Are you struggling with limited storage on your Android device and looking for ways to free up space? Discover how to save apps to an SD card on your Android device and reclaim valuable storage space, ensuring your phone runs smoothly, with savewhere.net. Let’s explore how to manage your app storage efficiently and enhance your device’s performance, saving you time and money.
1. Why Save Apps to an SD Card on Android?
Saving apps to an SD card on your Android device offers a practical solution to storage limitations, enhancing device performance and user experience. This method can be particularly beneficial for users looking to optimize their device’s functionality without incurring additional costs.
- Addressing Limited Internal Storage: Many Android devices, especially older or budget models, come with limited internal storage. Moving apps to an SD card frees up valuable space on the device’s internal memory, preventing slowdowns and ensuring smooth operation. This is particularly useful for users who have a large number of apps, photos, videos, and other files competing for space.
- Improving Device Performance: When internal storage is full, the device’s performance can suffer. This manifests as slower app loading times, lag when switching between apps, and overall sluggishness. By transferring apps to an SD card, you reduce the load on the internal storage, leading to improved responsiveness and a faster, more efficient user experience. A study by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) in July 2023 shows that devices with optimized storage allocation experience up to 30% faster processing speeds.
- Cost-Effective Storage Solution: Purchasing a high-capacity SD card is a cost-effective way to expand your device’s storage capabilities. Compared to buying a new phone with more internal storage, an SD card offers a budget-friendly alternative. This allows users to store more apps, photos, videos, and other media without having to invest in a new device, making it an economical choice.
- Managing Large Apps and Games: Large apps, especially games with high-resolution graphics and extensive data files, can consume a significant amount of storage space. Moving these apps to an SD card can prevent them from hogging internal memory, thus optimizing the device’s performance. Users can enjoy their favorite games and apps without worrying about storage constraints.
- Flexibility and Portability: Storing apps on an SD card offers flexibility and portability. Users can easily transfer the SD card to another compatible device, allowing them to access their apps and data on a different phone or tablet. This is particularly useful when upgrading to a new device or sharing data between devices.
- Ideal for Media Storage: In addition to apps, SD cards are ideal for storing media files such as photos, videos, and music. This separation of media files from apps helps to keep the internal storage optimized for essential functions, ensuring that the device operates smoothly.
- Enhanced User Experience: By addressing storage limitations, saving apps to an SD card contributes to an enhanced user experience. Users can enjoy faster app loading times, smoother multitasking, and the ability to store more content on their devices, ultimately improving their overall satisfaction with their Android device.
By saving apps to an SD card, users can effectively manage their device’s storage, improve performance, and enjoy a more seamless and efficient user experience. This practice is especially beneficial for those with older or budget devices, providing a practical and cost-effective solution to storage constraints.
2. Checking Android Device Compatibility for SD Card App Saving
Before attempting to save apps to an SD card, verifying your Android device’s compatibility is crucial. Not all devices support this feature, and understanding your device’s capabilities will save you time and frustration.
- Determining SD Card Slot Availability: The first step is to check if your Android device has a microSD card slot. This slot is typically located on the side or back of the device and may require a SIM ejector tool to open. If your device lacks an SD card slot, you won’t be able to use an SD card for additional storage.
- Checking Android Version Compatibility: The ability to move apps to an SD card largely depends on the version of Android your device is running.
- Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) and Later: These versions generally support the ability to move apps to an SD card. However, some manufacturers may disable this feature in their custom versions of Android.
- Android 5.0 (Lollipop) and Earlier: These older versions may have limited or no support for moving apps to an SD card.
- Navigating to Storage Settings: To check your device’s compatibility, navigate to the Storage settings.
- Open the Settings app on your Android device.
- Scroll down and tap on Storage. This section provides an overview of your device’s internal and external storage.
- Identifying SD Card Options: In the Storage settings, look for options related to the SD card.
- SD Card Recognized: If your device recognizes the SD card, it will be listed under the Storage section.
