Oman, officially known as the Sultanate of Oman, is a captivating country situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. This strategic location places Oman at the confluence of the Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea, marking it as a historically and geographically significant nation in the Middle East. Understanding Where Is Oman requires exploring its precise geographical coordinates and its relationships with surrounding countries and bodies of water.
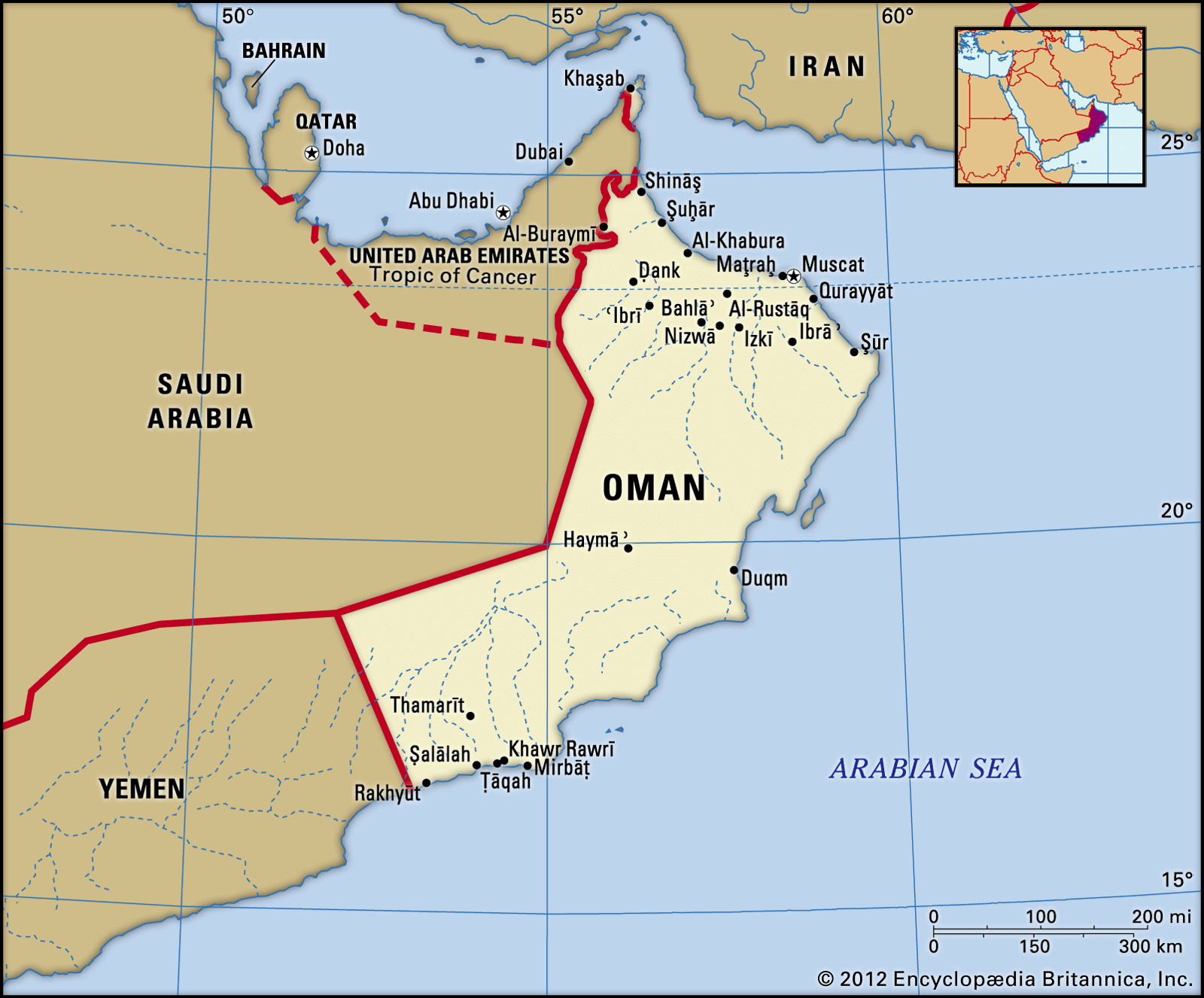 Political map of Oman
Political map of Oman
A detailed political map showcasing the location of Oman, its boundaries with neighboring countries, major cities, and locator features.
