Bulgaria, a country with a rich history and diverse landscapes, holds a fascinating position on the European continent. But Where In Europe Is Bulgaria exactly? Nestled in southeastern Europe, Bulgaria occupies the eastern portion of the Balkan Peninsula, a region known for its cultural crossroads and historical significance. This location places Bulgaria at the heart of connections between Europe and Asia, and between northern and southern Europe.
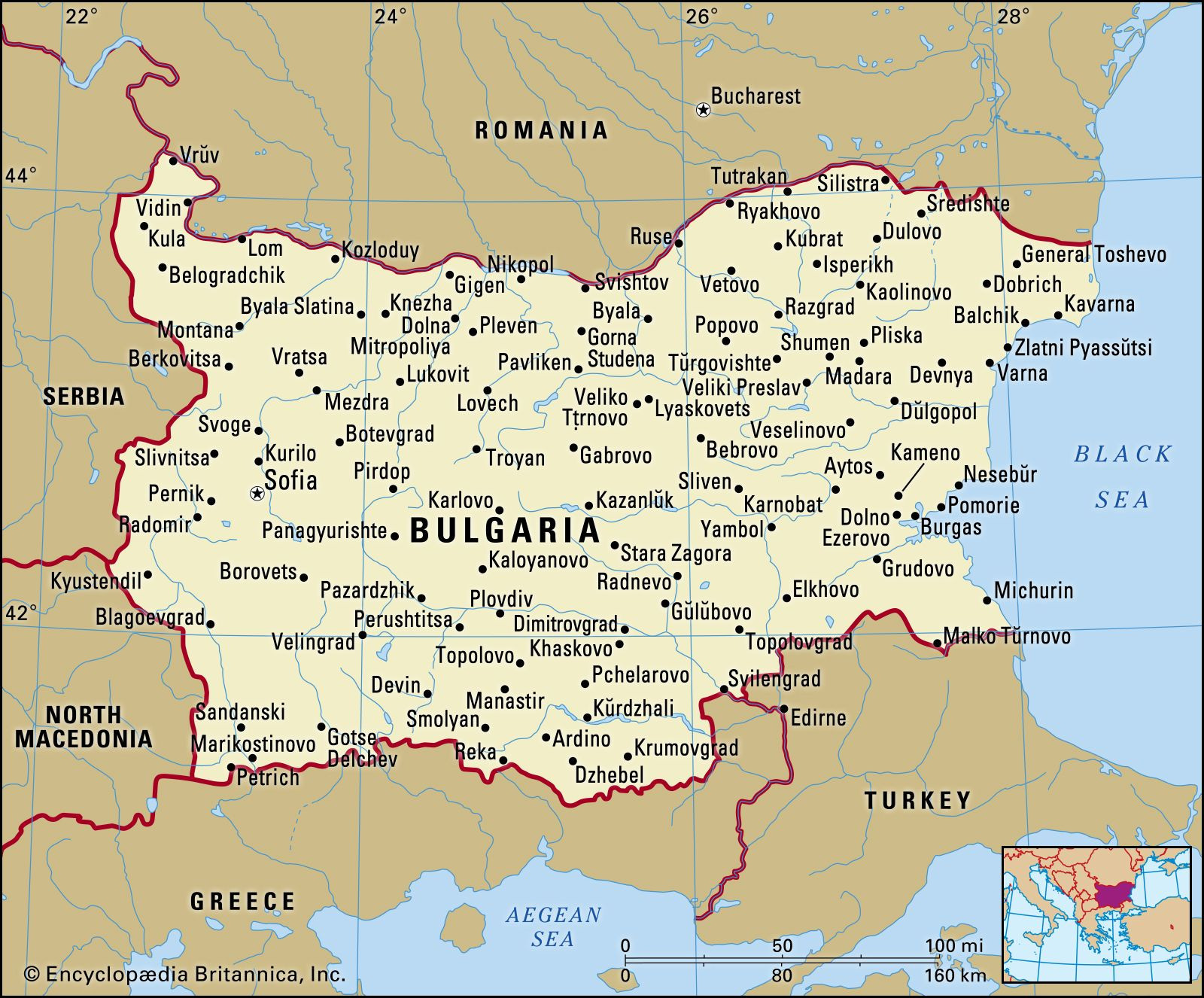 Bulgaria map highlighting its location in Europe
Bulgaria map highlighting its location in Europe
To understand where Bulgaria is located in Europe, it’s helpful to consider its neighbors. Bulgaria shares borders with Romania to the north, largely defined by the majestic Danube River. To the east, Bulgaria meets the Black Sea, offering a picturesque coastline. Turkey and Greece lie to the south, while North Macedonia is situated to the southwest, and Serbia to the west. This strategic location has shaped Bulgaria’s history, culture, and its role in European affairs.
