Saving emails from Outlook is a crucial skill for anyone looking to manage their digital correspondence effectively. At savewhere.net, we understand the importance of preserving vital information, be it for record-keeping, legal compliance, or simply for easy access later on. We’ll guide you through several methods to download email from Outlook, ensuring you can safeguard your important messages with ease. Whether you’re looking to archive essential communications, back up important data, or print email from Outlook, this comprehensive guide offers practical solutions.
1. Why Should I Save Emails from Outlook?
Saving emails from Outlook might seem like an extra step, but it offers a host of benefits for anyone looking to stay organized and protect their important data. Here’s why it’s a smart move:
- Important Records: Saving crucial emails creates a personal database that can be used for many purposes. Need to check back on a past agreement or a customer’s order? With saved emails, the information is right at your fingertips.
- Legal Protection: In the event of a dispute, saving emails can act as evidence. Clear communication records can be vital in showing agreements and details, providing an extra layer of legal safety.
- Offline Access: Emails are only accessible when connected to the internet, but saving them locally gives you the freedom to view them anytime, anywhere.
- Backup Security: Email servers aren’t immune to problems. By saving your most important emails, you create a backup that’s separate from the server, so you have a copy if something goes wrong.
- Organization: With saved emails, you can categorize and store data as needed.
- Compliance Requirements: Some industries require specific email retention to meet regulations. Saving emails is a simple step towards ensuring your compliance.
2. What Are the Different Ways to Save an Email from Outlook?
There are several ways to save an email from Outlook, each offering different advantages depending on your needs. Here’s a breakdown of the most common methods:
2.1. Saving as a File
Saving an email as a file is one of the most straightforward methods. This allows you to preserve the email in various formats for future access.
-
Open the Email: Double-click the email you want to save.
-
Go to File Menu: In the email window, click on “File” in the top left corner.
-
Select “Save As”: Choose “Save As” from the options.
-
Choose a Folder: In the “Save As” dialog box, select the folder where you want to save the email.
-
Name the File: Type a name for the file in the “File name” box.
-
Choose the File Type:
- MSG: This is the default format and saves the email as an Outlook Message file. It retains all the email’s original formatting and attributes.
- TXT: This saves the email as plain text, removing all formatting, images, and attachments.
- HTML: This format preserves formatting, images, and links but may not be supported by all email clients.
-
Click “Save”: Click the “Save” button to save the email to your chosen folder.
2.2. Saving as a PDF File
Saving an email as a PDF (Portable Document Format) is an excellent way to ensure the email can be viewed on any device without losing its formatting.
-
Open the Email: Open the email you wish to save.
-
Go to File Menu: Click on “File” in the top left corner.
-
Select “Print”: Choose “Print” from the menu.
-
Choose “Microsoft Print to PDF”: In the “Printer” drop-down menu, select “Microsoft Print to PDF.” This option is available in Windows 10 and later.
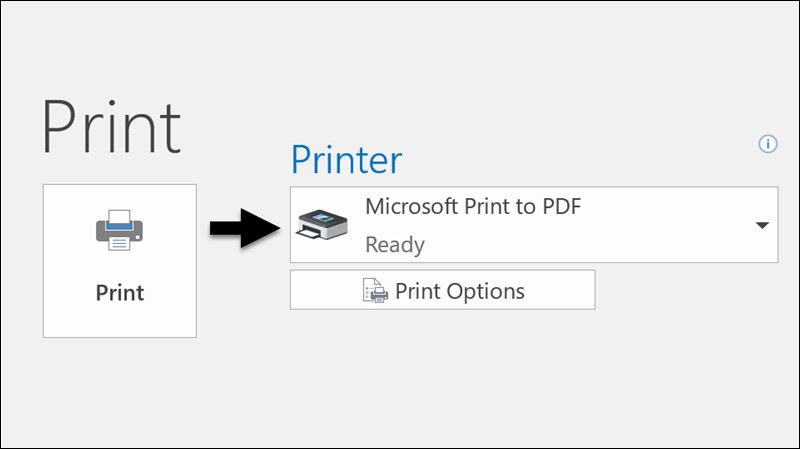 Print dialog box to print email to PDF file
Print dialog box to print email to PDF file -
Click “Print”: Click the “Print” button.
