Understanding your network security key is crucial in today’s connected world. Often referred to as a Wi-Fi password, this key is your first line of defense against unauthorized access to your wireless network. Think of it as the digital lock protecting your internet connection and all the devices connected to it. A strong network security key is essential for both personal and business use, safeguarding sensitive data and preventing unwanted intrusions. Without it, your network is essentially open to anyone within range, creating significant security vulnerabilities.
Just like strong passwords for your online accounts, a robust network security key is vital for protecting your business or home network from malicious activities, preventing unauthorized access to connected devices, and minimizing the risk of data breaches. This article will guide you through the process of finding your network security key across various platforms and operating systems, ensuring you can manage your network security effectively.
Locating Your Network Security Key: Platform-Specific Guides
The method to find your network security key varies depending on the device and operating system you are using. But before diving into platform-specific instructions, let’s clarify what exactly you’re looking for. Different manufacturers and operating systems might use different terms for the network security key, but they all refer to the same thing: the password required to securely connect to your Wi-Fi network.
Here’s a breakdown of how to find your network security key on different devices and operating systems:
Finding Your Network Security Key on Your Router/Modem
The most straightforward place to find your initial network security key is usually printed directly on your router or modem itself. This is the default password set by the manufacturer. Look for a sticker on the side, bottom, or back of your router. Manufacturers often label it clearly, though the terminology can vary. Common labels include:
- Password
- Network Key
- Wireless Password
- WPA Key
- Security Key
This key is primarily intended for the initial setup of your network. It’s strongly recommended to change this default key to a more secure, personalized password soon after setting up your router. If you reset your router to its factory settings, it will revert to this default network security key printed on the device.
How to Find Your Network Security Key on a Windows Device
If you have a Windows device (Windows 10, Windows 11, or Windows Server) that is already connected to your Wi-Fi network, you can retrieve the network security key from your saved Wi-Fi login information. Here’s how:
- Click on the Start Menu in Windows and type “Network Connections”. Select and open Network Connections.
- Locate your Wi-Fi network connection and double-click on it. In the Wi-Fi Status window that pops up, click on Wireless Properties.
- Navigate to the Security tab within the Wireless Properties window.
- Check the box labeled “Show characters”. You may be prompted to enter your administrator password to proceed. Once confirmed, your network security key will be displayed in the “Network security key” field.
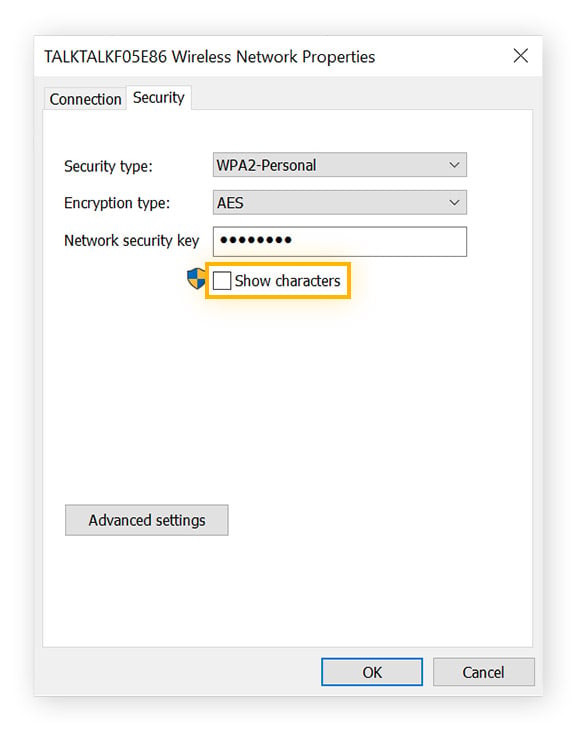 Finding WiFi password Windows 10: Show Characters option in Wireless Network Properties Security Tab.
Finding WiFi password Windows 10: Show Characters option in Wireless Network Properties Security Tab.
Retrieving Your Network Security Key on macOS
Finding your network security key on a macOS device is also a simple process, provided you know the name of your Wi-Fi network. Here are the steps:
- Open Finder, and in the Applications folder, navigate to the Utilities folder. Open Keychain Access. Alternatively, use Spotlight search (Command + Spacebar) and type “Keychain Access” to find and open the application.
- In Keychain Access, search for the name of your Wi-Fi network in the search bar in the top right corner.
- Double-click on the entry corresponding to your Wi-Fi network name. A pop-up window will appear with the network details.
- Check the box next to “Show Password”.