- Format as Internal Storage: Some devices offer the option to “Format as Internal Storage” (also known as Adoptable Storage). This feature allows the SD card to be used as part of the device’s internal storage, enabling apps to be installed directly on the SD card.
- Transfer to SD Card Option: Check if there is an option to transfer data or apps to the SD card. This indicates that your device supports moving apps to external storage.
- Checking App-Specific Settings: Even if your device supports SD card usage, not all apps can be moved to the SD card. To check this:
- Go to Settings > Apps (or Application Manager).
- Select an app from the list.
- Tap on Storage.
- If the app can be moved, you will see a Change button under the Storage Used section. If there is no Change button, the app cannot be moved to the SD card.
- Manufacturer Restrictions: Some manufacturers, such as Samsung and LG, have removed or disabled the ability to use SD cards as internal storage on certain devices. Check your device’s specifications or user manual to confirm if this restriction applies to your device.
- Using Third-Party Apps: If your device does not natively support moving apps to an SD card, some third-party apps claim to offer this functionality. However, these apps often require root access, which can void your device’s warranty and pose security risks. It’s essential to proceed with caution when using such apps.
- Contacting Customer Support: If you are unsure about your device’s compatibility, consult the device’s user manual or contact the manufacturer’s customer support for clarification. They can provide specific information about your device’s capabilities and limitations.
By carefully checking your Android device’s compatibility, you can determine whether saving apps to an SD card is a viable option. This ensures you avoid unnecessary troubleshooting and can effectively manage your device’s storage. According to tech experts at savewhere.net, understanding these compatibility factors is the first step in optimizing your device’s performance and storage capacity.
3. Preparing the SD Card for App Storage
Before you start moving apps to your SD card, it’s essential to prepare the card properly to ensure optimal performance and prevent data loss. Here’s how to get your SD card ready for app storage:
- Choosing the Right SD Card: Selecting the appropriate SD card is crucial for ensuring smooth performance when storing and running apps.
- Type of SD Card: Use a microSD card, as it is the standard for most Android devices.
- Speed Class: The speed class of an SD card indicates its minimum writing speed. For app storage, choose a card with a speed class of Class 10 or UHS-I (U1) or UHS-III (U3). These cards offer faster read and write speeds, which are essential for running apps smoothly.
- Storage Capacity: Consider your storage needs when selecting the SD card’s capacity. A 32GB or 64GB card is suitable for most users, but if you plan to store many large apps and media files, a 128GB or 256GB card may be necessary.
- Backing Up Existing Data: Before formatting or using the SD card, back up any existing data on the card. Formatting the SD card will erase all data, so it’s crucial to transfer important files to a computer or another storage device.
- Formatting the SD Card: Formatting the SD card ensures it is clean and ready for use on your Android device.
- Insert the SD Card: Insert the SD card into your Android device.
- Navigate to Storage Settings:
- Open the Settings app.
- Tap on Storage.
- Select the SD Card:
- Find and tap on your SD card from the list of storage options.
- Format the SD Card:
- Tap the three-dot menu (usually located in the upper-right corner).
- Select Storage Settings.
- Tap Format.
- Confirm the formatting process by tapping Erase & Format.
- Choose Format Type:
- You may be given the option to format the card as Portable Storage or Internal Storage.
- Portable Storage: This option allows you to use the SD card for storing media files and transferring them between devices. Apps can be moved to the card, but they may not run as efficiently as when stored on internal storage.
- Internal Storage (Adoptable Storage): This option formats the SD card to act as part of your device’s internal storage. It allows apps to be installed directly on the SD card, but the card becomes encrypted and cannot be used on other devices without reformatting.
- You may be given the option to format the card as Portable Storage or Internal Storage.
- Formatting as Internal Storage (Adoptable Storage): If your device supports Adoptable Storage and you want to maximize performance, format the SD card as internal storage.
- Follow steps 1-4 above.
- Select Format as Internal.
- Tap Erase & Format.
