Do you love the sweet taste of cantaloupe and want to enjoy it year after year? Saving cantaloupe seeds is a simple and rewarding process that allows you to cultivate your favorite variety. Savewhere.net provides easy-to-follow instructions and practical tips to help you succeed. Learn the steps to harvest, dry, and store your cantaloupe seeds, ensuring successful germination for future gardens. Let’s explore How To Save Cantaloupe Seeds effectively, with easy steps, maximizing your yield.
1. Why Should You Save Cantaloupe Seeds?
Saving cantaloupe seeds can be a very rewarding practice.
- Preserve Your Favorite Varieties: By saving seeds, you can ensure the continuation of specific cantaloupe types that you particularly enjoy.
- Cost-Effective Gardening: Saving seeds reduces the need to purchase new seeds each year, leading to significant cost savings.
- Adaptation to Local Conditions: Seeds saved from plants grown in your garden are better adapted to your local climate and soil conditions, potentially resulting in healthier and more productive plants.
- Genetic Diversity: Seed saving helps maintain genetic diversity, which is crucial for the resilience of plant populations.
- Self-Sufficiency: Seed saving empowers you to become more self-sufficient in your gardening endeavors.
2. What Are The Essential Steps To Prepare For Saving Cantaloupe Seeds?
Preparing for saving cantaloupe seeds involves several crucial steps to ensure the seeds you save are viable and true to type.
- Choose the Right Cantaloupe: Select cantaloupes from healthy, disease-free plants that have produced excellent fruit. According to the University of Minnesota Extension, selecting the best plants ensures you are saving seeds with desirable traits.
- Know Your Varieties: Be aware of the type of cantaloupe you’re growing. Heirloom or open-pollinated varieties are more likely to produce seeds that grow true to type, while hybrid varieties may not.
- Isolate Plants: If you are growing multiple cantaloupe varieties, isolate them to prevent cross-pollination, which can result in unexpected traits in the next generation.
- Allow Cantaloupe to Fully Ripen: Leave the cantaloupe on the vine until it is fully ripe. A ripe cantaloupe will have a sweet aroma and the stem will easily slip from the vine.
- Gather Supplies: Collect the necessary supplies, including a knife, spoon, bowl, colander, and paper towels.
3. How Do You Properly Harvest Cantaloupe Seeds?
Harvesting cantaloupe seeds correctly is essential for ensuring their viability and future success in your garden.
- Cut Open the Cantaloupe: Use a clean knife to carefully cut open the ripe cantaloupe. Avoid damaging the seeds inside.
- Remove the Seeds: Scoop out the seeds and surrounding pulp from the cantaloupe’s cavity.
- Separate Seeds from Pulp: Place the seeds and pulp into a bowl. Add water to help separate the seeds from the pulp.
- Clean the Seeds: Gently rub the seeds between your fingers to remove any remaining pulp. Rinse the seeds thoroughly with water until they are clean.
- Ferment (Optional): Fermenting the seeds can help remove any remaining pulp and kill any seed-borne diseases. Place the cleaned seeds and some water in a jar and let it sit for 2-3 days, stirring daily. A white film will form on top. Rinse the seeds thoroughly after fermentation.
4. What’s The Best Way To Dry Cantaloupe Seeds?
Proper drying is essential to prevent mold and ensure long-term viability.
- Spread Seeds on a Paper Towel: Lay the cleaned seeds in a single layer on a paper towel or screen. Make sure the seeds are not touching each other to allow for proper air circulation.
- Choose a Dry Location: Place the paper towel or screen in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can damage the seeds.
- Allow Seeds to Dry Completely: Let the seeds dry for 1-2 weeks, or until they are completely dry to the touch. Turn the seeds occasionally to ensure even drying.
- Test for Dryness: To ensure the seeds are dry enough for storage, try bending one. If it snaps, it is dry enough. If it bends, it needs more drying time.
- Avoid Heat: Do not use a dehydrator or oven to dry the seeds, as high temperatures can reduce their viability.