- You will be prompted to enter your Mac administrator password to reveal the network security key. Once authenticated, your network security key will be displayed.
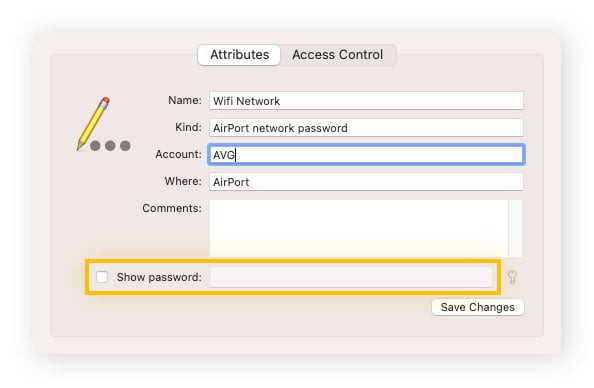 Finding WiFi password Mac: Keychain Access utility showing Show Password option.
Finding WiFi password Mac: Keychain Access utility showing Show Password option.
Accessing Your Network Security Key on Android Devices
The exact steps to find your network security key on Android can vary slightly depending on your phone manufacturer and Android version. Here’s a general guide, using a Samsung Galaxy S21 as an example:
- Open Settings on your Android device.
- Tap on Connections, and then select Wi-Fi.
- Tap the Settings icon (usually a gear icon) next to your currently connected Wi-Fi network.
- Look for an option like “QR code” or “Share”. Tapping on “QR code” typically displays a QR code that, when scanned, provides the network name and password. Sometimes, the password might be displayed directly beneath or alongside the QR code. On some devices, selecting “Share” might also reveal the password directly or offer options to share it via text or email, where you can then view it.
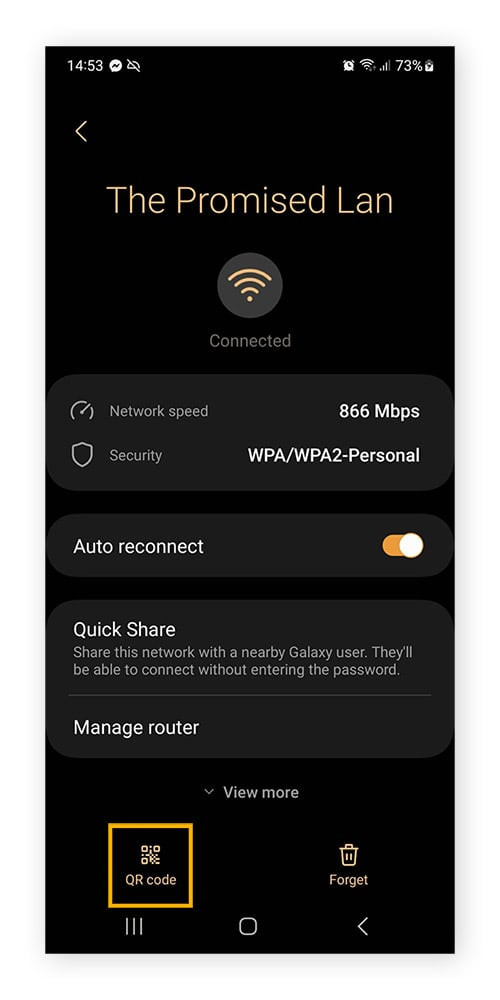 Finding WiFi password Android: QR code option within WiFi network settings.
Finding WiFi password Android: QR code option within WiFi network settings.
Finding Your Network Security Key on an iPhone
Locating your network security key directly on an iPhone is not possible due to iOS security restrictions. However, you can access your router’s settings through your iPhone to potentially find or change the password. Here’s a general approach:
- Open Settings on your iPhone and tap Wi-Fi.
- Tap the blue “information” icon (i) next to your connected Wi-Fi network name.
- Find the “Router” address listed. This is your router’s IP address.
- Open a web browser (like Safari or Chrome) on your iPhone and type the router’s IP address into the address bar. Go to this address.
- You will be prompted to log in to your router’s settings page. You’ll need your router’s administrator username and password (these are often different from your Wi-Fi password and are usually found in your router’s documentation or on the router itself).
- Once logged in, navigate to the Wireless settings or Wi-Fi settings section of your router’s interface. The location of the network security key within the router settings varies depending on the router manufacturer. Look for sections labeled “Security,” “Wireless Security,” or similar. Your network security key should be displayed there, often under labels like “Password,” “Pre-Shared Key,” or “Security Key.”