-
Choose a Folder and Name the File: In the “Save Print Output As” dialog box, select the folder where you want to save the PDF, and enter a name for the file.
-
Click “Save”: Click the “Save” button to save the email as a PDF.
2.3. Saving as a Word Document
While Outlook doesn’t directly support saving an email as a Word document, you can use a workaround to achieve this:
- Save as HTML: Follow the steps in section 2.1 to save the email as an HTML file.
- Open in Word: Open Microsoft Word.
- Open the HTML File: In Word, click “File” > “Open” and select the HTML file you saved.
- Save as Word Document: Click “File” > “Save As” and choose “Word Document (*.docx)” from the file type drop-down.
- Click “Save”: Click the “Save” button to save the email as a Word document.
2.4. Saving as a Template
Saving an email as a template is useful if you frequently send similar messages. This saves time and ensures consistency.
- Create a New Email: On the “Home” tab, click “New Email.”
- Enter the Content: In the message body, enter the content you want to save as a template.
- Go to File Menu: In the message window, click the “File” tab.
- Select “Save As”: Click “Save As.”
- Choose “Outlook Template”: In the “Save as type” list, select “Outlook Template.”
- Name the Template: Enter a name for your template in the “File name” box.
- Click “Save”: Click “Save” to save the email as a template.
2.5. Saving a Draft
Outlook automatically saves drafts of your emails. If you want to manually save a draft or return to it later:
To Manually Save a Draft:
- Click “Save”: On the Quick Access Toolbar, click “Save,” or on the “File” tab, click “Save.”
To Return to a Saved Draft:
- Open Drafts Folder: In “Mail,” in the Folder pane, click “Drafts,” and then double-click the message.
2.6. Saving to Another Outlook Folder
Saving emails to different folders helps keep your inbox organized. Here’s how you can move or copy an email to another Outlook folder:
- Select the Email: Click on the email you want to save in a different folder.
- Right-Click: Right-click on the selected email.
- Choose “Move” or “Copy”:
- Move: This will remove the email from its current folder and place it in the new folder.
- Copy: This will create a duplicate of the email in the new folder while leaving the original in its current location.
- Select the Destination Folder: A list of your Outlook folders will appear. Choose the folder where you want to move or copy the email.
- Click “OK”: The email will now be moved or copied to the selected folder.
3. How Do I Save Attachments from Outlook Emails?
Attachments in Outlook emails can include important documents, images, and other files. Saving these attachments is essential for keeping a complete record of your communications.
3.1. Saving a Single Attachment
- Open the Email: Open the email that contains the attachment you want to save.
- Right-Click the Attachment: In the email, right-click on the attachment icon.
- Select “Save As”: Choose “Save As” from the context menu.
- Choose a Folder: In the “Save Attachment” dialog box, select the folder where you want to save the attachment.
- Name the File: If desired, change the name of the file in the “File name” box.
- Click “Save”: Click the “Save” button to save the attachment to your chosen folder.
3.2. Saving All Attachments at Once
If an email contains multiple attachments, you can save all of them at once, saving time and effort.
- Open the Email: Open the email containing the attachments.
- Click the Drop-Down Arrow: Click the drop-down arrow on any of the attachments.
- Select “Save All Attachments”: Choose “Save All Attachments” from the drop-down menu.
- Choose a Folder: In the “Select Folder” dialog box, select the folder where you want to save the attachments.
- Click “OK”: Click “OK” to save all attachments to the selected folder.
4. How to Automate Saving Emails from Outlook?
Automating the process of saving emails from Outlook can save significant time and ensure that important emails are consistently backed up. Here are several methods to automate this process.
4.1. Using Outlook Rules
Outlook Rules allow you to automatically manage incoming and outgoing emails based on specified conditions. You can create a rule to automatically save certain emails to a specific folder.