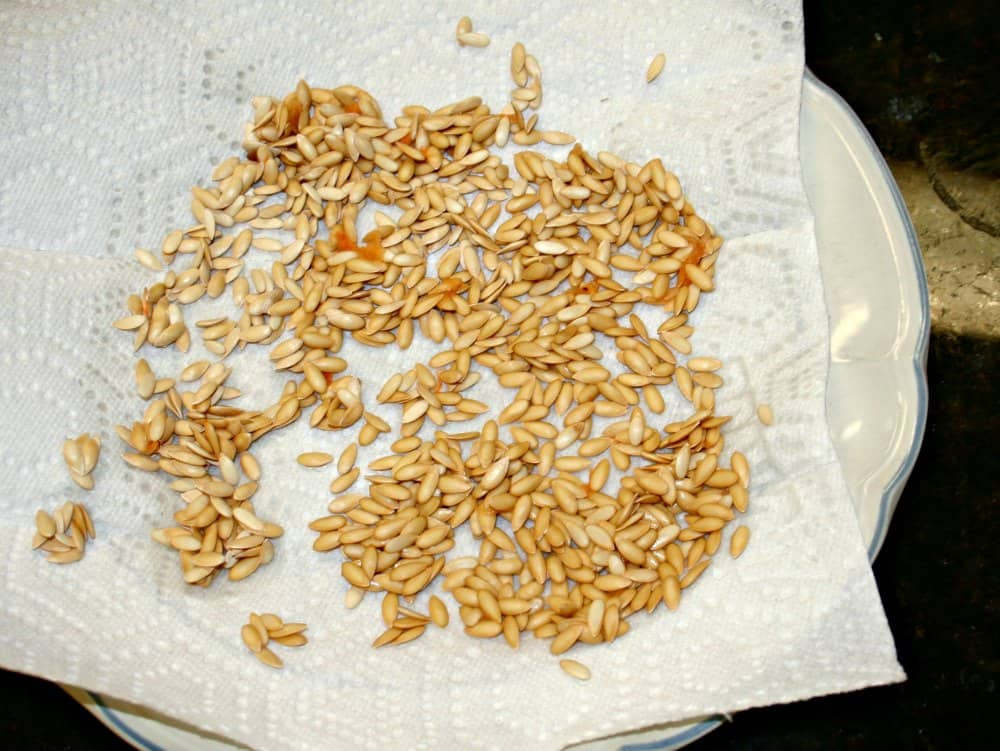 Cantaloupe seeds drying on a paper towel, a key step in preserving them for future planting, with a focus on ensuring proper air circulation
Cantaloupe seeds drying on a paper towel, a key step in preserving them for future planting, with a focus on ensuring proper air circulation
5. How Should You Store Cantaloupe Seeds For Optimal Preservation?
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the viability of cantaloupe seeds over the long term.
- Use an Airtight Container: Place the dried seeds in an airtight container, such as a glass jar or plastic bag.
- Add a Desiccant: Include a desiccant, such as silica gel packets or dry rice, to absorb any remaining moisture.
- Label the Container: Label the container with the date of harvest and the variety of cantaloupe.
- Store in a Cool, Dark Place: Store the container in a cool, dark, and dry place, such as a refrigerator or basement.
- Maintain Consistent Temperature: Keep the temperature consistent to prevent fluctuations that can damage the seeds.
- Avoid Sunlight: Protect the seeds from direct sunlight, as it can degrade their quality.
6. What Are The Common Problems To Avoid When Saving Cantaloupe Seeds?
Avoiding common problems during seed saving can significantly improve your success rate.
- Cross-Pollination: Cantaloupes can cross-pollinate with other melon varieties, resulting in seeds that do not grow true to type. To avoid this, isolate your cantaloupe plants or hand-pollinate them.
- Hybrid Seeds: Hybrid cantaloupe varieties (labeled as F1) do not produce seeds that grow true to type. Save seeds only from heirloom or open-pollinated varieties.
- Insufficient Drying: Inadequate drying can lead to mold growth and reduced seed viability. Ensure the seeds are completely dry before storing them.