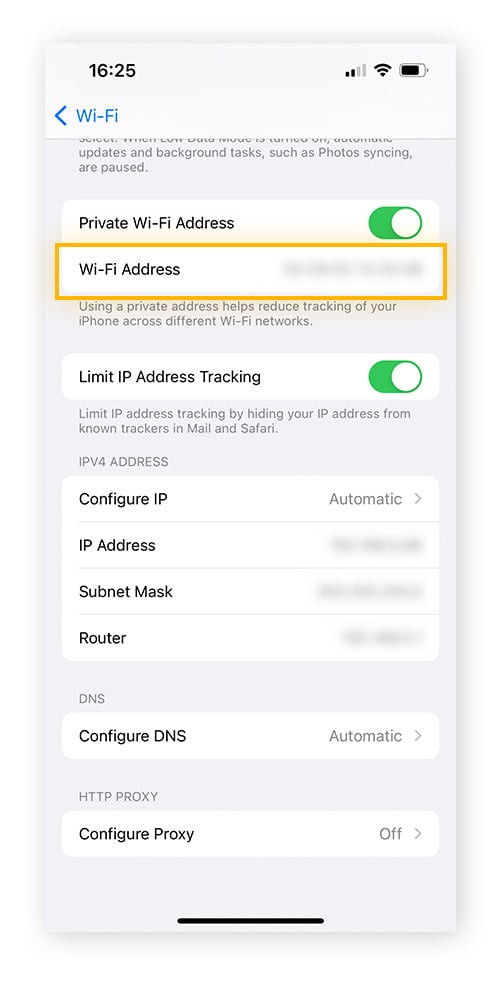 Finding WiFi password iPhone: Router IP address in WiFi network details.
Finding WiFi password iPhone: Router IP address in WiFi network details.
Finding the Network Security Key for a Mobile Hotspot on Android
When using your Android phone as a mobile hotspot, it essentially acts as a portable router. You can easily find the network security key (password) for your hotspot in your Android settings:
- Open Settings on your Android device.
- Tap on Connections, and then look for Mobile Hotspot and Tethering. The exact wording might vary slightly depending on your Android version.
- Tap on Mobile Hotspot.
- On the Mobile Hotspot settings screen, you should see your hotspot’s network name (SSID) and the password (network security key) displayed. You may need to tap on “Password” or a similar option to view it if it’s initially hidden. You can also often change the password on this screen.
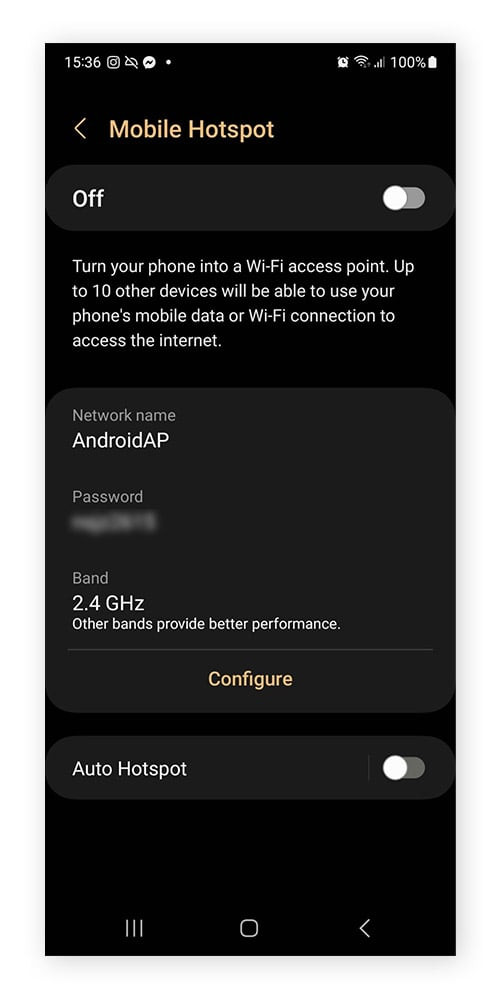 Finding hotspot password Android: Mobile Hotspot settings showing network name and password.
Finding hotspot password Android: Mobile Hotspot settings showing network name and password.
Finding the Network Security Key for a Personal Hotspot on iOS (iPhone)
Similar to Android hotspots, you can find the password for your iPhone’s Personal Hotspot within the iOS settings:
- Open Settings on your iPhone and tap on Personal Hotspot.
- The “Wi-Fi Password” for your Personal Hotspot is displayed directly on this screen. You can also change the password here if desired.
