An electrocardiogram (ECG) is an indispensable diagnostic tool in modern medicine. It non-invasively records the electrical activity of the heart, providing critical insights into its function and health. Accurate ECG readings depend significantly on the correct placement of ECG leads. This guide will explain where to put ECG leads for different types of ECG monitoring, ensuring you obtain the most accurate results.
Basic Landmarks for ECG Electrode Placement
Before delving into specific lead placements, understanding basic anatomical landmarks is crucial for accurate electrode positioning. These landmarks help ensure consistent and correct placement, leading to reliable ECG readings.
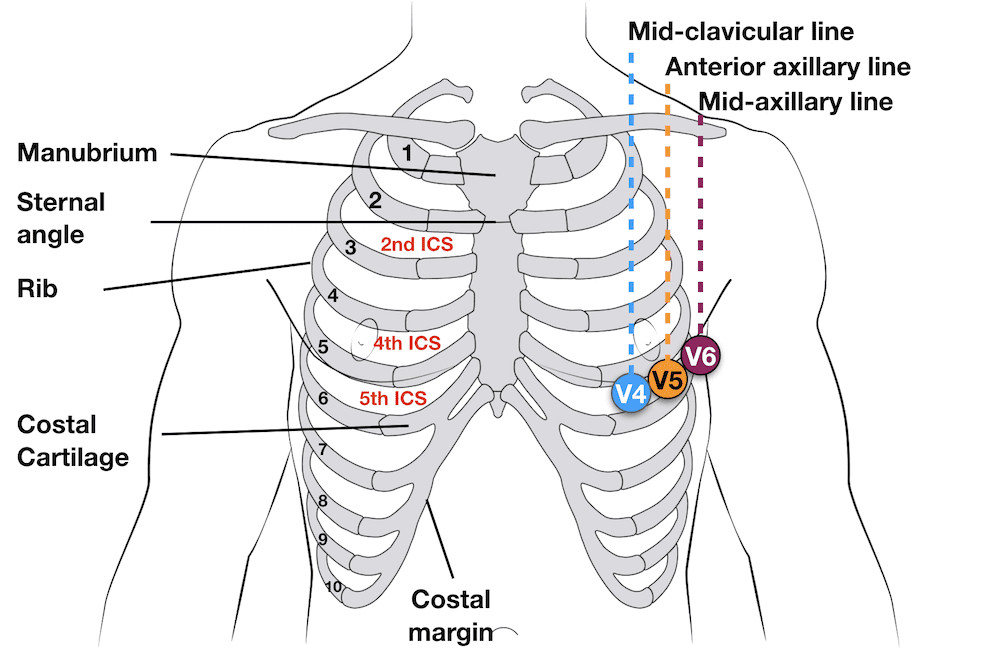 Diagram showing external chest landmarks for ECG electrode placement. Landmarks include the clavicle, sternum, rib cage, intercostal spaces and midclavicular line.
Diagram showing external chest landmarks for ECG electrode placement. Landmarks include the clavicle, sternum, rib cage, intercostal spaces and midclavicular line.
3-Electrode System for Basic ECG Monitoring
The 3-electrode system is a simplified approach used primarily for basic heart rate monitoring and rhythm analysis. It utilizes three electrodes: Right Arm (RA), Left Arm (LA), and Left Leg (LL).
- This system primarily displays bipolar leads I, II, and III, which represent the electrical activity between the limbs.
- For optimal signal quality, position the electrodes on the chest wall, equidistant from the heart, rather than directly on the limbs. This minimizes muscle artifact and provides a clearer ECG signal.
3-Lead Electrode Placement:
- RA (Right Arm): Place the electrode below the right clavicle, near the shoulder.
- LA (Left Arm): Place the electrode below the left clavicle, near the shoulder.
- LL (Left Leg): Place the electrode on the lower left abdomen, below the rib cage.
