Can You Save A Decaying Tooth? Yes, a decaying tooth can often be saved, especially if the decay is caught early, and savewhere.net provides numerous resources to help you understand how to manage and prevent tooth decay effectively, ensuring you keep more money in your pocket by avoiding costly dental procedures. With proactive dental care, affordable treatments, and financial planning, you can maintain a healthy smile and financial well-being.
1. Understanding Tooth Decay: The First Step to Saving Your Smile
Tooth decay is a prevalent issue, but understanding its causes and progression is key to preventing it from leading to severe problems. What exactly causes tooth decay, and what are the initial signs you should watch out for?
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is the destruction of tooth enamel, the hard, outer layer of your teeth. It’s primarily caused by bacteria in your mouth that feed on sugars and produce acids. These acids erode the enamel over time, leading to cavities. According to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, tooth decay is one of the most common chronic diseases in both children and adults in the U.S.
1.1 What Are the Early Signs of Tooth Decay?
Recognizing the early signs of tooth decay is crucial for timely intervention. So, what should you look for?
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks can be an early indicator.
- Toothache: Experiencing persistent toothache or pain when biting down.
- White Spots: The appearance of white spots on the enamel, indicating areas where minerals have been lost.
- Small Pits or Holes: Visible pits or holes in the teeth.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
 Tooth decay early stages
Tooth decay early stages
1.2 How Does Tooth Decay Progress?
Understanding the stages of tooth decay can help you grasp the urgency of early treatment. Can you identify how decay typically advances if left untreated?
- Enamel Erosion: The initial stage involves the demineralization of the enamel due to acid attacks from bacteria.
- Dentin Involvement: Once the enamel is breached, decay progresses to the dentin, the softer layer beneath the enamel. This stage often leads to increased sensitivity.
- Pulp Infection: If left untreated, decay can reach the pulp, the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels. This can cause severe pain and infection, often requiring a root canal.
- Abscess Formation: In advanced stages, an abscess (a pocket of pus) may form at the root of the tooth, leading to intense pain, swelling, and potential systemic infection.
1.3 How Does Diet Impact Tooth Decay?
Diet plays a significant role in the development of tooth decay. How does what you eat contribute to the problem, and what dietary changes can you make?
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: High consumption of sugary foods and drinks provides fuel for bacteria to produce enamel-eroding acids.
- Acidic Foods and Drinks: Acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits and sodas, can directly erode tooth enamel.
- Frequency of Consumption: Frequent snacking on sugary or acidic foods throughout the day keeps your teeth under constant acid attack.
Dietary Changes to Reduce Tooth Decay:
- Limit Sugar Intake: Reduce consumption of sugary snacks, candies, and sweetened beverages.
- Choose Healthy Snacks: Opt for tooth-friendly snacks like fruits, vegetables, cheese, and nuts.
- Drink Water: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, especially after meals.
- Avoid Frequent Snacking: Minimize snacking between meals to reduce the frequency of acid attacks.
1.4 The Role of Oral Hygiene in Preventing Decay
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing tooth decay. What are the key practices you should incorporate into your daily routine?
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth.
- Mouthwash: Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in your mouth.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups.
1.5 How Can SaveWhere.net Help?
SaveWhere.net offers resources to help you make informed decisions about your dental health and budget. How can our platform assist you in preventing and managing tooth decay?
- Find Affordable Dental Care: Locate dental clinics and providers offering competitive prices in your area.
- Access Dental Health Tips: Discover articles and guides on maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
- Compare Dental Plans: Evaluate and compare different dental insurance plans to find one that fits your needs and budget.
- Save on Dental Products: Find deals and discounts on essential dental products like toothpaste, toothbrushes, and mouthwash.
2. Can You Save a Decaying Tooth? Treatment Options Explained
When decay sets in, various treatment options can save a tooth, depending on the severity of the damage. So, what are the different treatments available?
2.1 Fluoride Treatment: Can It Reverse Early Decay?
Fluoride treatments are often recommended for early-stage tooth decay. Can this simple treatment really make a difference?
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that helps strengthen tooth enamel and reverse early signs of decay. Fluoride treatments work by remineralizing weakened areas of the enamel, making teeth more resistant to acid attacks.
How Fluoride Treatment Works:
- Remineralization: Fluoride helps to deposit minerals back into the enamel, strengthening it.
- Antibacterial Effect: Fluoride can inhibit the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay.
- Enamel Hardening: Fluoride makes the enamel more resistant to acid erosion.
Fluoride treatments are typically administered by a dentist or dental hygienist. They come in various forms, including:
- Fluoride Varnish: A concentrated fluoride coating applied to the teeth.