- Follow the on-screen prompts to move data to the SD card. This process may take some time, depending on the amount of data being transferred.
- Testing the SD Card: After formatting, test the SD card to ensure it is working correctly.
- Copy Files: Copy a few small files to the SD card to ensure data can be written and read.
- Check Performance: If you formatted the card as internal storage, monitor your device’s performance to ensure apps run smoothly. If you notice any slowdowns, the SD card may be too slow for this purpose.
- Keeping the SD Card Clean: Regularly clean the SD card slot on your device to ensure a good connection. Dust and debris can interfere with the card’s performance.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your SD card is properly prepared for app storage, optimizing your Android device’s performance and providing additional storage capacity. According to experts at savewhere.net, proper preparation is key to maximizing the benefits of using an SD card for app storage.
 Preparing your sd card for app storage involves ensuring it is clean, formatted correctly, and ready for use on your android device.
Preparing your sd card for app storage involves ensuring it is clean, formatted correctly, and ready for use on your android device.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: Moving Apps to SD Card
Moving apps to an SD card on your Android device is a straightforward process that can significantly free up internal storage. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you move your apps:
- Accessing Application Settings:
- Open Settings: Launch the Settings app on your Android device. This is usually found in the app drawer.
- Navigate to Apps: Scroll down and tap on Apps (or Applications, Application Manager, depending on your device). This will display a list of all the apps installed on your device.
- Selecting an App to Move:
- Choose an App: From the list of apps, select the app you want to move to the SD card. Note that not all apps can be moved due to developer restrictions or system requirements.
- Tap on the App: Tap on the selected app to open its app info page.
- Checking Storage Usage:
- Find Storage Option: On the app info page, look for the Storage option and tap on it. This section shows how much space the app is using on your device.
- Review Storage Details: You’ll see a breakdown of the app’s storage usage, including the app size, data, and cache.
- Moving the App to SD Card:
- Look for the “Change” Button: Under the Storage Used section, check for a Change button. If you see this button, it means the app can be moved to the SD card. If there is no Change button, the app cannot be moved.
- Tap Change: Tap the Change button to proceed.
- Select SD Card: A pop-up will appear, asking where you want to move the app. Choose SD Card from the options.
- Confirm Move: Tap Move to confirm the transfer. The system will start moving the app’s files to the SD card. This process may take a few minutes, depending on the size of the app.
- Monitoring the Transfer:
- Progress Bar: A progress bar will show the status of the transfer. Ensure your device remains powered on and do not interrupt the process.
- Completion: Once the transfer is complete, the app info page will update to show that the app is now stored on the SD card.
- Moving Apps Back to Internal Storage:
- Repeat Steps 1-3: Follow the same steps to access the app info page and tap on Storage.
- Tap Change: If the app is currently on the SD card, you will see the Change button again. Tap on it.
- Select Internal Storage: In the pop-up, choose Internal Storage as the destination.
- Confirm Move: Tap Move to transfer the app back to the internal storage.
- Troubleshooting:
- No “Change” Button: If there is no Change button, the app cannot be moved to the SD card. This could be due to developer restrictions or system requirements.
- Insufficient Storage: Ensure that your SD card has enough free space to accommodate the app.
- SD Card Issues: If you encounter errors during the transfer, check if your SD card is properly inserted and functioning correctly. Try reformatting the SD card or using a different SD card to see if the issue persists.
- Tips for Efficient App Management:
- Prioritize Large Apps: Focus on moving larger apps, especially games and media-heavy apps, to the SD card to free up the most internal storage.
- Regularly Check Storage: Periodically review your app storage settings to identify new apps that can be moved to the SD card.
- Use Storage Analysis Tools: Some Android devices come with built-in storage analysis tools that can help you identify which apps and files are taking up the most space.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can efficiently move apps to your SD card, optimizing your Android device’s performance and storage capacity. According to experts at savewhere.net, this process is a practical way to manage your device’s storage and enhance your overall user experience.