Geographical Location and Borders of Oman
To pinpoint where is Oman on a map, it helps to understand its neighboring countries. Oman shares land borders with:
- Yemen to the southwest.
- Saudi Arabia to the west.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE) to the northwest.
Oman’s extensive coastline stretches along two major bodies of water:
- Arabian Sea to the south and east.
- Gulf of Oman to the north.
Notably, Oman also possesses a unique exclave, Ru’us al-Jibal, situated at the northern tip of the Musandam Peninsula. This strategic territory grants Oman frontage on the Persian Gulf via the Strait of Hormuz, a critical maritime chokepoint. Additionally, Oman’s offshore territories include Masirah Island to the east and the Khuriyyā Muriyyā Islands off its southern coast, further extending its geographical reach.
A world data locator map highlighting Oman’s position within the global context, emphasizing its location in the Middle East and relative to other continents.
Exploring Oman’s Diverse Landscapes
The geography of Oman is remarkably diverse, ranging from fertile coastal plains to rugged mountains and vast deserts. Understanding these varied landscapes is crucial to appreciating where is Oman in a physical sense:
Coastal Plains
Oman’s northern coast features the Al-Batinah coastal plain, a long, narrow strip of land running along the Gulf of Oman. This region is known for its fertility and agricultural productivity. In the south, the Dhofar coastal plain also benefits from fertile soil, enhanced by the summer monsoon.
Hajar Mountains
Dominating northern Oman are the Al-Hajar Mountains, a dramatic range extending southeastward parallel to the Gulf coast. This mountain range features peaks reaching impressive heights, with Mount Shams being the highest point in the country. The Hajar Mountains significantly influence the climate and water resources of the region.
A scenic view of the Al-Hajar mountain range in Oman, showcasing the rugged terrain and elevated landscape that characterizes this region.
Interior Plateau and Rub’ al-Khali Desert
Southwest of the Hajar Mountains lies an inland plateau that gradually descends into the vast Rub’ al-Khali desert, also known as the “Empty Quarter.” This expansive desert, shared with Saudi Arabia and Yemen, covers much of Oman’s interior and is characterized by its arid and sandy environment.
Dhofar Region
Separated from northern Oman by desert, the Dhofar region in the south presents a unique landscape. Wooded mountain ranges and fertile plains define Dhofar, benefiting from the monsoon season which brings more moderate temperatures and rainfall compared to the rest of the country.
A depiction of the Rub’ al-Khali desert, illustrating the arid and desolate environment that dominates a significant portion of Oman’s interior.
Climate and Drainage
Oman’s climate is generally hot and dry, with coastal areas experiencing high humidity, especially during summer. Interior regions also face high summer temperatures, while higher elevations in the mountains offer some moderation. Dhofar stands out with a more temperate climate due to the summer monsoon.
Rainfall across Oman is scarce, averaging minimal amounts annually. The country lacks permanent freshwater bodies, relying on intermittent streams that result from seasonal rainfall. Efforts are made to manage water resources through dam construction to conserve runoff and mitigate flooding.