- Open Outlook: Launch the Outlook application on your computer.
- Go to “File”: Click on the “File” tab in the top left corner.
- Manage Rules & Alerts: Select “Manage Rules & Alerts.”
- New Rule: In the “Rules and Alerts” dialog box, click “New Rule.”
- Start from a Blank Rule: Under “Start from a blank rule,” choose “Apply rule on messages I receive” or “Apply rule on messages I send,” depending on your need. Click “Next.”
- Set Conditions: Specify the conditions for the rule. For example, you might choose “from people or public group” and then select specific email addresses from your contacts. Click “Next.”
- Choose Actions: Select the actions you want the rule to perform. You can choose to “move a copy to the specified folder” or “copy it to the specified folder.” Select the folder where you want the emails to be saved.
- Exceptions (Optional): If needed, specify any exceptions to the rule. Click “Next.”
- Name and Turn On the Rule: Give the rule a name and ensure the “Turn on this rule” box is checked. Click “Finish.”
4.2. Using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) Scripts
For more advanced automation, you can use VBA scripts in Outlook. These scripts can be customized to save emails based on complex criteria.
- Open VBA Editor:
- Press “Alt + F11” to open the VBA editor in Outlook.
- Insert a Module:
- In the VBA editor, go to “Insert” > “Module.”
- Write the VBA Script:
- Here’s an example script that saves incoming emails to a specific folder:
Sub SaveEmailAttachments(Item As Outlook.MailItem)
Dim objAttachments As Outlook.Attachments
Dim i As Integer
Dim strFolderPath As String
Dim strFileName As String
' Specify the folder path where you want to save the emails
strFolderPath = "C:SavedEmails"
' Create the folder if it doesn't exist
If Dir(strFolderPath, vbDirectory) = "" Then
MkDir strFolderPath
End If
Set objAttachments = Item.Attachments
' Save the email as a .msg file
strFileName = strFolderPath & Item.Subject & ".msg"
Item.SaveAs strFileName, OlSaveAsType.olMSG
' Clean up
Set objAttachments = Nothing
End Sub- Apply the Script:
- In Outlook, go to “File” > “Manage Rules & Alerts.”
- Create a new rule as described in section 4.1.
- In the actions step, select “run a script” and choose the VBA script you created.
4.3. Third-Party Tools and Add-ins
Several third-party tools and add-ins can automate the process of saving emails from Outlook. These tools often provide more advanced features and easier setup compared to Outlook Rules and VBA scripts. Some popular options include:
- MailStore Home: A free tool for archiving personal email.
- Email Parser: Automates email data extraction and saving.
- Save emails to PDF: Save your email in a PDF format
- QuickFile: For filing and saving emails in personal folders
5. What File Formats Are Available When Saving Emails from Outlook?
When saving emails from Outlook, you have several file format options, each with its own advantages and use cases. Here’s an overview of the most common formats:
5.1. .MSG (Outlook Message Format)
- Description: The default format for saving emails from Outlook. It preserves all elements of the email, including formatting, attachments, and metadata (sender, recipient, date, etc.).
- Advantages:
- Complete Preservation: Retains the entire email as it appears in Outlook.
- Attachments Included: Saves attachments within the .msg file.
- Metadata Retention: Preserves all email headers and metadata.
- Disadvantages:
- Outlook Required: Requires Microsoft Outlook or a compatible email client to open.
- File Size: Can result in larger file sizes compared to other formats.
- Use Cases:
- Archiving emails for legal or compliance reasons.
- Creating backups of important emails.
- Sharing emails with colleagues who use Outlook.
5.2. .TXT (Plain Text Format)
- Description: Saves the email content as plain, unformatted text. All formatting, images, and attachments are removed.
- Advantages:
- Small File Size: Creates very small files, saving storage space.
- Universally Readable: Can be opened with any text editor on any operating system.
- Disadvantages:
- Loss of Formatting: All formatting, images, and links are lost.
- Attachments Removed: Attachments are not saved.
- Metadata Loss: Email headers and metadata are not preserved.