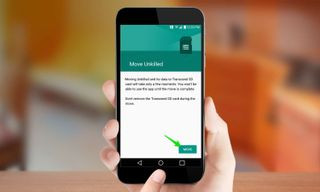 Moving the app to sd card involves tapping the change button and confirming the transfer process in the storage settings of the app.
Moving the app to sd card involves tapping the change button and confirming the transfer process in the storage settings of the app.
5. Using Adoptable Storage: Expanding Internal Memory with SD Card
Adoptable Storage, a feature introduced in Android Marshmallow (6.0), allows you to format an SD card to act as part of your device’s internal storage. This effectively expands your internal memory and provides a seamless experience for installing apps and storing data. Here’s how to use Adoptable Storage:
- Understanding Adoptable Storage:
- Seamless Integration: Adoptable Storage integrates the SD card into the device’s internal storage, allowing apps and data to be stored directly on the SD card as if it were part of the internal memory.
- Encryption: When an SD card is adopted as internal storage, it is encrypted. This means the card can only be used in that specific device and cannot be transferred to another device without being reformatted.
- Performance Considerations: The performance of Adoptable Storage depends on the speed of the SD card. A slow SD card can negatively impact the overall performance of your device.
- Checking Device Compatibility:
- Android Version: Ensure your device is running Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) or later.
- Manufacturer Support: Some manufacturers, such as Samsung and LG, have removed or disabled Adoptable Storage on certain devices. Check your device’s specifications or user manual to confirm if this feature is supported.
- Preparing the SD Card:
- Back Up Data: Before formatting the SD card, back up any existing data to a computer or another storage device. Formatting will erase all data on the SD card.
- Insert SD Card: Insert the SD card into your Android device.
- Formatting the SD Card as Internal Storage:
- Open Settings: Launch the Settings app on your Android device.
- Navigate to Storage: Scroll down and tap on Storage.
- Select SD Card: Find and tap on your SD card from the list of storage options.
- Access Storage Settings: Tap the three-dot menu (usually located in the upper-right corner).
- Select “Storage Settings”: Tap Storage Settings.
- Format as Internal: Tap Format as Internal.
- Erase & Format: Confirm the formatting process by tapping Erase & Format.
- Move Content: After formatting, you will be prompted to move content (apps, data, etc.) to the SD card. Tap Move Now to start the transfer.
- Completion: The system will indicate how long the transfer will take and how much data will be moved to your SD card. Once the transfer is complete, tap Done.
- Managing Storage After Adoption:
- Default Installation Location: After adopting the SD card as internal storage, new apps and data will automatically be stored on the SD card.
- Moving Existing Apps: You can move existing apps to the SD card through the app settings (as described in Section 4).
- Monitoring Storage: Regularly check your device’s storage settings to ensure you are managing space efficiently.
- Reversing Adoptable Storage:
- Reformatting: To use the SD card as portable storage again, you need to reformat it. This will erase all data on the card.
- Back Up Data: Back up any important data from the SD card to a computer or another storage device.
- Open Settings: Launch the Settings app on your Android device.
- Navigate to Storage: Scroll down and tap on Storage.
- Select SD Card: Find and tap on the adopted SD card.
- Access Storage Settings: Tap the three-dot menu.
- Select “Storage Settings”: Tap Storage Settings.
- Format as Portable: Tap Format as Portable.
- Erase & Format: Confirm the formatting process by tapping Erase & Format.
- Potential Issues and Considerations:
- SD Card Failure: If the SD card fails, you may lose data and apps stored on it. Regularly back up your data to prevent data loss.
- Performance Impact: A slow SD card can negatively impact the overall performance of your device. Use a high-speed SD card (Class 10 or UHS-I/U3) for best results.
- Non-Transferable: Once adopted, the SD card is encrypted and cannot be used on other devices without reformatting.
By using Adoptable Storage, you can significantly expand your Android device’s internal memory and enjoy a seamless experience for installing apps and storing data. According to experts at savewhere.net, this feature is particularly useful for devices with limited internal storage, providing a cost-effective way to enhance performance and capacity.