5-Electrode System for Enhanced ECG Monitoring
The 5-electrode system expands on the 3-lead system by adding two more electrodes: Right Leg (RL) and Chest (V). This configuration allows for monitoring of bipolar leads (I, II, and III) and a single unipolar chest lead (V). The position of the chest lead (V) can be varied (V1-V6 positions) to examine different aspects of the heart’s electrical activity.
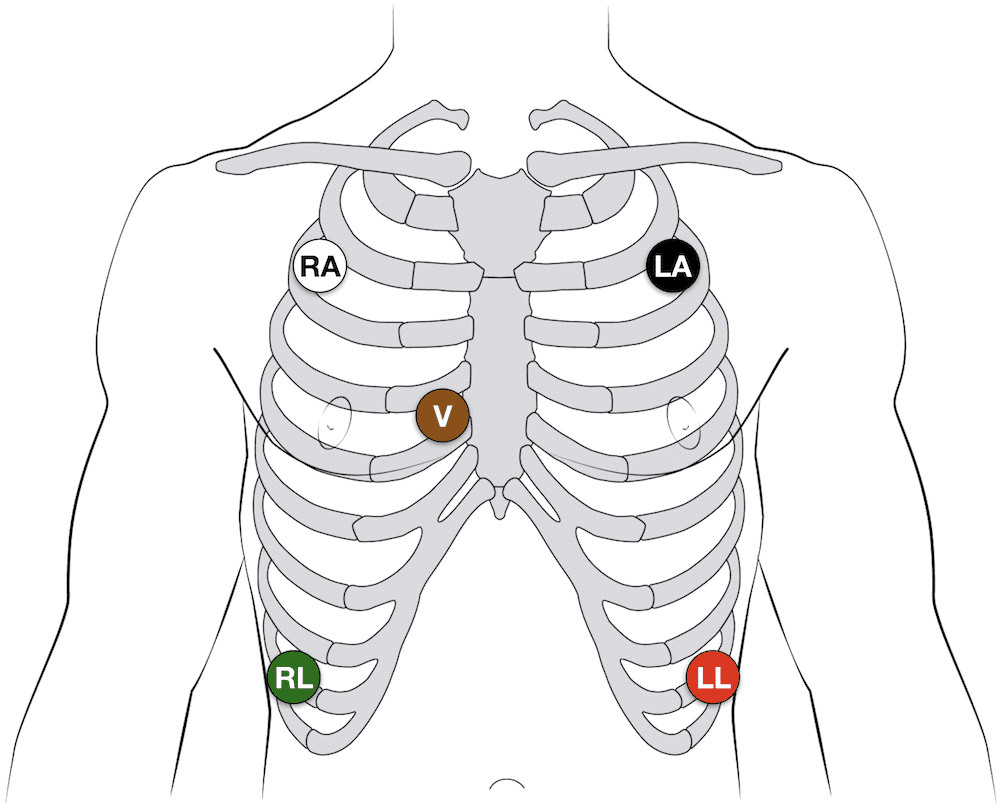 Diagram illustrating the 5-lead ECG electrode placement on a torso. Electrodes are placed on the right and left shoulders, right and left lower abdomen and the chest.
Diagram illustrating the 5-lead ECG electrode placement on a torso. Electrodes are placed on the right and left shoulders, right and left lower abdomen and the chest.
5-Lead Electrode Placement:
- RA (Right Arm): Place the electrode below the right clavicle.
- LA (Left Arm): Place the electrode below the left clavicle.
- RL (Right Leg): Place the electrode on the lower right abdomen. This electrode serves as a ground and does not contribute directly to the ECG reading.
- LL (Left Leg): Place the electrode on the lower left abdomen.
- V (Chest): The position of the chest lead can be adjusted based on the clinical need. Common positions include V1-V6 as described in the 12-lead ECG section.
12-Lead ECG: Comprehensive Cardiac Assessment
The 12-lead ECG is the gold standard for detailed cardiac evaluation. It utilizes 10 electrodes to record 12 different leads, providing a comprehensive view of the heart’s electrical activity from various angles. This system is essential for diagnosing a wide range of cardiac conditions, including myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, and conduction abnormalities.