- Improper Storage: Storing seeds in a warm, humid environment can also reduce their viability. Store seeds in a cool, dark, and dry place.
- Disease Transmission: Seeds from diseased plants can carry diseases to the next generation. Only save seeds from healthy, disease-free plants.
- Immature Seeds: Seeds from unripe cantaloupes may not be viable. Allow the cantaloupe to fully ripen before harvesting the seeds.
7. How Can You Test The Viability Of Your Saved Cantaloupe Seeds?
Testing the viability of your saved cantaloupe seeds is a practical step to ensure you’re planting seeds that are likely to germinate.
- Gather Supplies: You will need a paper towel, a plastic bag, and your saved cantaloupe seeds.
- Moisten the Paper Towel: Dampen the paper towel with water, but do not soak it.
- Place Seeds on the Towel: Arrange 10-20 seeds on one half of the paper towel, spacing them evenly.
- Fold the Towel: Fold the other half of the paper towel over the seeds.
- Place in a Plastic Bag: Put the paper towel with the seeds into a plastic bag. Seal the bag to maintain moisture.
- Store in a Warm Place: Place the bag in a warm location, such as on top of the refrigerator.
- Check for Germination: After 7-10 days, check the seeds for germination. Keep the paper towel moist during this time.
- Calculate Germination Rate: Count the number of seeds that have germinated (sprouted). Divide that number by the total number of seeds you tested, and multiply by 100 to get the germination rate. For example, if 15 out of 20 seeds germinated, the germination rate is 75%.
- Assess Seed Quality: A germination rate of 70% or higher is generally considered good. If the germination rate is low, you may need to use more seeds when planting or consider purchasing new seeds.
8. What Tools And Equipment Are Needed For Saving Cantaloupe Seeds?
Having the right tools and equipment can make the process of saving cantaloupe seeds more efficient and effective.
- Knife: A sharp knife for cutting open the cantaloupe.
- Spoon: A spoon for scooping out the seeds and pulp.
- Bowl: A bowl for collecting the seeds and pulp.
- Colander: A colander for rinsing the seeds.
- Paper Towels: Paper towels for drying the seeds.
- Screen or Mesh Tray: A screen or mesh tray for air-drying the seeds.
- Airtight Containers: Airtight containers (such as glass jars or plastic bags) for storing the dried seeds.
- Desiccant: A desiccant (such as silica gel packets or dry rice) to absorb moisture during storage.
- Labels and Marker: Labels and a marker for labeling the storage containers with the date of harvest and variety of cantaloupe.
9. What Are The Best Cantaloupe Varieties For Seed Saving?
Choosing the right cantaloupe varieties is crucial for successful seed saving.
- Heirloom Varieties: Heirloom varieties are open-pollinated and have been passed down for generations, ensuring they grow true to type.
- Hales Best: A classic heirloom variety known for its sweet flavor and reliable production.
- hearts of gold: Another popular heirloom, Hearts of Gold, is prized for its aromatic flavor and juicy flesh.
- Open-Pollinated Varieties: Open-pollinated varieties are also reliable for seed saving, as they produce seeds that grow true to type.
- Minnesota Midget: A small, early-maturing variety that is well-suited for cooler climates.
- Jenny Lind: An older variety with a distinctive turban shape and sweet, flavorful flesh.
- Avoid Hybrid Varieties: Hybrid varieties (labeled as F1) are the result of cross-breeding two different parent plants. Seeds from hybrid varieties will not grow true to type and may produce plants with undesirable traits.
 Cantaloupe varieties displayed at a local farmer's market, showcasing the diversity and options for seed saving enthusiasts, with a focus on heirloom and open-pollinated choices
Cantaloupe varieties displayed at a local farmer's market, showcasing the diversity and options for seed saving enthusiasts, with a focus on heirloom and open-pollinated choices
10. How Do Environmental Factors Affect Cantaloupe Seed Saving?
Environmental factors play a significant role in the success of cantaloupe seed saving.