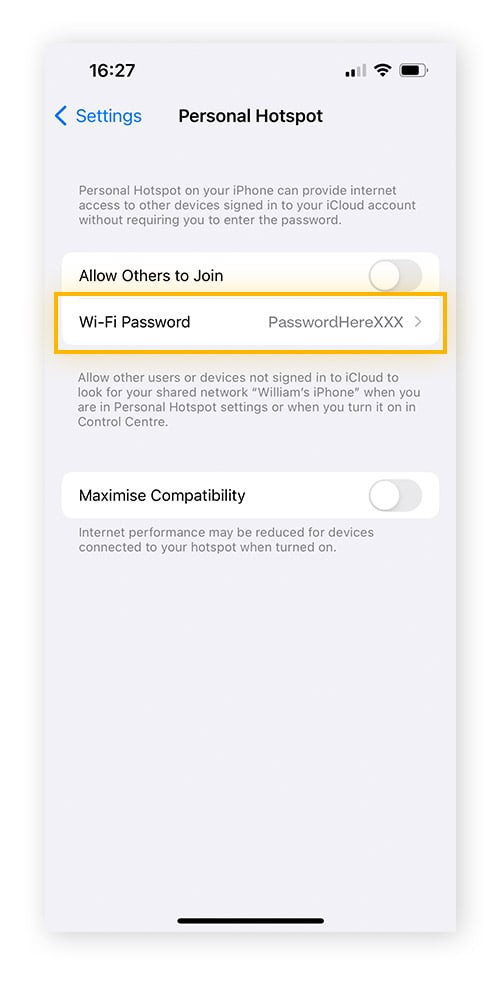 Finding hotspot password iPhone: Personal Hotspot settings showing WiFi Password.
Finding hotspot password iPhone: Personal Hotspot settings showing WiFi Password.
Finding Your Network Security Key Without an Internet Connection
You typically do not need an active internet connection to find your network security key using the methods described above, especially if you are accessing it from a device already connected to the network or directly from the router. However, you do need to be connected to your local Wi-Fi network to use the device-specific methods (Windows, macOS, Android).
If you cannot connect to the network at all, or if none of the device-based methods work, your best option is to find the default network security key printed on your router itself (as described in the “Router/Modem” section). Alternatively, if you are in a business or managed network environment, contact your IT administrator for assistance in retrieving the network security key.
Understanding Types of Network Security Keys: WEP, WPA, and WPA2
Network security keys operate using different security protocols, with the most common being WEP, WPA, and WPA2. These protocols differ primarily in their encryption methods, which directly impacts the security level of your wireless network.
Here’s a brief overview of these network security key protocols:
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
WEP is the oldest and least secure of the three protocols. It utilizes a static encryption key, making it relatively easy to crack by modern hacking tools. Due to its significant vulnerabilities, WEP is now considered outdated and is strongly discouraged for use. Using WEP leaves your network highly susceptible to unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
WPA was developed as an improvement over WEP. It introduced the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which uses dynamic encryption keys, making it more secure than WEP. However, TKIP was later also found to have vulnerabilities. While WPA was a step up from WEP, it is now largely superseded by WPA2.
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2)
WPA2 is currently the most secure and recommended wireless security protocol for most users. It employs Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption, a significantly stronger encryption method than those used in WEP and WPA. While WPA2 offers robust security, it is not completely impenetrable. Security threats are constantly evolving, and even WPA2 networks can be vulnerable if passwords are weak or if other security measures are lacking. This is why a comprehensive security strategy, including firewalls, VPNs, and robust antivirus software, remains crucial for optimal network protection. The newer WPA3 protocol offers even greater security, but WPA2 remains the most widely used and generally secure option today.
Changing Your Network Security Key for Enhanced Security
Regularly changing your network security key is a proactive step to improve your network security posture. It’s crucial to remember that changing the network security key requires administrator access to your router and will temporarily disconnect all devices connected to your Wi-Fi network. Therefore, it’s best to plan this change and communicate it to anyone who uses your network.
Here’s how to change your network security key:
- Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar. (Refer to the iPhone section above for how to find your router’s IP address if you don’t know it).
- Log in to your router’s settings page using your administrator username and password. These are usually different from your Wi-Fi password.
- Navigate to the Wireless settings, Wi-Fi settings, or Wireless Security section of your router’s interface. The exact location and naming will vary depending on your router model.
- Look for the field labeled “Password,” “Pre-Shared Key,” “Security Key,” or similar. This is where your current network security key is displayed or can be changed.
- Enter your new, strong network security key in the designated field.
- Save or Apply the changes. Your router will likely reboot or restart its wireless service to apply the new settings. Once completed, all devices will need to reconnect to the Wi-Fi network using the new network security key.