- To achieve a 12-lead ECG, 4 electrodes are placed on the limbs and 6 precordial electrodes are positioned across the chest.
- The 12 leads monitored are: Leads I, II, III (bipolar limb leads), aVR, aVL, aVF (augmented limb leads), and V1-V6 (precordial leads).
- Each lead provides information about specific areas of the heart:
- Inferior leads (II, III, aVF): View the inferior wall of the left ventricle.
- Lateral leads (I, aVL, V5, V6): View the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
- Anterior leads (V1-V4): View the anterior wall of the left ventricle and the septum.
12-Lead Precordial Lead Placement: Step-by-Step
Accurate placement of precordial leads is critical for a diagnostic 12-lead ECG. Follow these steps for correct positioning:
- V1: Locate the 4th intercostal space (ICS) to the right of the sternum. Place the V1 electrode at the right sternal border in the 4th ICS.
- V2: Find the 4th intercostal space (ICS) to the left of the sternum. Place the V2 electrode at the left sternal border in the 4th ICS, directly opposite V1.
- V4: Palpate the 5th intercostal space (ICS). Locate the mid-clavicular line (an imaginary vertical line downwards from the midpoint of the clavicle). Place the V4 electrode at the intersection of the 5th ICS and the mid-clavicular line.
- V3: Position V3 midway between V2 and V4.
- V5: Locate the 5th intercostal space (ICS) at the anterior axillary line (an imaginary vertical line downwards from the front of the armpit). Place the V5 electrode in the 5th ICS at the anterior axillary line, at the same horizontal level as V4.
- V6: Locate the 5th intercostal space (ICS) at the mid-axillary line (an imaginary vertical line downwards from the middle of the armpit). Place the V6 electrode in the 5th ICS at the mid-axillary line, at the same horizontal level as V4 and V5.
Additional ECG Lead Placements for Specific Diagnoses