- Temperature: High temperatures during seed development can reduce seed viability. Ideal temperatures for cantaloupe growth are between 70°F and 85°F (21°C and 29°C).
- Humidity: High humidity can promote fungal growth and disease, which can affect seed quality. Ensure good air circulation around the plants and dry the seeds thoroughly after harvesting.
- Sunlight: Adequate sunlight is essential for healthy plant growth and seed development. Cantaloupes require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
- Water: Consistent watering is important, but avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot and other diseases.
- Soil: Well-draining soil is crucial for cantaloupe growth. Amend heavy soils with organic matter to improve drainage.
- Pests and Diseases: Protect cantaloupe plants from pests and diseases, as these can affect seed quality. Use organic pest control methods and disease-resistant varieties.
11. What Are Some Advanced Techniques For Cantaloupe Seed Saving?
For those looking to take their seed saving to the next level, there are several advanced techniques to consider.
- Hand Pollination: To ensure true-to-type seeds, hand-pollinate your cantaloupe flowers. Cover the female flowers with a bag before they open, and then use a small brush to transfer pollen from a male flower to the female flower. Re-cover the female flower after pollination.
- Population Size: When saving seeds, save from a large population of plants (at least 20) to maintain genetic diversity.
- Record Keeping: Keep detailed records of your seed saving activities, including the date of harvest, variety of cantaloupe, and any observations about plant health or fruit quality.
- Selection: Select seeds from plants that exhibit desirable traits, such as disease resistance, high yield, or excellent flavor.
- Seed Cleaning: Use advanced seed cleaning methods, such as screening or winnowing, to remove any remaining debris from the seeds.
- Germination Testing: Regularly test the germination rate of your saved seeds to ensure they are still viable.
12. How Does Seed Saving Contribute To Sustainable Gardening?
Seed saving is a fundamental practice that significantly contributes to sustainable gardening.
- Preserves Genetic Diversity: Seed saving helps maintain a wide range of plant varieties, ensuring that valuable genetic traits are not lost.
- Reduces Reliance on Commercial Seeds: By saving seeds, gardeners become less dependent on commercial seed companies, which often prioritize hybrid varieties that do not breed true.
- Promotes Local Adaptation: Saved seeds are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, resulting in healthier and more resilient plants.
- Conserves Resources: Seed saving reduces the need for packaging, transportation, and other resources associated with commercial seed production.
- Empowers Gardeners: Seed saving empowers gardeners to become more self-sufficient and knowledgeable about the plants they grow.
- Supports Biodiversity: By growing a diverse range of plants from saved seeds, gardeners contribute to the overall biodiversity of their local ecosystem.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), preserving plant genetic resources is essential for ensuring food security and adapting to climate change.
13. Can You Save Seeds From Store-Bought Cantaloupes?
Saving seeds from store-bought cantaloupes can be a bit of a gamble.
- Hybrid Varieties: Most store-bought cantaloupes are hybrid varieties, which means their seeds will not grow true to type. The resulting plants may not produce fruit that is the same as the parent cantaloupe.
- Unknown Pollination: Store-bought cantaloupes may have been cross-pollinated with other melon varieties, resulting in seeds that produce unexpected traits.
- Potential for Disease: Seeds from store-bought cantaloupes may carry diseases that can affect your garden.
- Experimentation: If you want to experiment, you can try saving seeds from store-bought cantaloupes, but be aware that the results may not be predictable.
- Better Options: For more reliable results, save seeds from heirloom or open-pollinated cantaloupe varieties grown in your own garden.
14. What Are The Benefits Of Using Savewhere.net For Seed Saving Advice?
Savewhere.net is your ultimate resource for saving money and gardening tips.
- Comprehensive Guides: Savewhere.net provides detailed, step-by-step guides on how to save seeds from various plants, including cantaloupes.
- Expert Advice: Savewhere.net offers expert advice from experienced gardeners and horticulturalists.
- Community Forum: Savewhere.net has a community forum where you can ask questions, share your experiences, and connect with other gardeners.
- Money-Saving Tips: Savewhere.net provides tips on how to save money on gardening supplies and other expenses.