- Fluoride Gel: Applied via a tray that fits over your teeth.
- Fluoride Rinse: A mouthwash containing fluoride.
The American Dental Association recommends regular fluoride treatments, especially for children and individuals at high risk of developing tooth decay.
2.2 Dental Fillings: The Go-To Solution for Cavities
Dental fillings are a common treatment for cavities that have progressed beyond the early stages of enamel erosion. What types of fillings are available, and how effective are they?
Dental fillings involve removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling the space with a material that restores the tooth’s shape and function. This prevents further decay and protects the tooth from damage.
Types of Dental Fillings:
- Amalgam Fillings: Made from a mixture of metals, including silver, tin, copper, and mercury. They are durable and cost-effective.
- Composite Fillings: Made from a tooth-colored resin. They are aesthetically pleasing and bond directly to the tooth structure.
- Porcelain Fillings: Made from ceramic material. They are highly durable and match the natural color of your teeth.
- Gold Fillings: Made from gold alloy. They are long-lasting and resistant to corrosion but are more expensive than other options.
The choice of filling material depends on factors such as the size and location of the cavity, the patient’s aesthetic preferences, and cost considerations.
2.3 Root Canal Therapy: Saving Teeth from Extraction
When decay reaches the pulp of the tooth, root canal therapy may be necessary to save the tooth from extraction. What does this procedure involve?
Root canal therapy involves removing the infected or damaged pulp from the tooth, cleaning and disinfecting the inside of the tooth, and filling and sealing the space. This eliminates the source of infection and preserves the tooth.
Steps of Root Canal Therapy:
- Accessing the Pulp: The dentist creates an opening in the tooth to access the pulp chamber.
- Removing the Pulp: The infected or damaged pulp is carefully removed using specialized instruments.
- Cleaning and Shaping: The inside of the tooth is cleaned and shaped to prepare it for filling.
- Filling and Sealing: The tooth is filled with a biocompatible material, typically gutta-percha, and sealed to prevent reinfection.
- Restoration: A crown is usually placed over the tooth to provide strength and protection.
Root canal therapy has a high success rate and can save teeth that would otherwise need to be extracted.
2.4 Crowns: Protecting Weakened Teeth
Dental crowns are used to cover and protect teeth that are weakened, damaged, or have undergone root canal therapy. What are the benefits of crowns, and what materials are they made from?
A dental crown is a tooth-shaped cap that is placed over a tooth to restore its shape, size, strength, and appearance. Crowns provide support and protection for weakened teeth, preventing further damage.
Materials Used for Dental Crowns:
- Porcelain Crowns: Provide a natural-looking appearance and are suitable for front teeth.
- Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal Crowns: Offer a combination of strength and aesthetics.
- Gold Crowns: Highly durable and resistant to wear, ideal for back teeth.
- Zirconia Crowns: Strong, biocompatible, and provide excellent aesthetics.
The choice of crown material depends on factors such as the tooth’s location, the patient’s aesthetic preferences, and cost considerations.
2.5 Extractions: When Saving the Tooth Isn’t Possible
In some cases, a tooth may be too severely decayed or damaged to be saved, and extraction becomes necessary. What are the reasons for tooth extraction, and what are the replacement options?
Tooth extraction involves removing the tooth from its socket in the bone. While it’s always preferable to save a tooth, extraction may be necessary in certain situations.
Reasons for Tooth Extraction:
- Severe Decay: When decay has extensively damaged the tooth structure, making it impossible to restore.
- Infection: When infection has spread beyond the tooth and into the surrounding tissues.
- Crowding: To create space for orthodontic treatment.
- Impacted Teeth: When a tooth is unable to erupt properly, such as impacted wisdom teeth.
Replacement Options After Extraction:
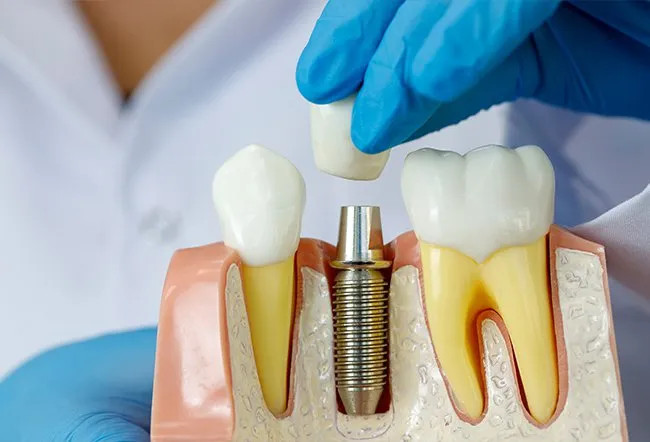
- Dental Implants: A permanent solution involving the placement of a titanium post into the jawbone, which supports a crown.