Beyond the standard 12-lead ECG, there are additional lead placements that can be used in specific clinical scenarios to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Right-Sided ECG for Right Ventricular Infarction
A right-sided ECG is crucial when right ventricular myocardial infarction (RVMI) is suspected, often in the context of an inferior ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Standard ECG leads are less sensitive to RVMI, making right-sided leads essential.
- Right-sided leads are obtained by mirroring the precordial leads V1-V6 on the right side of the chest.
- A simplified approach involves keeping V1 and V2 in their standard positions and transposing V3-V6 to the right side (V3R-V6R).
- V4R is the most important right-sided lead for diagnosing RVMI.
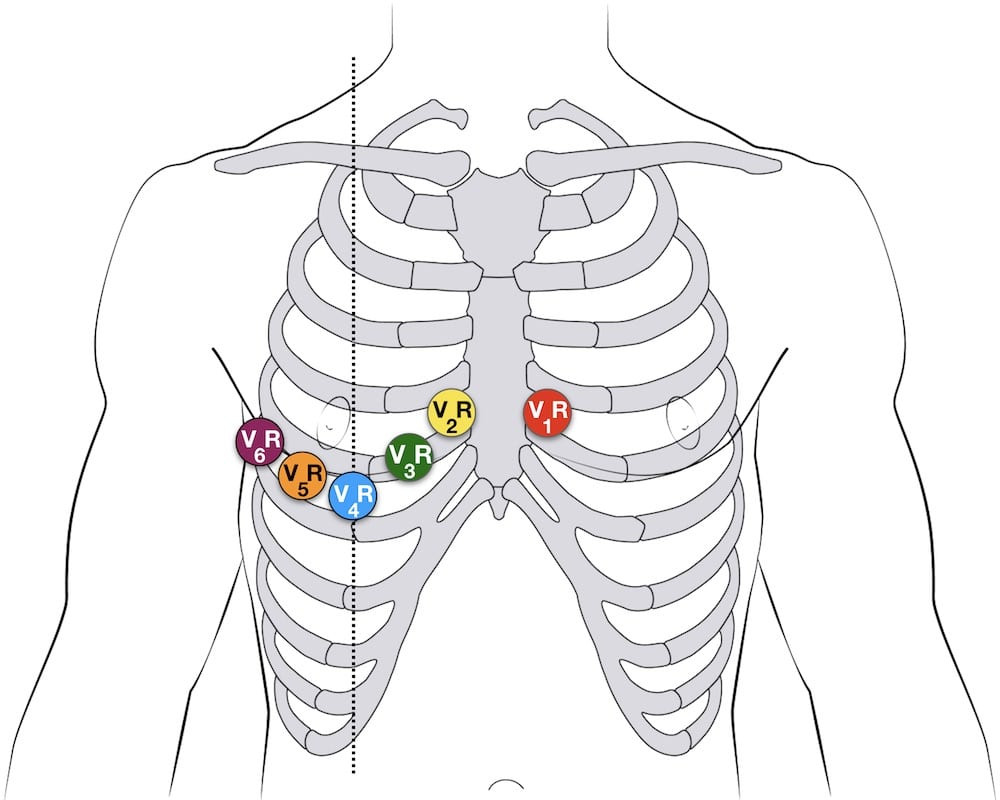 Diagram demonstrating right-sided 12 lead ECG lead placement by mirroring the standard precordial leads to the right side of the chest.
Diagram demonstrating right-sided 12 lead ECG lead placement by mirroring the standard precordial leads to the right side of the chest.
V4R ECG Lead Placement:
- V4R: Place the V4R electrode in the 5th right intercostal space at the mid-clavicular line – mirroring the standard V4 position on the right side of the chest.
Posterior Leads (V7-V9) for Posterior Myocardial Infarction
Posterior myocardial infarction (PMI) can be subtle on a standard 12-lead ECG. Posterior leads V7-V9 improve the detection of PMI by providing a direct view of the posterior wall of the left ventricle.
Posterior Lead Placement:
- V7: Positioned at the left posterior axillary line, in the same horizontal plane as V6.
- V8: Positioned at the tip of the left scapula, in the same horizontal plane as V6.
- V9: Positioned in the left paraspinal region, in the same horizontal plane as V6.
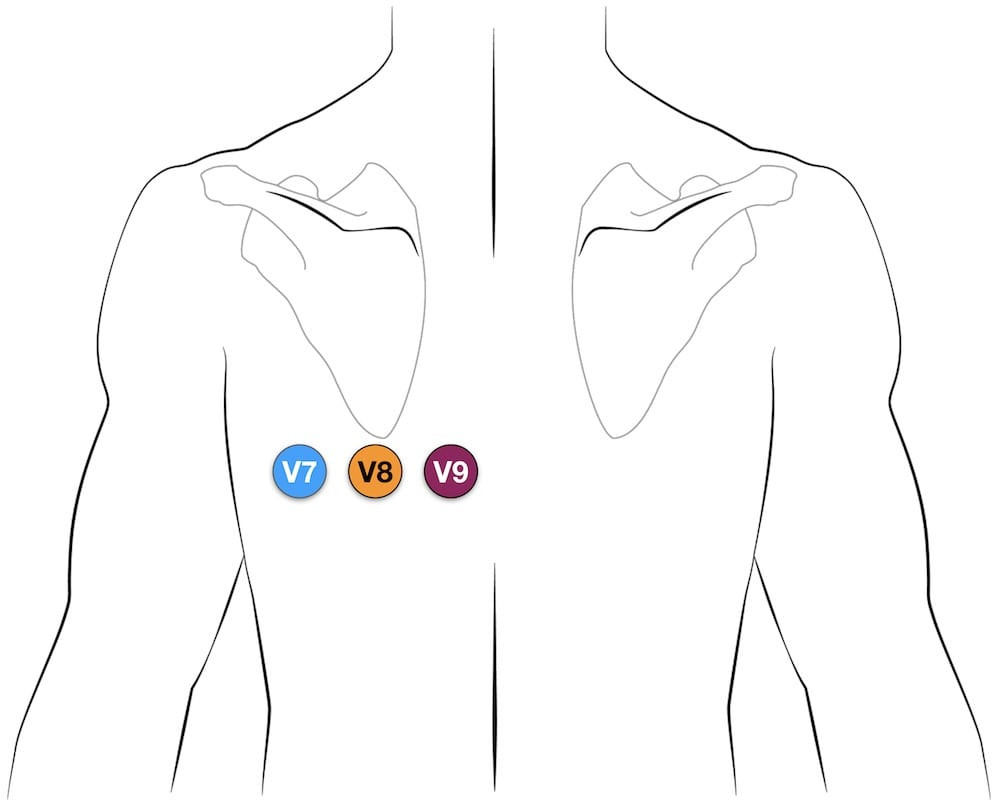 Diagram illustrating posterior leads V7, V8, and V9 ECG placement on the back, extending horizontally from the V6 position.