- Local Resources: Savewhere.net can help you find local seed saving resources, such as seed exchanges and workshops.
- Up-to-Date Information: Savewhere.net provides up-to-date information on the latest gardening techniques and trends.
15. How Can Saving Cantaloupe Seeds Help You Save Money?
Saving cantaloupe seeds can lead to significant cost savings over time.
- Reduced Seed Costs: By saving your own seeds, you can avoid the need to purchase new seeds each year.
- Increased Self-Sufficiency: Seed saving reduces your reliance on commercial seed companies, making you more self-sufficient.
- Bartering and Trading: You can barter or trade your saved seeds with other gardeners, further reducing your costs.
- Preserving Valuable Varieties: Saving seeds from your favorite cantaloupe varieties ensures you can continue to grow them year after year, without having to pay for new seeds.
- Adapting to Local Conditions: Saved seeds are adapted to your local climate and soil conditions, potentially leading to higher yields and reduced need for fertilizers and other inputs.
- Sustainable Gardening: Seed saving is a sustainable gardening practice that reduces waste and conserves resources.
16. Where Can You Find Reputable Sources For Additional Seed Saving Information?
Finding reliable information is crucial for successful seed saving.
- University Extension Services: Contact your local university extension service for research-based information on seed saving.
- Seed Saving Organizations: Join a seed saving organization, such as Seed Savers Exchange, for access to resources and a community of fellow seed savers.
- Gardening Books: Consult reputable gardening books that cover seed saving techniques.
- Online Forums: Participate in online gardening forums to ask questions and share your experiences with other seed savers.
- Government Agencies: Check with government agencies, such as the USDA, for information on seed saving and plant genetic resources.
- Local Libraries: Visit your local library for access to gardening books, magazines, and other resources on seed saving.
17. What Are The Legal Considerations For Saving Cantaloupe Seeds?
Understanding the legal aspects of seed saving is essential to ensure you are not violating any intellectual property rights.
- Plant Variety Protection Act (PVPA): The PVPA grants breeders of new plant varieties certain exclusive rights, similar to patents. However, there is a research exemption that allows farmers and gardeners to save seeds for research purposes.
- Patented Seeds: Some seeds are patented, which means you cannot save and replant them without permission from the patent holder.
- Contractual Agreements: When purchasing seeds, be aware of any contractual agreements that may restrict your ability to save and replant the seeds.
- Open Source Seed Initiative (OSSI): The OSSI is an organization that promotes the free exchange of plant genetic resources. Seeds pledged under the OSSI can be saved and shared without restriction.
- Local Laws: Check with your local government for any laws or regulations that may affect seed saving.
- Ethical Considerations: Respect the intellectual property rights of plant breeders and seed companies, and only save seeds from varieties that are not protected by patents or contractual agreements. According to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), understanding intellectual property rights is essential for innovation and economic growth.
18. What Should You Do If Your Saved Cantaloupe Seeds Fail To Germinate?
If your saved cantaloupe seeds fail to germinate, there are several possible reasons and steps you can take.
- Check Seed Viability: Perform a germination test to determine the viability of your seeds. If the germination rate is low, the seeds may be too old or have been stored improperly.
- Ensure Proper Planting Conditions: Make sure you are planting the seeds at the correct depth, in well-draining soil, and at the appropriate temperature. Cantaloupe seeds germinate best at temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C and 29°C).
- Provide Adequate Moisture: Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, until the seeds germinate.
- Protect from Pests and Diseases: Protect the seedlings from pests and diseases, which can prevent germination or kill young plants.
- Consider Seed Treatment: Treat the seeds with a fungicide before planting to protect them from soil-borne diseases.
- Purchase New Seeds: If your saved seeds consistently fail to germinate, consider purchasing new seeds from a reputable source.
19. How Does Climate Change Impact Cantaloupe Seed Saving?
Climate change poses several challenges to cantaloupe seed saving.
- Changing Weather Patterns: Climate change is causing more frequent and severe weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heat waves, which can affect seed production and viability.