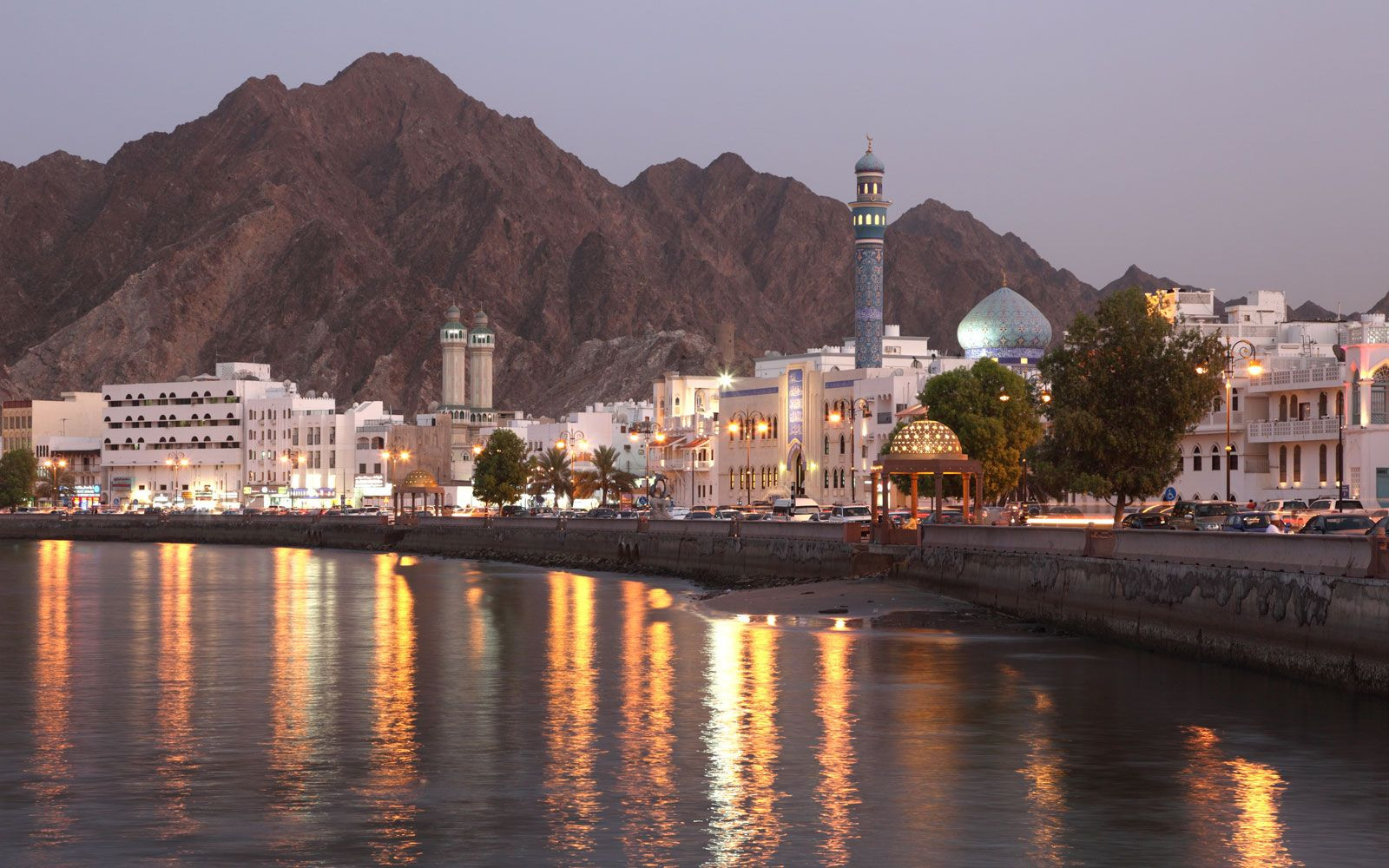 Muscat, Oman
Muscat, Oman
An image of Muscat, the capital city of Oman, highlighting its coastal location and blend of modern and traditional architecture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, where is Oman is in the southeastern Arabian Peninsula, a location of immense geographical and historical significance. Bordered by Yemen, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, and with coastlines along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman, Oman’s location is both strategic and diverse. From its fertile coasts and rugged mountains to its interior deserts and unique Dhofar region, Oman offers a rich tapestry of landscapes within its Arabian Peninsula setting. Understanding where is Oman geographically provides a foundation for appreciating its culture, history, and strategic importance in the Middle East.