Diagram illustrating posterior leads V7, V8, and V9 ECG placement on the back, extending horizontally from the V6 position.
Lewis Lead (S5-Lead) for Atrial Activity
The Lewis lead configuration is a modified lead system designed to enhance the detection of atrial activity, particularly P waves and flutter waves. It is especially useful in diagnosing atrial flutter and differentiating wide complex tachycardias.
Lewis Lead Placement:
- RA (Right Arm): Place the RA electrode on the manubrium (upper part of the sternum).
- LA (Left Arm): Place the LA electrode in the 5th intercostal space at the right sternal border.
- LL (Left Leg): Place the LL electrode over the right lower costal margin.
- Monitor Lead I: Select Lead I on the ECG monitor to view the Lewis lead tracing.
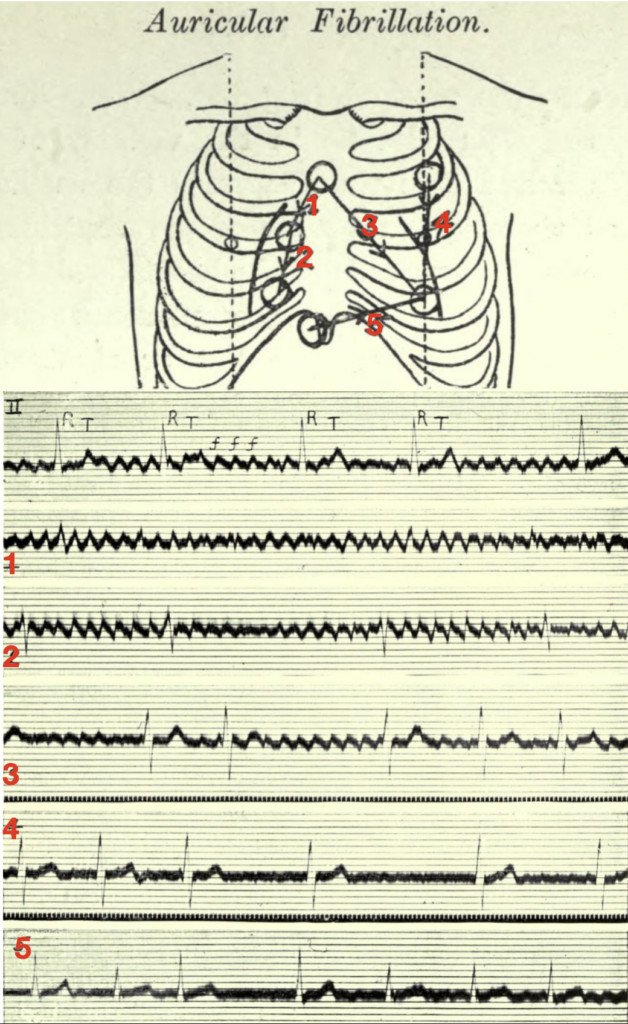 Diagram showing Lewis lead placement with RA electrode on manubrium, LA electrode over 5th ICS at right sternal border and LL electrode over right lower costal margin.
