Egypt, a nation steeped in history and vibrant culture, occupies a unique and strategically significant location on the globe. Understanding Where Is Located Egypt is key to grasping its historical importance and contemporary role in the world. This article delves into the geographical positioning of Egypt, exploring its continental placement, regional context, and the pivotal features that have shaped its destiny.
Geographical Location of Egypt: A Continental Crossroads
Egypt is situated in the northeastern corner of Africa, making it a transcontinental country with a portion of its territory, the Sinai Peninsula, extending into Asia. This placement at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East has profoundly influenced Egypt’s history, culture, and geopolitics. Specifically, Egypt is located in North Africa, bordered by:
- Libya to the west
- Sudan to the south
- Israel and the Gaza Strip to the northeast
- The Mediterranean Sea to the north
- The Red Sea to the east
This strategic positioning has made Egypt a crucial link between Africa, Asia, and Europe throughout history. The country’s heartland is centered around the Nile River valley and delta, a fertile strip of land that has been the cradle of Egyptian civilization for millennia.
 Pyramids of Giza, Egypt, showcasing ancient Egyptian civilization near Cairo
Pyramids of Giza, Egypt, showcasing ancient Egyptian civilization near Cairo
Egypt’s Location: A Historical Hotspot
The geographical location of Egypt has been instrumental in its historical prominence. The fertile Nile Valley allowed for the development of one of the earliest and most enduring civilizations in human history. Ancient Egypt flourished for approximately 3000 years, leaving behind a legacy of monumental architecture, sophisticated governance, and rich cultural traditions.
Egypt’s location also placed it at the center of ancient trade routes. It served as a vital link between the Mediterranean world, Africa, and the Middle East, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. After being conquered by Alexander the Great in 323 BCE, Egypt became a central part of the Hellenistic world, further enhancing its cosmopolitan character. Alexandria, founded by Alexander, became a renowned center of learning and commerce under the Greek Ptolemaic dynasty.
Subsequently, Egypt was incorporated into the Roman Empire and then the Byzantine Empire, continuing its role as a significant province due to its agricultural wealth and strategic location. The Arab conquest in the 7th century CE marked another turning point, integrating Egypt into the Islamic world and shaping its cultural and linguistic landscape.