- Dental Bridges: A fixed appliance that spans the gap created by a missing tooth, using adjacent teeth for support.
- Dentures: Removable appliances that replace multiple missing teeth.
The choice of replacement option depends on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the number of missing teeth, and cost considerations.
3. Home Remedies to Slow Down Tooth Decay
While professional dental treatments are essential for addressing tooth decay, several home remedies can help slow down its progression and maintain oral health. What are some effective home remedies?
3.1 Oil Pulling: An Ancient Practice for Oral Health
Oil pulling is an ancient Ayurvedic practice that involves swishing oil in your mouth to remove bacteria and promote oral hygiene. How effective is it, and how do you perform it?
Oil pulling is believed to have moisturizing and antiseptic capabilities, creating a soap-like cleansing effect on teeth. It can help reduce plaque buildup, gingivitis, and bad breath.
How to Perform Oil Pulling:
- Choose an Oil: Use sesame, sunflower, or coconut oil.
- Swish: Take one tablespoon of oil and swish it in your mouth for 10-20 minutes.
- Spit: Spit the oil into a trash can (not the sink) to avoid clogging the pipes.
- Rinse: Rinse your mouth with water and brush your teeth.
According to a study published in the Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, oil pulling can significantly reduce plaque and gingivitis in as little as one month.
3.2 Salt Water Rinse: A Simple Yet Effective Solution
Salt water rinses are a simple and effective way to reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and promote healing in the mouth. How often should you rinse, and what are the benefits?
Benefits of Salt Water Rinse:
- Reduces Inflammation: Salt water can help reduce inflammation and swelling in the gums.
- Kills Bacteria: Salt has antibacterial properties that can help kill bacteria in the mouth.
- Promotes Healing: Salt water can promote healing of minor cuts and wounds in the mouth.
How to Perform a Salt Water Rinse:
- Mix: Dissolve one teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water.
- Swish: Swish the solution in your mouth for 30 seconds.
- Spit: Spit out the solution.
You can rinse with salt water several times a day, especially after meals.
3.3 Aloe Vera: Nature’s Soothing Remedy
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can promote oral health. How can you use aloe vera to combat tooth decay?
Aloe vera gel can help reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and promote healing in the mouth. It can also help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay.
How to Use Aloe Vera for Oral Health:
- Choose Aloe Vera Gel: Use pure aloe vera gel without added sugars or chemicals.
- Apply: Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel to your teeth and gums.
- Massage: Gently massage the gel into your gums.
- Rinse: Rinse your mouth with water.
You can use aloe vera gel several times a day to promote oral health.
3.4 Turmeric: The Golden Spice for Oral Hygiene
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. How can turmeric benefit your oral health?
Turmeric can help reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and promote healing in the mouth. It can also help prevent plaque buildup and gingivitis.
How to Use Turmeric for Oral Health:
- Make a Paste: Mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste.
- Apply: Apply the paste to your teeth and gums.
- Massage: Gently massage the paste into your gums.
- Rinse: Rinse your mouth with water.
You can use turmeric paste several times a week to promote oral health.
3.5 Proper Brushing Techniques: The Foundation of Oral Care
Proper brushing techniques are essential for removing plaque and preventing tooth decay. What are the key steps to effective brushing?
Key Steps to Effective Brushing:
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Choose a toothpaste that contains fluoride.
- Brush at a 45-Degree Angle: Hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to your gums.
- Use Gentle Circular Motions: Brush gently in small, circular motions.
- Brush All Surfaces: Brush the front, back, and top surfaces of each tooth.
- Brush Your Tongue: Brush your tongue to remove bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Brush for Two Minutes: Brush for at least two minutes each time.
The American Dental Association recommends brushing your teeth at least twice a day.
3.6 Flossing: Reaching the Unreachable
Flossing is essential for removing plaque and food particles from between your teeth, where your toothbrush can’t reach. How often should you floss, and what’s the proper technique?
Proper Flossing Technique:
- Use About 18 Inches of Floss: Break off about 18 inches of floss.
- Wrap Floss Around Fingers: Wrap the floss around your middle fingers, leaving a few inches to work with.
- Gently Guide Floss Between Teeth: Gently slide the floss between your teeth using a back-and-forth motion.
- Curve Floss Around Each Tooth: Curve the floss around each tooth in a C-shape.