- Use Cases:
- Saving email content for quick reference.
- Extracting text from emails for analysis.
- Storing email content in a database or other text-based system.
5.3. .HTML (Hypertext Markup Language)
- Description: Saves the email content in HTML format, preserving much of the original formatting, images, and links.
- Advantages:
- Formatting Retention: Retains most of the email’s original formatting.
- Images Included: Saves images embedded in the email.
- Links Preserved: Keeps hyperlinks active.
- Disadvantages:
- Potential Compatibility Issues: May not render perfectly in all browsers or text editors.
- Attachments Not Included: Attachments are not saved directly within the HTML file.
- Use Cases:
- Archiving emails with rich formatting and images.
- Viewing emails in a web browser.
- Editing email content in an HTML editor.
5.4. .PDF (Portable Document Format)
- Description: Saves the email as a PDF document, ensuring the email can be viewed on any device without losing its formatting.
- Advantages:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Can be opened on any device with a PDF viewer.
- Formatting Retention: Preserves the email’s formatting, layout, and embedded images.
- Print-Ready: Ideal for printing emails while maintaining their appearance.
- Disadvantages:
- Editing Limitations: Editing a PDF file can be more complex than editing a .msg or .HTML file.
- Attachments Handling: Attachments are typically not embedded directly within the PDF (though some PDF software allows embedding).
- Use Cases:
- Archiving emails for long-term storage.
- Sharing emails with recipients who may not have Outlook.
- Printing emails while preserving their original appearance.
5.5. .OFT (Outlook Template Format)
- Description: Saves the email as an Outlook Template, allowing you to reuse the email’s content and formatting for future messages.
- Advantages:
- Reusability: Easily create new emails based on the template.
- Consistency: Ensures consistent formatting and content across multiple emails.
- Disadvantages:
- Outlook Required: Requires Microsoft Outlook to use the template.
- Not for Archiving: Primarily for creating reusable email content rather than archiving.
- Use Cases:
- Creating standard email responses.
- Developing email newsletters.
- Sending out regular updates with consistent branding.
6. How Do I Change the Default File Format for Saving Messages in Outlook?
Classic Outlook supports Unicode, a character encoding standard that enables most of the written languages in the world to be represented by using a single character set. If you work in a multinational organization or share messages and items with people who use classic Outlook on computers that run in other languages, you can take advantage of Unicode support in classic Outlook.
To save your messages in a Unicode encoding by default:
- On the File tab. choose Options > Mail.
- Under Save messages, select the Use Unicode Format check box.
7. How to Save Outlook Emails for Legal or Compliance Reasons?
Saving Outlook emails for legal or compliance reasons requires a systematic approach to ensure data integrity, security, and accessibility. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you manage this process effectively:
7.1. Define Retention Policies
- Identify Requirements: Understand the legal and regulatory requirements specific to your industry and region. This includes knowing how long different types of emails need to be retained (e.g., financial records, HR communications).
- Create a Policy: Develop a clear and comprehensive email retention policy that outlines:
- Types of emails to be retained.
- Retention periods for each type of email.
- Procedures for saving and archiving emails.
- Protocols for accessing and retrieving archived emails.
- Guidelines for employees on email usage and compliance.
- Communicate the Policy: Ensure all employees are aware of the email retention policy and receive training on how to comply with it.
7.2. Choose an Archiving Method
- Manual Archiving:
- Description: Manually saving emails to a designated folder or storage device.
- Pros: Simple, low-cost.
- Cons: Time-consuming, prone to human error, difficult to manage large volumes of emails.
- Automated Archiving:
- Description: Using software or tools to automatically save emails based on predefined rules.
- Pros: Efficient, reliable, scalable, reduces the risk of human error.
- Cons: Requires an initial investment in software, may require technical expertise.
- Third-Party Archiving Solutions:
- Description: Utilizing specialized email archiving services that provide secure, compliant storage and advanced features such as e-discovery and legal hold.
- Pros: Comprehensive features, compliance-focused, scalable, reduces administrative burden.
