checkup” or “Check passwords” option. Click on it to run a security scan of your saved passwords.
- Review Results: Chrome will identify any passwords that need to be updated. Follow the prompts to change any weak or compromised passwords.
4.4. Avoiding Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them vulnerable to eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Avoid accessing sensitive accounts like your bank or email when using public Wi-Fi. If you must use public Wi-Fi, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your data.
4.5. Staying Alert for Phishing Attempts
Phishing is a type of online fraud where attackers try to trick you into revealing your passwords or other sensitive information. Be wary of suspicious emails, messages, or websites that ask for your login credentials. Always verify the legitimacy of a website before entering your username and password.
5. Comparing Chrome’s Password Manager to Third-Party Alternatives
While Chrome’s password manager is convenient for basic password storage, dedicated third-party password managers offer more advanced features and enhanced security. Let’s compare Chrome’s password manager to some popular alternatives. Choosing the right password manager depends on your specific needs and security priorities.
5.1. Key Features Comparison
| Feature | Chrome Password Manager | Third-Party Password Managers (e.g., LastPass, 1Password) |
|---|---|---|
| Password Generation | Yes | Yes, with more advanced options |
| Password Storage | Yes | Yes, with secure encryption |
| Autofill | Yes | Yes, across all apps and browsers |
| Two-Factor Authentication | Relies on Google Account 2FA | Built-in 2FA options |
| Password Sharing | No | Yes, with secure sharing options |
| Password Organization | Basic search | Folders, tags, and advanced organization tools |
| Cross-Platform Support | Limited to Chrome | Wide support for various devices and operating systems |
| Security Audits | Basic checks | Regular security audits by third-party firms |
| Breach Monitoring | Yes, basic | Advanced monitoring and alerts |
| Customer Support | Limited | Dedicated support teams |
5.2. Popular Third-Party Password Managers
-
LastPass: A popular password manager with a free plan and premium features like password sharing and advanced 2FA.
-
1Password: A subscription-based password manager with a focus on security and features like travel mode and masked emails.
-
Bitwarden: An open-source password manager with a free plan and affordable premium options.
-
Dashlane: A password manager with a built-in VPN and identity theft protection features.
 The Bitwarden login page
The Bitwarden login page
5.3. Choosing the Right Password Manager
When choosing a password manager, consider the following factors:
- Security: Look for a password manager with strong encryption and a good security track record.
- Features: Choose a password manager with the features you need, such as password sharing, cross-platform support, and advanced 2FA.
- Ease of Use: Pick a password manager that is easy to use and integrates well with your devices and browsers.
- Price: Consider your budget and choose a password manager that offers good value for the price.
6. What To Do If Your Password Has Been Compromised
Discovering that your password has been compromised can be alarming. Act quickly to mitigate the damage and secure your accounts. Let’s explore the necessary steps. Prompt action can minimize the impact of a security breach.
6.1. Changing the Password Immediately
The first step is to change the compromised password immediately. Use a strong, unique password that you haven’t used before. If the password was used on multiple accounts, change it on all of those accounts.
To change your password:
- Log in to the Account: Access the account that was compromised.
- Navigate to Settings: Go to the account settings or security settings.
- Change Password: Find the option to change your password and follow the instructions.
- Create New Password: Create a strong, unique password.
6.2. Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
If you haven’t already, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on the compromised account and any other accounts that support it. 2FA adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for hackers to access your accounts even if they have your password.
6.3. Checking for Unauthorized Activity
Review your account activity for any signs of unauthorized access, such as suspicious transactions, emails, or posts. If you find any unauthorized activity, report it to the service provider immediately.
6.4. Reporting the Breach
If your password was compromised as part of a data breach, report the breach to the service provider. This will help them investigate the breach and take steps to prevent future incidents.
6.5. Monitoring Your Credit Report
If your password was used to access financial accounts, monitor your credit report for any signs of identity theft. You can get a free copy of your credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) once a year.
6.6. Using a Password Manager to Generate Strong Passwords
After resolving the immediate issue, use a password manager to generate strong, unique passwords for all of your accounts. This will help prevent future password compromises.
7. Staying Informed About Data Breaches
Staying informed about data breaches is crucial for protecting your online security. Data breaches can expose your passwords and other sensitive information, putting you at risk of identity theft and other online threats. Let’s explore how to stay informed and take proactive steps. Knowledge is power when it comes to online security.
7.1. Monitoring Breach Notification Websites
Several websites track and report data breaches. Monitor these websites to stay informed about recent breaches that may affect your accounts.
- Have I Been Pwned: A popular website that allows you to check if your email address or phone number has been compromised in a data breach.
- Security News Websites: Follow reputable security news websites and blogs to stay informed about the latest data breaches and security threats.
7.2. Setting Up Breach Alerts
Many password managers and security services offer breach alerts that notify you if your email address or password has been compromised in a data breach. Set up these alerts to receive timely notifications and take action quickly.
7.3. Following Security Experts on Social Media
Follow security experts and organizations on social media to stay informed about the latest security news and threats. They often share valuable insights and tips for protecting your online security.
7.4. Regularly Reviewing Your Accounts
Regularly review your accounts for any signs of unauthorized activity. This can help you detect and respond to potential security breaches early on.
8. Practical Tips for Creating Strong Passwords
Creating strong passwords is one of the most effective ways to protect your online accounts. A strong password is difficult to guess and can help prevent unauthorized access. Let’s explore some practical tips. Implementing these tips will significantly enhance your password security.
8.1. Using a Combination of Characters
A strong password should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. The more diverse the characters, the stronger the password.
- Example:
P@sswOrd123!
8.2. Avoiding Personal Information
Avoid using personal information like your name, birthday, or pet’s name in your passwords. This information is easily accessible and makes your passwords easier to guess.