- Shifting Growing Zones: As temperatures rise, growing zones are shifting, which may require gardeners to adapt their seed saving practices.
- Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: Climate change can alter the distribution and abundance of pests and diseases, making it more difficult to save seeds from healthy plants.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: As some plant varieties become less adapted to changing climate conditions, there is a risk of losing valuable genetic diversity.
- Adaptation Strategies: Gardeners can adapt to climate change by saving seeds from plants that are more resilient to extreme weather events, pests, and diseases.
- Community Seed Banks: Community seed banks can play a crucial role in preserving plant genetic resources and adapting to climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), adaptation is essential for reducing the impacts of climate change on agriculture and food security.
20. How Can You Get Involved In Community Seed Saving Initiatives?
Participating in community seed saving initiatives is a great way to learn, share, and contribute to the preservation of plant genetic resources.
- Join a Local Seed Library: Seed libraries are community-based organizations that allow members to borrow and save seeds.
- Attend Seed Exchanges: Seed exchanges are events where gardeners can trade seeds and knowledge.
- Volunteer at a Community Garden: Community gardens often have seed saving programs that you can volunteer with.
- Start Your Own Seed Saving Group: If there are no seed saving initiatives in your area, consider starting your own group.
- Donate Seeds to Seed Banks: Donate your saved seeds to seed banks to help preserve plant genetic resources.
- Educate Others: Share your knowledge and passion for seed saving with others in your community.
21. What Are Some Fun Facts About Cantaloupe Seeds?
Learning about cantaloupe seeds can be both fun and informative.
- Seed Count: A single cantaloupe can contain hundreds of seeds.
- Seed Color: Cantaloupe seeds are typically cream-colored or light tan.
- Seed Shape: Cantaloupe seeds are flat and oval-shaped.
- Seed Size: Cantaloupe seeds are relatively small, measuring about 1/4 inch long.
- Seed Viability: Cantaloupe seeds can remain viable for up to 5 years if stored properly.
- Seed Germination: Cantaloupe seeds typically germinate in 7-10 days under optimal conditions.
22. How Does Saving Cantaloupe Seeds Support Biodiversity?
Saving cantaloupe seeds is a simple yet powerful way to support biodiversity.
- Preserving Heirloom Varieties: By saving seeds from heirloom cantaloupe varieties, you help maintain genetic diversity that might otherwise be lost.
- Adapting to Local Conditions: When you save seeds from cantaloupes that have thrived in your garden, you are selecting for traits that are well-suited to your local environment.
- Reducing Reliance on Monoculture: Seed saving encourages the cultivation of a wide range of cantaloupe varieties, reducing the reliance on monoculture, which can be harmful to ecosystems.
- Supporting Pollinators: By growing cantaloupes from saved seeds, you provide food and habitat for pollinators, such as bees and butterflies.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Seed saving is an integral part of sustainable agriculture, which aims to protect biodiversity and natural resources.
- Educating Others: By sharing your knowledge of seed saving, you can inspire others to take action and support biodiversity in their own gardens.
23. Where Can You Find Support From Savewhere.Net If You Encounter Problems?
Savewhere.net is committed to providing support and assistance to help you succeed in saving cantaloupe seeds.
- Comprehensive Guides: Savewhere.net offers detailed, step-by-step guides on how to save seeds from various plants, including cantaloupes.
- Expert Advice: Savewhere.net provides expert advice from experienced gardeners and horticulturalists.
- Community Forum: Savewhere.net has a community forum where you can ask questions, share your experiences, and connect with other gardeners.
- Contact Us Form: If you have specific questions or concerns, you can contact Savewhere.net through our contact us form.
- FAQ Section: Savewhere.net has a FAQ section that answers common questions about seed saving.
- Regular Updates: Savewhere.net provides regular updates on the latest gardening techniques and trends.
24. How To Deal With Common Cantaloupe Diseases When Saving Seeds?
Dealing with common cantaloupe diseases is crucial when saving seeds to ensure the health of future plants.