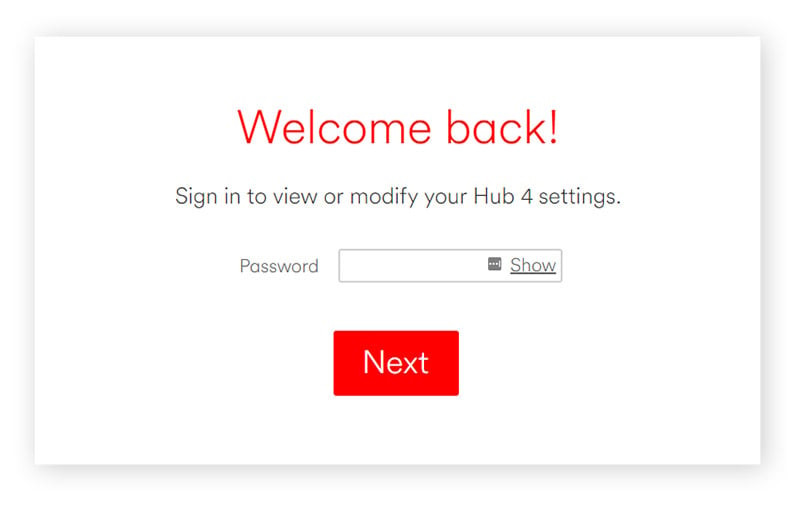 Changing WiFi password router: Router login page with Wireless Security settings highlighted.
Changing WiFi password router: Router login page with Wireless Security settings highlighted.
Creating a Strong Network Security Key: Best Practices
When changing your network security key, prioritize creating a strong, secure password to maximize your network protection. Avoid using easily guessable passwords like “12345678,” “password,” or personal information.
Here are key guidelines for creating a strong network security key:
- Length is crucial: Aim for a password that is at least 12 characters long, and ideally longer. Longer passwords are exponentially harder to crack.
- Complexity is key: Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters (!@#$%^&* etc.). This increases the password’s complexity and resistance to cracking attempts.
- Uniqueness matters: Avoid reusing passwords across different accounts and networks. If one password is compromised, all accounts using the same password become vulnerable.
- Regularly update your password: Change your network security key periodically, especially for sensitive business networks, to minimize the window of opportunity for potential attackers.
- Consider using a password manager: Password managers can help you generate, store, and manage complex, unique passwords securely. They also reduce the need to memorize multiple passwords.
For more in-depth guidance, explore resources dedicated to creating strong passwords and password management best practices.
Troubleshooting Network Security Key Mismatch Errors
Encountering a “network security key mismatch” error when trying to connect to a Wi-Fi network means the password you are entering is not being recognized as correct by the router. This can happen even if you believe you are using the right password.
Common causes of network security key mismatch errors include:
- Incorrect password entry: The most frequent cause is simply typing the password incorrectly. Double-check for typos, ensure Caps Lock is off if case sensitivity is a factor, and pay attention to special characters.
- Router restart needed: Like any electronic device, routers can sometimes experience glitches. Restarting your router can often resolve temporary issues and password recognition problems. Unplug your router from the power outlet, wait for about 30 seconds, and plug it back in.
- Device incompatibility: In rare cases, older devices using outdated security protocols (like WEP) might not be compatible with newer routers or network configurations using WPA2 or WPA3. If you suspect incompatibility, consider updating the security protocols on your older device if possible, or ensure your router is configured to support a compatible protocol (though using WEP is not recommended for security reasons).
Strengthen Your Business Network Security Beyond Just Passwords
While a strong network security key is a fundamental component of Wi-Fi security, it’s only one piece of the puzzle for robust business network protection. Comprehensive security requires a layered approach that goes beyond just strong passwords.
To truly safeguard your business network, consider implementing a dedicated security suite that includes:
- Firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier, monitoring and controlling network traffic to block unauthorized access and malicious intrusions.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: Essential for detecting and removing viruses, malware, spyware, and other malicious software that can compromise your network and devices.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, providing an extra layer of security and privacy, especially for remote workers or when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Regular Security Audits and Updates: Proactively assess your network security vulnerabilities and keep your router firmware, operating systems, and security software up to date with the latest patches and security enhancements.
AVG Antivirus Business Edition offers a comprehensive suite of security tools, including a built-in firewall, remote access detection, and a powerful web shield, designed to provide real-time protection for your business network and connected devices. Invest in robust security solutions to create a secure and resilient network environment.
Get AVG AntiVirus Business Edition