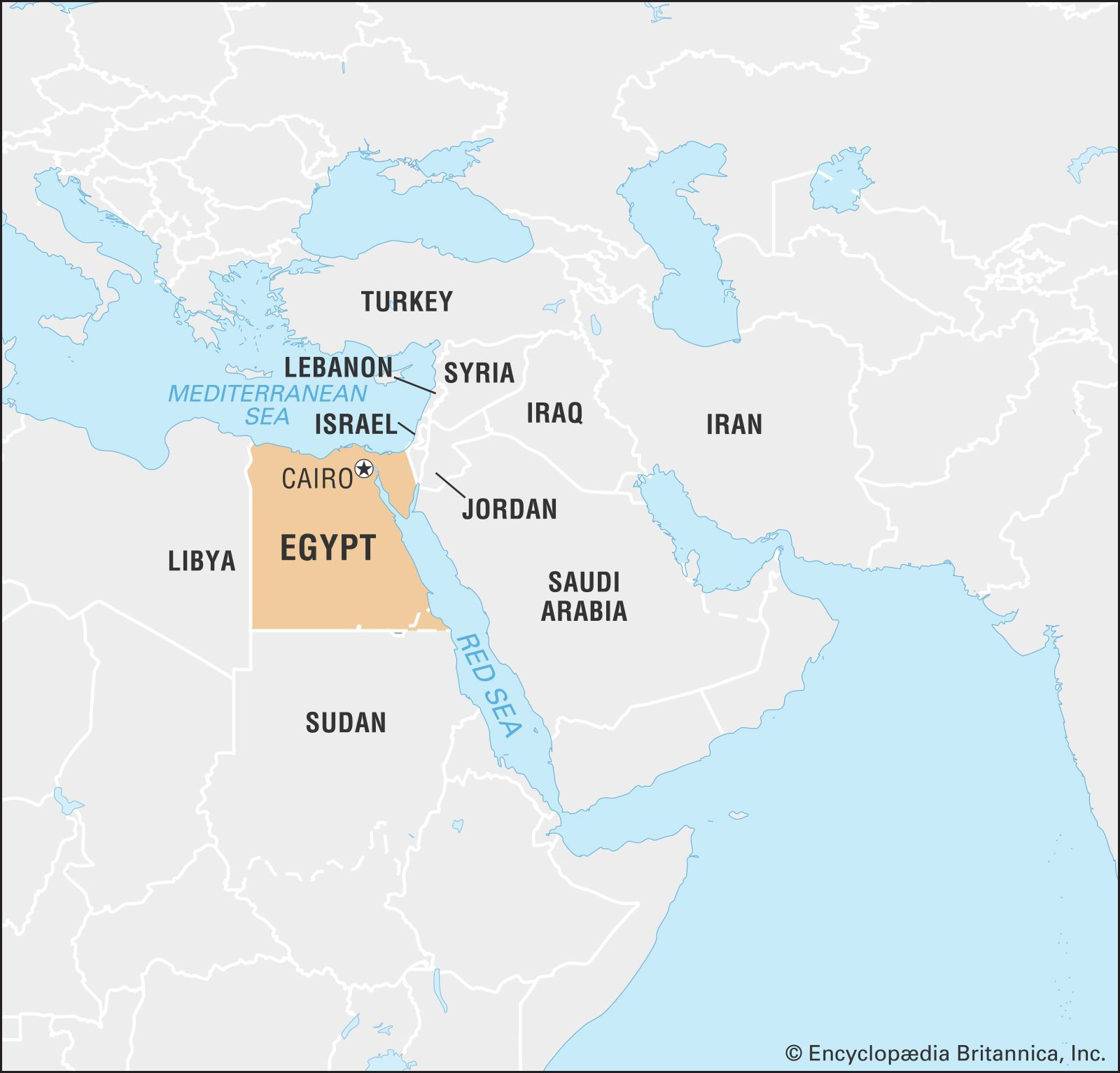 Map of Egypt highlighting its location in Northeast Africa and the Middle East region
Map of Egypt highlighting its location in Northeast Africa and the Middle East region
The Suez Canal: Enhancing Egypt’s Strategic Importance
Egypt’s strategic importance was dramatically amplified in 1869 with the opening of the Suez Canal. This artificial waterway connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, providing the shortest maritime route between Europe and Asia. The Suez Canal transformed global trade, significantly reducing travel time and costs.
The canal’s construction and operation became a focal point of European interest in Egypt, particularly for Britain and France, who were major shareholders. The desire to control and safeguard the Suez Canal was a key factor in Britain’s occupation of Egypt in 1882, which lasted until after World War II.
Modern Egypt in its Geographical Context
In the modern era, Egypt’s location continues to be of paramount importance. It remains a pivotal player in the Middle East and North Africa, both geographically and politically. Egypt is the most populous Arab country and has historically played a leading role in Arab affairs.
Its location has made it central to regional conflicts and peace initiatives, including the Arab-Israeli conflict. Egypt was the first Arab state to make peace with Israel in 1979, a move that reshaped regional dynamics.
Egypt’s major cities, including the capital Cairo, are located along the Nile. Cairo, one of the largest cities in Africa and the Middle East, is situated in the Nile Delta and serves as a major cultural, economic, and political hub. Other significant cities include Alexandria on the Mediterranean coast and Port Said at the northern entrance of the Suez Canal.
 The national flag of Egypt, representing the Arab Republic of Egypt
The national flag of Egypt, representing the Arab Republic of Egypt
Conclusion: Egypt’s Enduring Significance
In conclusion, Egypt is located in a geographically strategic position in the northeastern corner of Africa, bridging the continent with the Middle East. This location has been a defining factor in Egypt’s long and influential history, from the ancient pharaohs to its modern role in regional and global affairs. The Nile River, the Suez Canal, and its position as a land bridge have all contributed to Egypt’s enduring significance as a crossroads of civilizations and a vital link in the global landscape.