- Slide Floss Up and Down: Slide the floss up and down against the tooth surface, going below the gumline.
- Use a Clean Section of Floss: Use a clean section of floss for each tooth.
The American Dental Association recommends flossing at least once a day.
4. The Importance of Professional Dental Care
While home remedies and good oral hygiene practices can help slow down tooth decay, professional dental care is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. Why are regular dental visits so important?
4.1 Regular Check-Ups: Detecting Problems Early
Regular dental check-ups allow your dentist to detect and address problems early, before they become more serious and costly. What happens during a typical check-up?
What Happens During a Typical Check-Up:
- Dental Exam: The dentist will examine your teeth and gums for signs of decay, gum disease, and other oral health problems.
- Professional Cleaning: A dental hygienist will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth.
- X-Rays: X-rays may be taken to detect hidden problems, such as decay between teeth or bone loss.
- Oral Cancer Screening: The dentist will screen for signs of oral cancer.
The American Dental Association recommends visiting your dentist at least once or twice a year.
4.2 Professional Cleanings: Removing Stubborn Plaque
Professional dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar that you can’t remove with brushing and flossing alone. Why is this important?
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth. If it’s not removed, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Tartar can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health problems.
4.3 Early Intervention: Preventing More Extensive Damage
Early intervention is key to preventing more extensive damage from tooth decay. How can your dentist help?
Your dentist can identify and address early signs of tooth decay, such as white spots on the enamel or small cavities. They can recommend treatments like fluoride applications or fillings to prevent the decay from progressing.
4.4 Personalized Advice: Tailored to Your Needs
Your dentist can provide personalized advice on how to improve your oral hygiene and prevent tooth decay based on your individual needs and risk factors. What kind of advice can you expect?
- Brushing and Flossing Techniques: Your dentist can demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques.
- Dietary Recommendations: Your dentist can provide advice on how to modify your diet to reduce your risk of tooth decay.
- Fluoride Recommendations: Your dentist can recommend the appropriate amount of fluoride for your needs.
- Product Recommendations: Your dentist can recommend specific oral hygiene products, such as toothpaste and mouthwash.
4.5 Financial Benefits: Preventing Costly Procedures
Regular dental care can save you money in the long run by preventing the need for more extensive and costly procedures. How does prevention help your wallet?
By detecting and addressing problems early, your dentist can prevent the need for treatments like root canals, crowns, and extractions, which can be expensive. Regular check-ups and cleanings are a cost-effective way to maintain your oral health.
5. SaveWhere.net: Your Partner in Affordable Dental Care
SaveWhere.net is dedicated to helping you find affordable dental care and make informed decisions about your oral health. How can our platform benefit you?
5.1 Finding Affordable Dental Providers
SaveWhere.net helps you locate dental clinics and providers in your area that offer competitive prices. How does our search tool work?
Our search tool allows you to compare prices, read reviews, and find providers that fit your budget and needs. We partner with dental clinics to offer exclusive discounts and promotions to our users.
5.2 Accessing Dental Health Tips and Resources
SaveWhere.net provides a wealth of articles, guides, and resources on maintaining optimal oral hygiene. What topics do we cover?
We cover topics such as:
- Proper Brushing and Flossing Techniques
- Dietary Tips for Healthy Teeth
- Home Remedies for Tooth Decay
- Understanding Dental Insurance
- Finding Affordable Dental Care
5.3 Comparing Dental Insurance Plans
SaveWhere.net helps you evaluate and compare different dental insurance plans to find one that fits your needs and budget. What factors should you consider when choosing a dental plan?
When choosing a dental plan, consider factors such as:
- Monthly Premiums
- Deductibles
- Co-pays
- Annual Maximums
- Coverage for Different Procedures
SaveWhere.net provides tools and resources to help you compare plans and make an informed decision.
5.4 Saving on Dental Products
SaveWhere.net helps you find deals and discounts on essential dental products like toothpaste, toothbrushes, and mouthwash. How can you take advantage of these savings?
We partner with retailers to offer exclusive discounts to our users. Visit our website to find coupons, promo codes, and special offers on dental products.
5.5 Community Support and Resources
SaveWhere.net offers a supportive community where you can connect with others, share tips, and find encouragement on your journey to better oral health and financial well-being. How can you get involved?
Join our forums, participate in discussions, and share your experiences. Our community is here to support you every step of the way.
6. Real-Life Examples: Saving Teeth and Saving Money
To illustrate the benefits of proactive dental care and financial planning, let’s look at a few real-life examples. How have others managed to save their teeth and their money?