- Cons: Can be more expensive than in-house solutions, requires trusting a third-party provider.
7.3. Implement Automated Archiving
- Set Up Rules: Configure Outlook rules to automatically move or copy specific emails to a designated archive folder.
- VBA Scripts: Use VBA scripts for more advanced automation, such as saving emails to specific file formats or locations based on complex criteria.
- Third-Party Tools: Implement tools or add-ins that offer automated email archiving features, such as MailStore Home or Email Parser.
7.4. Use Third-Party Archiving Solutions
- Research and Select a Provider:
- Look for providers with strong security credentials, compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR), and positive customer reviews.
- Configure the Solution:
- Work with the provider to configure the archiving solution to meet your specific requirements, including retention policies, user access controls, and data storage locations.
- Test and Validate:
- Thoroughly test the archiving solution to ensure it is capturing emails correctly and that archived emails can be easily accessed and retrieved.
7.5. Maintain Data Integrity and Security
- Encryption: Encrypt archived emails to protect them from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit who can view, modify, or delete archived emails.
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed audit trails of all actions performed on archived emails, including access, modifications, and deletions.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your archived email data to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
7.6. Ensure Compliance
- Legal Hold: Implement legal hold procedures to prevent the deletion of emails that may be relevant to pending or ongoing legal matters.
- E-Discovery: Ensure your archiving solution supports e-discovery, allowing you to quickly and efficiently search and retrieve emails in response to legal requests.
- Compliance Monitoring: Regularly monitor your email archiving practices to ensure they comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
7.7. Document Your Processes
- Create Documentation: Develop detailed documentation of your email archiving processes, including retention policies, archiving methods, security measures, and compliance procedures.
- Regularly Update: Regularly review and update your documentation to reflect changes in legal requirements, technology, and your organization’s needs.
7.8. Train Your Employees
- Provide Training: Train employees on the importance of email compliance and their roles in the email archiving process.
- Ongoing Education: Provide ongoing education to keep employees up-to-date on changes to policies, regulations, and best practices.
8. How to Overcome Common Issues When Saving Emails from Outlook?
Saving emails from Outlook can sometimes present challenges. Here are some common issues you might encounter and how to troubleshoot them:
8.1. Issue: Cannot Save Emails Due to Permissions
Problem: You receive an error message indicating you do not have the necessary permissions to save emails to a specific location.
Solutions:
- Check Folder Permissions:
- Right-click the folder where you are trying to save the email.
- Select “Properties.”
- Go to the “Security” tab.
- Ensure your user account has “Write” and “Modify” permissions. If not, click “Edit” to change the permissions.
- Run Outlook as Administrator:
- Close Outlook.
- Right-click the Outlook icon on your desktop or in the Start menu.
- Select “Run as administrator.” This can sometimes bypass permission issues.
- Save to a Different Location:
- Try saving the email to a different folder, such as your “Documents” folder, to see if the issue is specific to the original location.
8.2. Issue: Saved Emails Are Corrupted or Unreadable
Problem: Saved emails appear to be corrupted or cannot be opened.
Solutions:
- Try a Different File Format:
- If you are saving emails as .msg files, try saving them as .HTML or .PDF to see if the issue persists.
- Repair Outlook Data Files:
- Close Outlook.
- Open the “Run” dialog box by pressing “Windows Key + R.”
- Type
Outlook.exe /safeand press Enter to start Outlook in Safe Mode. - If Outlook works in Safe Mode, the issue may be due to an add-in. Disable add-ins one by one to identify the culprit.
- Use the Inbox Repair Tool (SCANPST.EXE):
- Close Outlook.
- Locate the SCANPST.EXE tool on your computer. The location varies depending on your version of Outlook but is typically found in the
C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficerootOffice16directory (or a similar path). - Run SCANPST.EXE and follow the prompts to scan and repair your Outlook data file (.pst or .ost).
- Check for Disk Errors:
- Run a disk check utility (such as CHKDSK on Windows) to identify and fix any file system errors on your hard drive.
