The pineal gland, though tiny, plays a vital role in your body’s overall well-being. Often referred to as the “third eye,” this enigmatic gland is nestled deep within the brain and is crucial for regulating sleep and various bodily functions. Understanding its location and function is key to appreciating its significance.
Pinpointing the Pineal Gland’s Location in Your Brain
So, Where Is The Pineal Gland Located precisely? This small endocrine gland resides near the center of your brain, positioned between the two hemispheres. To be more specific, it’s situated behind and just above the pituitary gland, in a groove between the superior colliculi, which are part of the midbrain. Imagine a tiny pine cone, about the size of a grain of rice, tucked away almost in the very heart of your head – that’s your pineal gland.
Its name originates from its pinecone-like shape (from the Latin pinea, meaning “pine cone”). This tiny gland, part of your endocrine system, might be small in size, but it’s mighty in function.
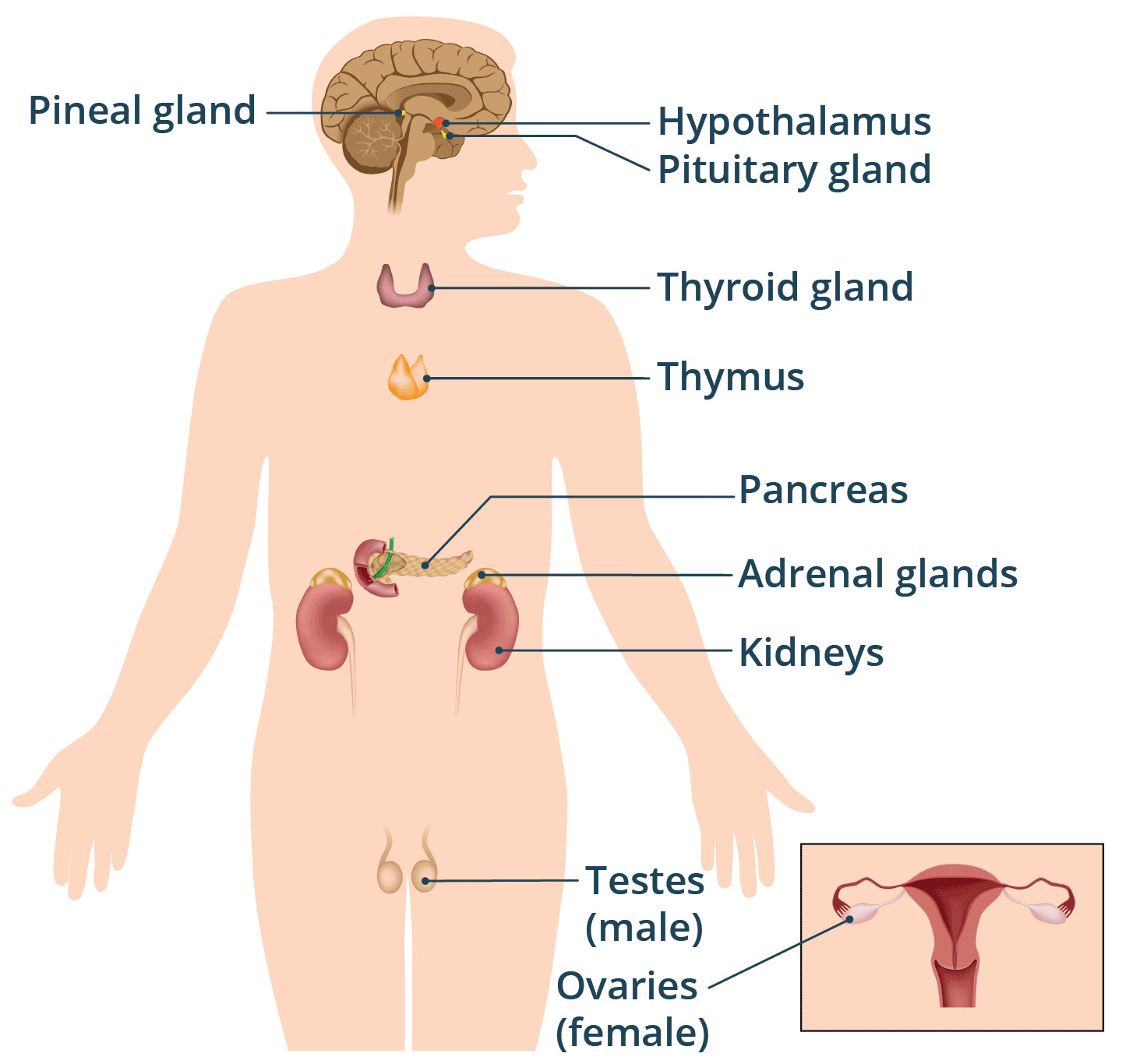 illustration of the endocrine glands
illustration of the endocrine glands
What Does the Pineal Gland Do? Key Functions
The primary function of the pineal gland is the production of melatonin, a hormone that orchestrates your sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms. Melatonin production is highly sensitive to light. Darkness stimulates the pineal gland to produce more melatonin, signaling to your body that it’s time to rest. Conversely, light exposure reduces melatonin production, promoting wakefulness.
Beyond sleep regulation, melatonin also influences other bodily processes, including:
- Reproductive Hormones: The pineal gland and melatonin are thought to have a role in the reproductive system.
- Cellular Protection: Melatonin acts as an antioxidant, helping to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Pineal Gland Conditions and Symptoms
While conditions directly affecting the pineal gland are not common, cysts and tumors can sometimes develop. Pineal cysts are more frequently observed and are usually benign. Pineal gland tumors, although rarer, can be more serious.
Symptoms associated with pineal gland issues can vary but may include:
- Vision Changes: Double vision or blurred vision.
- Eye Movement Problems: Difficulty controlling eye movements.
- Headaches: Persistent or severe headaches.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Especially in cases of tumors causing increased pressure within the skull.
- Balance Issues and Difficulty Walking: Problems with coordination and gait.
- Excessive Sleepiness (Hypersomnia): Feeling unusually tired and sleeping more than usual.
- Drowsiness: Persistent feelings of lethargy.
Often, pineal cysts are discovered incidentally during MRI scans performed for other reasons and do not cause any noticeable symptoms. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and guidance. A specialist can provide the necessary expertise and advice for any pineal gland related concerns.
For further information on hormones and related health issues, resources like Hormones Australia and healthdirect helpline are available to provide support and reliable information.