8.3. Using a Password Length of at Least 12 Characters
The longer the password, the more difficult it is to crack. Aim for a password length of at least 12 characters.
8.4. Using Passphrases
Passphrases are longer and more complex than traditional passwords. They consist of a string of random words that are easy to remember but difficult to guess.
- Example:
red elephant blue bicycle green tree
8.5. Avoiding Common Words and Phrases
Avoid using common words and phrases in your passwords. Hackers often use dictionaries of common words to crack passwords.
8.6. Testing Your Password Strength
Use online password strength testers to evaluate the strength of your passwords. These tools can help you identify weak passwords and provide suggestions for improvement.
9. Addressing Common Password-Related Issues
Users often encounter various password-related issues, such as forgetting passwords, dealing with weak passwords, and managing multiple accounts. Let’s address these common problems. Understanding these issues and their solutions can improve your overall password management.
9.1. Forgetting Passwords
Forgetting passwords is a common problem. Most websites offer a “Forgot Password” option that allows you to reset your password via email or phone number.
To reset your password:
- Click “Forgot Password”: On the login page, click the “Forgot Password” or similar option.
- Verify Identity: Follow the instructions to verify your identity, usually via email or phone number.
- Create New Password: Create a new, strong password.
9.2. Dealing with Weak Passwords
Weak passwords are a security risk. Use a password manager to generate strong, unique passwords for all of your accounts.
To improve weak passwords:
- Identify Weak Passwords: Use a password manager to identify weak passwords.
- Generate Strong Passwords: Use the password manager to generate strong, unique passwords.
- Update Passwords: Update the weak passwords with the new, strong passwords.
9.3. Managing Multiple Accounts
Managing multiple accounts can be challenging. Use a password manager to store and manage your passwords securely.
To manage multiple accounts:
- Store Passwords in Password Manager: Store all of your passwords in a password manager.
- Organize Passwords: Use the password manager to organize your passwords by website or account type.
- Use Autofill: Use the password manager’s autofill feature to log in to your accounts quickly and easily.
9.4. Password Reuse
Reusing passwords across multiple accounts is a security risk. If one account is compromised, all accounts with the same password are at risk. Use a unique password for every account.
10. Leveraging Savewhere.net for Financial Security
At savewhere.net, we understand the importance of financial security and offer a range of resources to help you manage your money effectively. One key aspect of financial security is protecting your online accounts, and that starts with strong password management.
10.1. Accessing Exclusive Deals and Discounts
savewhere.net provides access to exclusive deals and discounts that can help you save money on everyday expenses. By securing your accounts with strong passwords, you can ensure that only you have access to these valuable savings.
10.2. Utilizing Financial Management Tools
savewhere.net offers a variety of financial management tools, including budgeting templates, expense trackers, and investment calculators. Protecting your login credentials for these tools is essential for maintaining control over your finances.
10.3. Connecting with a Community of Savers
savewhere.net connects you with a community of like-minded individuals who are passionate about saving money and achieving financial freedom. By sharing tips and strategies, you can learn from others and improve your financial habits. Securing your account on savewhere.net is crucial for participating in this community.
10.4. Staying Updated on Financial News and Trends
savewhere.net keeps you informed about the latest financial news and trends, helping you make informed decisions about your money. Protecting your access to this information is essential for staying ahead of the curve.
10.5. Contact Information
For more information about financial security and how savewhere.net can help you save money, visit our website or contact us at:
- Address: 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States
- Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000
- Website: savewhere.net
In conclusion, mastering how to see saved passwords on Chrome is just the beginning. By understanding Chrome’s password manager, enhancing your password security, and leveraging resources like savewhere.net, you can take control of your financial life and achieve your savings goals. Remember, a secure online presence is a foundation for financial well-being.
FAQ: How to See Saved Passwords on Chrome
1. How do I find my saved passwords in Chrome?
You can find your saved passwords in Chrome by going to Settings > Autofill > Password Manager. Here, you’ll see a list of websites and their corresponding saved passwords.
2. Can I view my saved passwords on Chrome mobile?
Yes, you can view your saved passwords on Chrome mobile by opening the Chrome app, tapping the three dots menu, selecting Settings, and then tapping Password Manager.
3. Is it safe to save passwords in Chrome?
Saving passwords in Chrome is generally safe, as Chrome encrypts your passwords. However, it’s essential to use a strong Google account password and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
4. How can I edit a saved password in Chrome?
To edit a saved password in Chrome, go to the Password Manager, select the website, click the Edit button (pencil icon), update the password, and click Save.
5. How do I delete a saved password in Chrome?
To delete a saved password in Chrome, go to the Password Manager, select the website, click the Delete button (trash can icon), and confirm the deletion.
6. Can I import passwords into Chrome from another browser?
Yes, you can import passwords into Chrome from a CSV file. Go to the Password Manager, click the three dots icon, select Import passwords, and choose the CSV file.
7. How do I export my saved passwords from Chrome?
You can export your saved passwords from Chrome by going to the Password Manager, clicking the three dots icon, selecting Export passwords, and saving the CSV file.
8. What should I do if I think my saved passwords in Chrome have been compromised?
If you suspect your saved passwords have been compromised, change your Google account password immediately, enable 2FA, and review your account activity for any unauthorized access.
9. Are there alternatives to Chrome’s password manager?
Yes, there are many third-party password managers like LastPass, 1Password, and Bitwarden that offer more advanced features and enhanced security compared to Chrome’s built-in password manager.
10. How can I stay informed about data breaches that may affect my saved passwords?
You can stay informed about data breaches by monitoring breach notification websites like Have I Been Pwned, setting up breach alerts, and following security experts on social media.