Historically, Bulgaria’s location has been pivotal. It sits at the intersection of vital routes connecting northern and eastern Europe with the Mediterranean, and western and central Europe with the Middle East. Before Bulgaria’s formation in the 7th century, the powerful empires of ancient Rome, Greece, and Byzantium traversed this land, leaving their mark and facilitating the movement of people and goods. This heritage as a crossroads remains a defining characteristic of Bulgaria’s geographical identity within Europe.
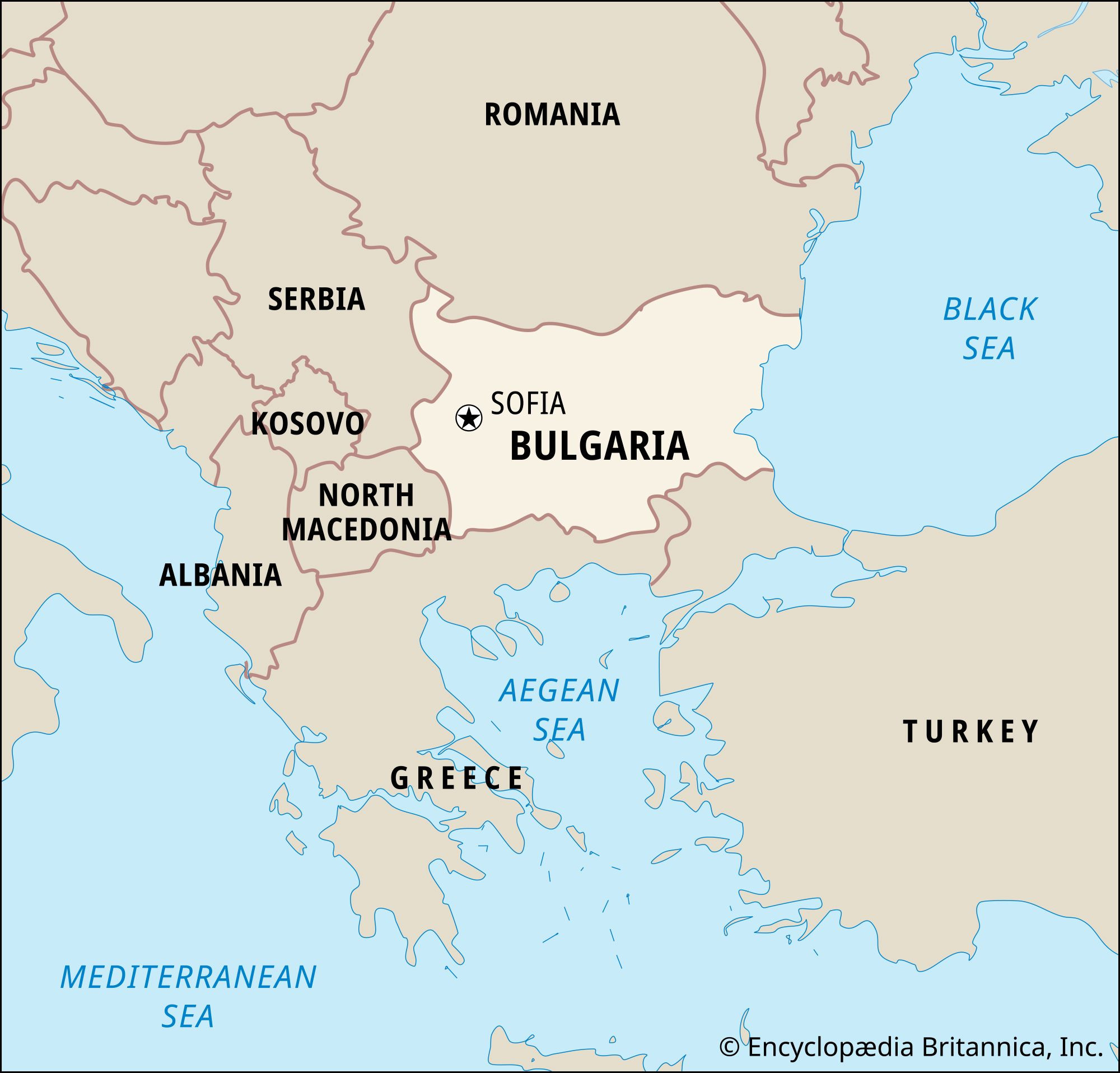 Bulgaria within the Balkan Peninsula and Southeastern Europe
Bulgaria within the Balkan Peninsula and Southeastern Europe
Emerging from Ottoman rule in the late 19th century, Bulgaria’s 20th-century history saw it navigate complex geopolitical landscapes. Initially gravitating towards the Axis powers in World War II, Bulgaria later found itself aligned with the Soviet Union during the Cold War. This Soviet influence significantly impacted Bulgaria until the fall of communist regimes in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Since then, Bulgaria has firmly set its sights westward, joining NATO in 2004 and the European Union in 2007, solidifying its place as a European nation both geographically and politically.