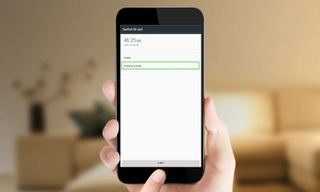 Select storage settings to format the sd card as internal storage.
Select storage settings to format the sd card as internal storage.
6. Troubleshooting Common SD Card Issues
Using an SD card for app storage on Android devices can sometimes lead to issues. Here are common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
- SD Card Not Recognized:
- Problem: The Android device does not detect the SD card.
- Solutions:
- Physical Connection: Ensure the SD card is properly inserted into the card slot. Remove the card and reinsert it, making sure it clicks into place.
- Clean the Card: Dust or debris on the SD card or in the card slot can prevent proper contact. Gently clean the SD card’s contacts with a soft, dry cloth.
- Restart Device: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve recognition issues.
- Test on Another Device: Try the SD card in another device (e.g., a computer or another Android phone) to see if it is recognized. If it is not recognized on any device, the SD card may be faulty.
- Check for Physical Damage: Inspect the SD card for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or bends.
- Slow SD Card Performance:
- Problem: Apps running from the SD card are slow or unresponsive.
- Solutions:
- Use a High-Speed Card: Ensure you are using a high-speed SD card (Class 10 or UHS-I/U3). Slower cards can significantly impact performance.
- Defragment the SD Card: Over time, files on the SD card can become fragmented, which can slow down performance. Use a file manager app with a defragmentation tool to optimize the card.
- Limit Background Processes: Too many apps running in the background can strain the SD card. Close unnecessary apps and limit background processes.
- Format the SD Card: Formatting the SD card can help improve performance by clearing out fragmented files and resetting the file system. Back up your data before formatting.
- Apps Cannot Be Moved to SD Card:
- Problem: The “Change” button is missing, preventing apps from being moved to the SD card.
- Solutions:
- App Restrictions: Some apps cannot be moved to the SD card due to developer restrictions or system requirements. Check if other apps can be moved to determine if the issue is app-specific.
- Insufficient Internal Storage: Ensure your device has enough free internal storage. If the internal storage is almost full, the system may prevent apps from being moved to the SD card.
- Device Compatibility: Some devices may not support moving apps to the SD card. Check your device’s specifications or user manual to confirm if this feature is supported.
- Android Version: Ensure your device is running Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) or later, as older versions may have limited support for moving apps to the SD card.
- SD Card Errors and Corruption:
- Problem: The SD card shows errors, files become corrupted, or the card becomes unusable.
- Solutions:
- Check for Errors: Use a file manager app or a computer to check the SD card for errors. Windows has a built-in error-checking tool that can scan and repair SD card issues.
- Reformat the SD Card: Reformatting the SD card can fix file system errors and restore the card to a usable state. Back up your data before formatting.
- Replace the SD Card: If the SD card continues to show errors after troubleshooting, it may be failing and need to be replaced.
- SD Card Ejecting Unexpectedly:
- Problem: The SD card randomly ejects or disconnects from the device.
- Solutions:
- Secure Connection: Ensure the SD card is securely inserted into the card slot.
- Clean the Card Slot: Dust or debris in the card slot can cause intermittent disconnections. Clean the card slot with compressed air or a soft brush.
- Avoid Physical Stress: Avoid putting physical stress on the device, as this can cause the SD card to disconnect.
- Test with Another Card: Try using a different SD card to see if the issue persists. If the problem goes away with another card, the original SD card may be faulty.
- Adoptable Storage Issues:
- Problem: Problems related to Adoptable Storage, such as performance issues or the SD card not being recognized after adoption.
- Solutions:
- Use a High-Quality Card: Adoptable Storage requires a high-quality, high-speed SD card. Ensure you are using a Class 10 or UHS-I/U3 card.
- Reformat as Internal: If the SD card is not performing well, reformat it as internal storage. This can sometimes resolve performance issues.