- Identify the Disease: Accurately identify the disease affecting your cantaloupe plants. Common diseases include powdery mildew, downy mildew, and fusarium wilt.
- Select Healthy Plants: Only save seeds from healthy, disease-free plants. Avoid saving seeds from plants that show symptoms of disease.
- Practice Crop Rotation: Rotate your cantaloupe crops to prevent the buildup of soil-borne diseases.
- Improve Air Circulation: Ensure good air circulation around your cantaloupe plants to reduce humidity and prevent fungal diseases.
- Use Disease-Resistant Varieties: Choose cantaloupe varieties that are resistant to common diseases in your area.
- Sanitize Tools: Sanitize your gardening tools regularly to prevent the spread of disease.
- Remove Infected Plants: Remove and destroy any infected plants to prevent the disease from spreading to healthy plants.
- Consider Seed Treatment: Treat the seeds with a fungicide before planting to protect them from soil-borne diseases.
25. What Role Does Genetics Play In Cantaloupe Seed Saving?
Genetics plays a vital role in cantaloupe seed saving, influencing the traits that are passed on to future generations.
- Heirloom Varieties: Heirloom varieties are open-pollinated and have been passed down for generations, ensuring they grow true to type.
- Open-Pollinated Varieties: Open-pollinated varieties are also reliable for seed saving, as they produce seeds that grow true to type.
- Hybrid Varieties: Hybrid varieties (labeled as F1) are the result of cross-breeding two different parent plants. Seeds from hybrid varieties will not grow true to type and may produce plants with undesirable traits.
- Cross-Pollination: Cantaloupes can cross-pollinate with other melon varieties, resulting in seeds that do not grow true to type.
- Genetic Diversity: Saving seeds from a large population of plants helps maintain genetic diversity, which is crucial for the resilience of plant populations.
- Selection: Selecting seeds from plants that exhibit desirable traits, such as disease resistance, high yield, or excellent flavor, can improve the genetics of future generations.
Saving cantaloupe seeds is more than just a gardening activity; it’s a step towards preserving biodiversity, promoting sustainability, and ensuring access to your favorite cantaloupe varieties for years to come. With the right knowledge and techniques, you can successfully save cantaloupe seeds and enjoy the fruits (literally) of your labor.
Ready to start saving cantaloupe seeds and enjoy a bountiful harvest year after year? Visit Savewhere.net for more tips, tricks, and resources to help you succeed. Join our community of gardeners in Atlanta, USA, and beyond, and let’s cultivate a greener future together.
Address: 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States. Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000. Visit savewhere.net today!
FAQ Section
1. How long do cantaloupe seeds last?
Cantaloupe seeds can remain viable for up to five years if stored properly in a cool, dry place.
2. Can I save seeds from any cantaloupe?
It’s best to save seeds from heirloom or open-pollinated varieties, as hybrid varieties may not grow true to type.
3. How do I know if my cantaloupe seeds are viable?
Perform a germination test by placing a few seeds on a damp paper towel, enclosing them in a plastic bag, and waiting for them to sprout.
4. What’s the best way to dry cantaloupe seeds?
Spread the seeds on a paper towel in a cool, dry place for about a week, ensuring they are completely dry before storing.
5. How do I prevent cross-pollination when saving cantaloupe seeds?
Isolate different cantaloupe varieties by a significant distance or hand-pollinate the flowers to ensure true-to-type seeds.
6. What are the ideal conditions for storing cantaloupe seeds?
Store seeds in an airtight container in a cool, dark, and dry place, such as a refrigerator.
7. Can I save seeds from store-bought cantaloupes?
While possible, store-bought cantaloupes are often hybrids, so the seeds may not produce the same fruit.
8. What are common problems when saving cantaloupe seeds?
Common issues include cross-pollination, improper drying, and storing seeds in humid conditions.
9. How do I clean cantaloupe seeds properly?
Rinse the seeds thoroughly to remove any pulp, then dry them completely to prevent mold.
10. What if my saved cantaloupe seeds don’t germinate?
Ensure proper planting conditions, test seed viability, and consider purchasing new seeds if the germination rate is low.