8.3. Issue: Attachments Are Not Saved with the Email
Problem: When saving an email, the attachments are not included.
Solutions:
- Save Attachments Separately:
- Manually save each attachment before saving the email. Right-click each attachment and select “Save As.”
- Use .MSG Format:
- Ensure you are saving the email in the .MSG format, as this format typically includes attachments.
- Check Outlook Settings:
- Go to “File” > “Options” > “Mail.”
- Under the “Save messages” section, ensure that there are no settings that might be preventing attachments from being saved.
8.4. Issue: Emails Are Saved Without Formatting
Problem: Saved emails lose their original formatting and appear as plain text.
Solutions:
- Use .HTML or .PDF Format:
- Save the email in .HTML or .PDF format to preserve formatting.
- Adjust Text Encoding:
- When saving as .TXT, try different text encodings (e.g., UTF-8) to see if it improves the display of characters.
8.5. Issue: Automated Saving Is Not Working
Problem: Outlook rules or VBA scripts for automated saving are not functioning as expected.
Solutions:
- Check Rule Settings:
- Go to “File” > “Manage Rules & Alerts.”
- Ensure the rule is enabled, and the conditions and actions are configured correctly.
- Test the Rule:
- Send a test email that meets the rule’s conditions to see if the rule is triggered.
- Check VBA Script:
- Open the VBA editor (Alt + F11).
- Review the script for any errors.
- Ensure the script is properly associated with the rule (if applicable).
- Third-Party Tool Compatibility:
- If using a third-party tool, ensure it is compatible with your version of Outlook and that it is properly configured.
9. Tips for Efficiently Managing Saved Emails
Managing saved emails efficiently is crucial for maintaining organization and quickly accessing important information. Here are some tips to help you streamline your email management process:
9.1. Create a Clear Folder Structure
- Categorize by Project: Organize emails into folders based on specific projects or initiatives.
- Group by Sender/Recipient: Create folders for frequent contacts or specific clients.
- Organize by Date: Use date-based folders for time-sensitive communications.
- Use Subfolders: Create subfolders within main folders for more granular organization.
9.2. Use Consistent Naming Conventions
- Descriptive File Names: Use clear and descriptive names for saved emails, including keywords, dates, and sender/recipient information.
- Standardize File Naming: Develop a consistent naming convention for all saved emails to make them easier to find and sort.
- Include Dates: Incorporate dates in the file names to quickly identify the age of the email (e.g., YYYYMMDD_Subject_Sender.msg).
9.3. Leverage Search Functionality
- Use Keywords: Utilize relevant keywords when searching for specific emails.
- Advanced Search Options: Take advantage of advanced search options in your file explorer or email client to narrow down your search by date, sender, recipient, or content.
- Index Your Folders: Ensure your saved email folders are indexed for faster searching.
9.4. Regularly Review and Archive
- Schedule Regular Reviews: Set aside time each month to review your saved emails and archive or delete outdated or irrelevant items.
- Archive to External Storage: Move older emails to external storage devices or cloud-based archives to free up space on your primary storage.
- Delete Unnecessary Emails: Delete any emails that are no longer needed to reduce clutter and improve search efficiency.
9.5. Use Email Management Tools
- Document Management Systems (DMS): Consider using a DMS to manage and organize saved emails along with other documents.
- Email Archiving Solutions: Implement dedicated email archiving solutions for long-term storage and compliance.
- Note-Taking Apps: Use note-taking apps like Evernote or OneNote to summarize and organize key information from saved emails.
9.6. Back Up Your Saved Emails
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your saved email folders to protect against data loss.
- Cloud Storage: Use cloud storage services like Google Drive, OneDrive, or Dropbox for automatic backups.
- External Hard Drives: Create backups on external hard drives or network-attached storage (NAS) devices.
9.7. Secure Your Saved Emails
- Encryption: Encrypt your saved email folders to protect sensitive information.
- Password Protection: Use strong passwords to protect your computer and storage devices.
- Access Controls: Implement access controls to limit who can view or modify your saved emails.