Bulgaria’s capital city, Sofia, further emphasizes its central location within the Balkan region. While situated in western Bulgaria, Sofia is geographically near the center of the Balkan Peninsula. As Bulgaria’s largest city, Sofia acts as the nation’s focal point and a key urban center in southeastern Europe. Bulgarian writer Yordan Radichkov aptly described Sofia’s location as the “universal core of Bulgaria,” positioned at the crossroads of the ancient Silk Road and a major migratory bird route, highlighting its importance as a meeting point of diverse influences within Europe and beyond.
Exploring Bulgaria’s Diverse Landscape
Beyond simply stating where Bulgaria is in Europe, understanding its internal geography reveals a country of remarkable diversity. Bulgaria’s landscape is a captivating blend of mountains, plains, and a scenic coastline, contributing to its appeal as a travel destination and shaping regional variations within the country.
Bulgaria can be broadly divided into three east-west zones: North Bulgaria, South Bulgaria, and a transitional region in between. North Bulgaria is dominated by the Danubian Plain, a fertile, hilly expanse stretching south from the Danube River to the Balkan Mountains. This plain is crucial for agriculture and represents a significant portion of Bulgaria’s landmass.
The Balkan Mountains themselves form a central spine across the country, separating the Danubian Plain from the southern regions. While not exceedingly high in average elevation, they are significant geographical feature, rising to their peak at Mount Botev.
South Bulgaria is characterized by the Rila-Rhodope Massif, a region of high mountains including the Rila, Rhodope, and Pirin ranges. These mountains are home to the highest peaks in Bulgaria and the Balkan Peninsula, with Musala Peak in the Rila Mountains being the highest point. This area is known for its dramatic scenery, glacial lakes, and is a haven for biodiversity.
Finally, the eastern edge of Bulgaria is defined by the Black Sea coastal region. This narrow strip features sandy beaches, coastal lakes, and important port cities like Varna and Burgas. The Black Sea coast is a popular tourist destination and a vital component of Bulgaria’s economic geography.
 Steppe grasslands along Bulgaria's Black Sea coast
Steppe grasslands along Bulgaria's Black Sea coast
Rivers, Lakes, and Climate
Bulgaria’s location in Europe also influences its climate and water systems. The country experiences a moderate continental climate across most of its territory, with Mediterranean influences more pronounced in the southern regions. This results in distinct seasons, with cold winters and warm summers. Precipitation varies across the country, with higher amounts in mountainous regions and lower levels in the northeast.
Bulgaria’s river network is complex, with the Danube being the only major river. Other significant rivers include the Maritsa, Iskŭr, Struma, and Arda, most of which are relatively short. A significant portion of Bulgaria’s water runoff drains into the Black Sea, while the rest flows towards the Aegean Sea.
The country is dotted with numerous lakes, including coastal lagoons, glacial lakes in the high mountains, and lakes of structural and karst origin. Bulgaria is also rich in mineral springs, with around 500 sources, some reaching high temperatures, indicating geothermal activity beneath the surface.
 Danube River basin, a major feature of Bulgaria's northern border
Danube River basin, a major feature of Bulgaria's northern border
Biodiversity and Conservation
Bulgaria’s geographic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia contributes to its rich biodiversity. The country is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, influenced by various biogeographic zones. During glacial periods, Bulgaria served as a refuge, preserving species that disappeared from other parts of Europe and even gaining new species from the north and the steppes of Asia.
Regions like Rila National Park serve as crucial habitats for local fauna, including various bird species, mammals, and fish. Recognizing the importance of its natural heritage, Bulgaria has implemented conservation measures, including protected areas and efforts to combat pollution. The Srebarna Nature Reserve, a vital wetland bird sanctuary on the Danube, is a UNESCO World Heritage site, highlighting Bulgaria’s commitment to preserving its unique natural environment within Europe.
Conclusion
So, where in Europe is Bulgaria? Bulgaria is situated in southeastern Europe, on the eastern Balkan Peninsula. Its location is not just a point on a map; it’s a defining aspect of its identity. Bulgaria’s geography has shaped its history as a bridge between cultures, influenced its diverse landscapes, and contributed to its rich natural heritage. From its Black Sea coast to its high mountain ranges and fertile plains, Bulgaria offers a microcosm of European geographical diversity within a relatively compact nation. Understanding Bulgaria’s location in Europe is key to appreciating its unique place in the continent’s tapestry.