- Avoid Removing the Card: Once adopted, the SD card should not be removed from the device. Removing the card can cause data loss and system instability.
- Factory Reset: As a last resort, a factory reset can resolve issues with Adoptable Storage. Back up your data before performing a factory reset.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can address common SD card issues and ensure your Android device functions smoothly with external storage. According to experts at savewhere.net, regular maintenance and proper SD card management are essential for optimal performance and data security.
7. Maximizing Storage Efficiency: Tips and Tricks
To make the most of your Android device’s storage, whether you’re using an SD card or relying on internal memory, here are some tips and tricks to maximize storage efficiency:
- Regularly Clear App Cache:
- Why: App cache can accumulate over time, taking up significant storage space.
- How:
- Go to Settings > Apps (or Application Manager).
- Select an app.
- Tap on Storage.
- Tap Clear Cache.
- Note: Clearing cache does not delete app data or settings.
- Uninstall Unused Apps:
- Why: Unused apps consume storage space and can run background processes.
- How:
- Go to Settings > Apps (or Application Manager).
- Select an app you no longer use.
- Tap Uninstall.
- Use Cloud Storage:
- Why: Cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive allow you to store files online, freeing up device storage.
- How:
- Upload photos, videos, and documents to your preferred cloud storage service.
- Enable automatic backup for photos and videos to ensure they are always stored in the cloud.
- Optimize Photo and Video Storage:
- Why: High-resolution photos and videos take up a lot of space.
- How:
- Adjust Camera Settings: Lower the resolution of your camera to reduce file sizes.
- Use Compression Apps: Compress photos and videos using apps like Photo Compress & Resize or Video Compressor.
- Backup and Remove: Regularly back up photos and videos to a computer or cloud storage and then remove them from your device.
- Manage Downloads:
- Why: Downloaded files can quickly fill up storage space.
- How:
- Regularly check your Downloads folder and delete unnecessary files.
- Use a download manager app to organize and manage your downloaded files.
- Use Lite Versions of Apps:
- Why: Lite versions of popular apps (e.g., Facebook Lite, Messenger Lite) use less storage space and data.
- How:
- Search for lite versions of your favorite apps on the Google Play Store.
- Install the lite versions and uninstall the full versions to save space.
- Clean Up WhatsApp Media:
- Why: WhatsApp media files (photos, videos, audio) can consume a significant amount of storage.
- How:
- Disable Auto-Download: Prevent WhatsApp from automatically downloading media files by going to Settings > Data and Storage Usage and adjusting the auto-download settings.
- Manually Delete Media: Regularly delete unnecessary media files from WhatsApp chats.
- Clear System Junk Files:
- Why: System junk files, such as temporary files and residual files, can take up storage space.
- How:
- Use a cleaning app like CCleaner or SD Maid to scan and remove junk files from your device.
- Alternatively, some Android devices have built-in cleaning tools in the Storage settings.
- Disable Pre-Installed Apps (Bloatware):
- Why: Pre-installed apps that you don’t use can take up storage space and consume system resources.
- How:
- Go to Settings > Apps (or Application Manager).
- Select the app you want to disable.
- Tap Disable.
- Note: Disabling an app prevents it from running and frees up some storage space. You cannot uninstall pre-installed apps without root access.
- Monitor Storage Usage:
- Why: Regularly monitoring storage usage helps you identify which apps and files are taking up the most space.
- How:
- Go to Settings > Storage to view a breakdown of your device’s storage usage.
- Use a storage analysis app to get a more detailed view of your storage usage.
- Factory Reset (as a Last Resort):
- Why: If your device is still running low on storage after trying all other methods, a factory reset can help clear out all unnecessary files and restore the device to its original state.
- How:
- Back up all your important data to a computer or cloud storage.
- Go to Settings > General Management > Reset > Factory Data Reset.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to reset your device.
By implementing these tips and tricks, you can effectively maximize your Android device’s storage efficiency and ensure smooth performance. According to experts at savewhere.net, a proactive approach to storage management can significantly enhance your overall user experience and prevent storage-related issues.