6.1 Case Study 1: Early Detection and Fluoride Treatment
Sarah, a 25-year-old from Atlanta, noticed increased sensitivity in one of her molars. She visited her dentist, who detected early-stage decay and recommended a fluoride treatment. The treatment cost $100, but it prevented the need for a filling, which would have cost $300. Sarah saved $200 by addressing the problem early.
6.2 Case Study 2: Filling a Cavity and Preventing a Root Canal
Michael, a 40-year-old teacher, had a small cavity filled promptly. The filling cost $150, but it prevented the decay from reaching the pulp, which would have required a root canal costing $1,000. Michael saved $850 by taking care of the cavity.
6.3 Case Study 3: Regular Cleanings and Preventing Gum Disease
Emily, a 35-year-old entrepreneur, committed to regular dental cleanings every six months. The cleanings cost $100 each time, but they prevented the development of gum disease, which would have required extensive and costly treatments. Emily saved thousands of dollars by maintaining good oral hygiene and getting regular cleanings.
6.4 Case Study 4: Choosing an Affordable Dental Plan
David, a 50-year-old engineer, compared dental insurance plans on SaveWhere.net and chose a plan with a lower monthly premium. The plan covered preventive care and basic procedures, allowing David to maintain his oral health without breaking the bank.
6.5 Case Study 5: Using Home Remedies to Supplement Professional Care
Lisa, a 28-year-old student, used home remedies like oil pulling and salt water rinses to supplement her professional dental care. These practices helped reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in her mouth, supporting her overall oral health.
7. Tooth Decay FAQs: Answers to Your Burning Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about tooth decay, along with comprehensive answers to address your concerns.
7.1 Can you reverse tooth decay naturally?
Yes, early-stage tooth decay can sometimes be reversed naturally through remineralization. This involves improving oral hygiene, reducing sugar intake, and using fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel.
7.2 How long does it take for a cavity to form?
The formation of a cavity varies depending on factors like diet, oral hygiene, and saliva flow. It can take months or even years for a cavity to develop.
7.3 Is tooth decay contagious?
Yes, the bacteria that cause tooth decay can be transmitted through saliva. Sharing utensils, drinks, or toothbrushes can spread these bacteria.
7.4 What are the risk factors for tooth decay?
Risk factors for tooth decay include high sugar intake, poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, smoking, and certain medical conditions.
7.5 Can tooth decay cause other health problems?
Yes, untreated tooth decay can lead to infections that spread to other parts of the body. It has also been linked to heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems.
7.6 What is the best toothpaste for preventing tooth decay?
The best toothpaste for preventing tooth decay is one that contains fluoride. Fluoride helps strengthen enamel and prevent acid erosion.
7.7 How often should I replace my toothbrush?
You should replace your toothbrush every three months or sooner if the bristles are frayed or worn.
7.8 Can children get tooth decay?
Yes, children are susceptible to tooth decay, especially if they consume sugary foods and drinks and don’t practice good oral hygiene.
7.9 How can I protect my teeth from decay while wearing braces?
While wearing braces, it’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene. Brush after every meal, floss daily, and use a fluoride mouthwash to protect your teeth from decay.
7.10 Is tooth decay always painful?
No, tooth decay isn’t always painful, especially in the early stages. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for detecting and addressing decay before it causes pain.
8. Take Action Today: Saving Your Teeth and Your Wallet
Saving a decaying tooth is possible with timely intervention and proper care. Now, what steps can you take today to protect your oral health and your wallet?
8.1 Schedule a Dental Check-Up
If you suspect you have tooth decay, schedule a dental check-up as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can save you from more extensive and costly procedures.
8.2 Improve Your Oral Hygiene
Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and use a fluoride mouthwash. Proper oral hygiene is essential for preventing tooth decay.
8.3 Modify Your Diet
Limit your intake of sugary and acidic foods and drinks. Choose healthy snacks like fruits, vegetables, cheese, and nuts.
8.4 Explore Affordable Dental Options on SaveWhere.net
Visit savewhere.net to find affordable dental providers, access dental health tips, compare dental insurance plans, and save on dental products. Our platform is here to help you make informed decisions about your oral health and budget.
8.5 Join the SaveWhere.net Community
Connect with others in the savewhere.net community to share tips, find encouragement, and learn from each other’s experiences. Together, we can achieve better oral health and financial well-being.
Ready to take control of your oral health and your finances?
Visit savewhere.net today to discover tips for saving, explore deals, and connect with a community that values smart financial decisions. Your journey to a healthy smile and a healthy bank account starts now.
Address: 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States
Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000
Website: savewhere.net