Diagram showing Lewis lead placement with RA electrode on manubrium, LA electrode over 5th ICS at right sternal border and LL electrode over right lower costal margin.
Fontaine Leads (F-ECG) for Epsilon Wave Detection
Fontaine leads, or F-ECG, are bipolar precordial leads specifically designed to increase the sensitivity for detecting epsilon waves, which are late potentials associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
Fontaine Lead Placement:
- RA (Right Arm): Place the RA electrode over the manubrium.
- LA (Left Arm): Place the LA electrode over the xiphoid process (inferior part of the sternum).
- LL (Left Leg): Place the LL electrode in the standard V4 position (5th ICS, mid-clavicular line).
- This configuration creates three bipolar chest leads (FI, FII, and FIII) instead of standard leads I, II, and III.
ECG Electrode Color Guide
Understanding the color coding for ECG electrodes is essential for quick and accurate placement, especially in emergency situations.
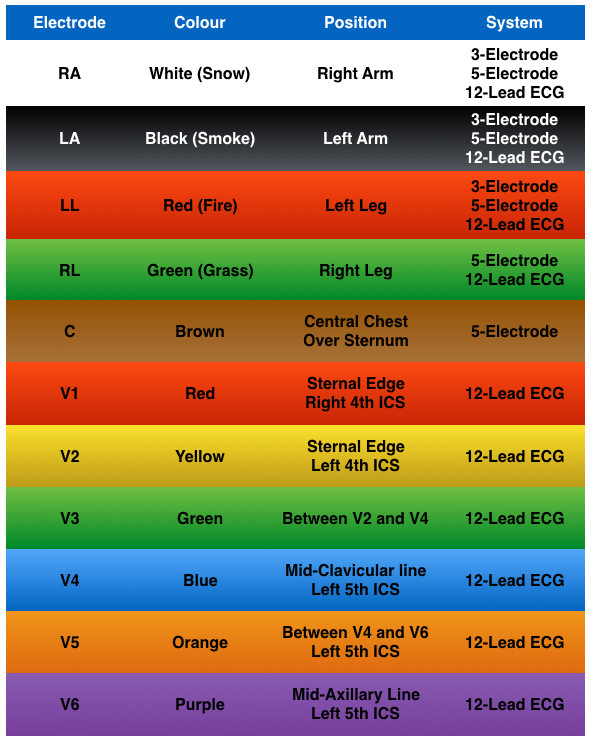 Chart showing ECG electrode system and colors according to AHA and IEC standards. Colors are listed for Right Arm, Left Arm, Left Leg, Right Leg and Chest electrodes.
Chart showing ECG electrode system and colors according to AHA and IEC standards. Colors are listed for Right Arm, Left Arm, Left Leg, Right Leg and Chest electrodes.
ECG Learning Resources
To further enhance your understanding of ECG lead placement and ECG interpretation, consider these video resources:
- The ECG Lead: Link to Video (if available)
- The Limb Leads: Link to Video (if available)
- The Precordial Leads: Link to Video (if available)
Related Topics for Further Exploration:
- Advanced ECG Reading: Link to Advanced Reading Resources (if available)
- ECG Textbooks: Link to ECG Textbook Recommendations (if available)
- LITFL ECG Library: Link to LITFL ECG Library
Conclusion
Correct ECG lead placement is paramount for obtaining accurate and reliable ECG recordings. Whether performing a basic 3-lead monitoring or a comprehensive 12-lead ECG, understanding the anatomical landmarks and proper electrode positions is crucial. For specialized diagnostic needs, knowledge of right-sided, posterior, Lewis, and Fontaine leads can significantly enhance diagnostic capabilities. By mastering ECG lead placement techniques, healthcare professionals can ensure optimal patient assessment and care.