9.8. Automate with Scripts
- Batch Processing: Use scripts to automate repetitive tasks such as renaming files, moving emails to specific folders, or creating backups.
- Customized Solutions: Develop custom scripts tailored to your specific email management needs.
9.9. Stay Organized on Mobile Devices
- Mobile Apps: Use mobile apps that allow you to access and manage your saved emails on the go.
- Cloud Synchronization: Sync your saved email folders across devices using cloud storage services.
- Mobile-Friendly Naming: Use mobile-friendly naming conventions for saved emails to make them easier to find on smaller screens.
9.10. Optimize Storage Space
- Compress Files: Compress large email files or folders to save storage space.
- Remove Duplicates: Use duplicate file finders to identify and remove duplicate emails.
- External Storage: Move large files or folders to external storage devices or cloud-based archives.
By implementing these tips, you can efficiently manage your saved emails, ensure they are easily accessible when needed, and protect them from loss or unauthorized access. Stay organized and maximize the value of your saved email data with these best practices.
10. FAQ about Saving Emails from Outlook
10.1. How do I save an email from Outlook to my computer?
To save an email from Outlook to your computer, open the email, click “File,” then “Save As.” Choose a location on your computer, select a file format (such as .msg, .html, or .txt), and click “Save.”
10.2. Can I save multiple emails from Outlook at once?
Yes, you can save multiple emails at once by selecting them, then dragging and dropping them into a folder on your computer. Outlook will save each email as an individual .msg file.
10.3. How do I save an email from Outlook as a PDF?
To save an email from Outlook as a PDF, open the email, click “File,” then “Print.” Choose “Microsoft Print to PDF” as your printer, and click “Print.” You will then be prompted to choose a location to save the PDF file.
10.4. What file format should I use to save emails from Outlook?
The best file format depends on your needs. .MSG is ideal for preserving all email elements (including attachments) but requires Outlook to open. .HTML preserves formatting and images. .TXT saves as plain text, removing all formatting. .PDF is great for universal viewing and printing.
10.5. How do I save attachments from an Outlook email?
To save attachments from an Outlook email, open the email, right-click on the attachment, and select “Save As.” Choose a location on your computer and click “Save.” To save all attachments at once, click the dropdown arrow on any attachment and select “Save All Attachments.”
10.6. Can I automate the process of saving emails from Outlook?
Yes, you can automate the process of saving emails using Outlook rules or VBA scripts. Outlook rules can automatically move or copy specific emails to a designated folder. VBA scripts offer more advanced automation options.
10.7. How do I change the default file format for saving messages in Outlook?
To change the default file format for saving messages in Outlook, go to “File,” “Options,” “Mail.” Under “Save messages,” select the “Use Unicode Format” check box to save messages in a Unicode encoding by default.
10.8. How do I save Outlook emails for legal or compliance reasons?
Saving emails for legal or compliance reasons requires a systematic approach. Define retention policies, choose an archiving method (manual, automated, or third-party solutions), maintain data integrity and security, and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
10.9. What should I do if I cannot save emails due to permissions?
If you cannot save emails due to permissions, check the folder permissions, run Outlook as administrator, or try saving to a different location. Ensure your user account has “Write” and “Modify” permissions for the folder.
10.10. How can I efficiently manage my saved emails?
To efficiently manage saved emails, create a clear folder structure, use consistent naming conventions, leverage search functionality, regularly review and archive emails, use email management tools, back up your saved emails, and secure your saved emails.
By mastering these methods and understanding the nuances of each file format, you can effectively save and manage your Outlook emails, ensuring you always have access to important information. Remember to visit savewhere.net for more tips, tricks, and resources to optimize your digital life and save money along the way!
Ready to take control of your finances and make your money work harder? Visit savewhere.net today for a treasure trove of tips, tricks, and resources designed to help you save money in every aspect of your life. From savvy shopping strategies to expert financial advice, savewhere.net is your go-to destination for smart savings.
Address: 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States
Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000
Website: savewhere.net
Join the savewhere.net community today and start saving smarter!