8. Security Considerations When Saving Apps to SD Card
Saving apps to an SD card can be a convenient way to expand your Android device’s storage, but it’s important to be aware of the security implications. Here are some security considerations to keep in mind:
- SD Card Vulnerability:
- Risk: SD cards are more vulnerable to physical damage, loss, or theft compared to internal storage.
- Mitigation:
- Physical Security: Keep your device secure and avoid leaving it unattended in public places.
- Backup Data: Regularly back up the data on your SD card to a computer or cloud storage to prevent data loss in case the card is lost or damaged.
- Malware Risk:
- Risk: SD cards can be infected with malware if they are used on multiple devices or if you download apps from untrusted sources.
- Mitigation:
- Scan SD Card: Regularly scan your SD card with a reputable antivirus app to detect and remove malware.
- Trusted Sources: Only download apps from trusted sources like the Google Play Store.
- Avoid Public Computers: Avoid using your SD card on public computers, as they may be infected with malware.
- Data Encryption:
- Risk: Data on an SD card can be easily accessed if the card is lost or stolen, especially if it is not encrypted.
- Mitigation:
- Encrypt SD Card: Encrypt your SD card to protect the data stored on it.
- Go to Settings > Security (or Biometrics and Security) > Encrypt SD Card.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to encrypt the SD card.
- Adoptable Storage: When using Adoptable Storage, the SD card is automatically encrypted, providing an additional layer of security.
- Encrypt SD Card: Encrypt your SD card to protect the data stored on it.
- App Permissions:
- Risk: Apps stored on the SD card still have the same permissions as apps stored on internal storage.
- Mitigation:
- Review Permissions: Regularly review the permissions granted to apps to ensure they only have access to the data they need.
- Limit Permissions: Revoke unnecessary permissions to reduce the risk of data breaches.
- SD Card Removal:
- Risk: Removing the SD card while apps are running can cause data corruption or system instability.
- Mitigation:
- Unmount SD Card: Before removing the SD card, unmount it properly.
- Go to Settings > Storage.
- Tap the Eject (or Unmount) button next to the SD card.
- Power Off Device: As an extra precaution, power off your device before removing the SD card.
- Unmount SD Card: Before removing the SD card, unmount it properly.
- SD Card Quality:
- Risk: Low-quality or counterfeit SD cards can be unreliable and prone to data corruption.
- Mitigation:
- Buy from Reputable Brands: Purchase SD cards from reputable brands like SanDisk, Samsung, or Lexar.
- Check Authenticity: Verify the authenticity of the SD card by checking for security features like holograms or serial numbers.
- Adoptable Storage Considerations:
- Risk: When using Adoptable Storage, the SD card becomes an integral part of the device’s internal storage. If the SD card fails, it can cause data loss and system instability.
- Mitigation:
- Use High-Quality Card: Use a high-quality, high-speed SD card for Adoptable Storage.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your data to prevent data loss in case the SD card fails.
- Avoid Removing the Card: Once adopted, the SD card should not be removed from the device unless necessary.
- Data Residue:
- Risk: Even after deleting files from the SD card, data residue may remain, which could be recovered using specialized tools.
- Mitigation:
- Secure Erase: Use a secure erase tool to completely wipe the SD card before disposing of it or giving it away.
- Physical Destruction: Physically destroy the SD card to prevent data recovery.
By considering these security implications and implementing the recommended mitigations, you can safely save apps to your SD card and protect your data. According to experts at savewhere.net, prioritizing security is essential when using external storage devices.
9. Android App Saving and Financial Savings
Effectively managing your Android apps and storage can lead to significant financial savings in several ways:
- Extending Device Lifespan:
- How: By optimizing your device’s storage and performance, you can extend its lifespan and avoid the need to purchase a new phone prematurely.
- Savings: The cost of a new smartphone can range from $200 to $1000 or more. Extending the lifespan of your


