WiFi extenders, also known as range extenders or WiFi boosters, are invaluable tools for broadening your wireless network’s reach. They capture the existing WiFi signal from your router and rebroadcast it, effectively eliminating dead zones and ensuring a more consistent connection throughout your home or office. However, simply plugging in a WiFi extender isn’t enough to guarantee optimal performance. Where a WiFi extender is located significantly impacts its effectiveness. Proper placement is crucial to maximizing your extender’s ability to boost your WiFi signal and deliver the speeds you need. This guide will walk you through the key considerations for finding the ideal location for your WiFi extender, ensuring a stronger and more reliable wireless network.
Key Factors for WiFi Extender Placement
To ensure your WiFi extender performs at its best, several factors related to its location need careful consideration. These range from the distance to your main router to the physical environment and potential sources of interference. Understanding and addressing these factors will significantly enhance your WiFi experience.
Distance from the Main Router: Finding the Sweet Spot
The distance between your WiFi extender and your main router is a critical factor in its performance. Think of your extender as a relay race runner; it needs a strong baton (WiFi signal) to pass on effectively. If placed too far from the router, the extender will receive a weak signal, which it can only rebroadcast weakly, defeating its purpose.
For extenders with external antennas, positioning them approximately 25 to 40 feet away from the main router, assuming minimal obstacles and a good initial router signal (like 100Mbps on 5GHz or 50Mbps on 2.4GHz at that distance), is generally recommended. For extenders with internal antennas, a closer range of 20 to 35 feet is more suitable. This distance usually represents the sweet spot where the extender receives a strong enough signal to effectively amplify without being too close to cause signal interference.
However, if walls or other obstructions exist between the router and extender, closer placement might be necessary, or alternative strategies like those discussed later in this article should be considered.
Height Matters: Elevating Your Extender
Just like your main router benefits from being elevated, so does your WiFi extender. Placing your extender at a similar height to your main router, ideally around 4 feet high, can significantly improve signal reception and transmission. This height often corresponds to the typical placement of routers on desks or shelves, optimizing the line of sight and reducing ground-level obstructions.
Consider placing your extender on a bookcase, shelf, or another elevated surface rather than directly on the floor or tucked away in a corner. This simple adjustment can lead to a noticeably stronger and more stable WiFi signal throughout your extended coverage area.
Antenna Orientation: Go Vertical
The orientation of your extender’s antennas plays a crucial role in signal quality. For optimal performance, ensure that the antennas are positioned vertically, perpendicular to the ground. This vertical alignment allows the antennas to receive and transmit wireless signals most efficiently, maximizing data transfer rates and coverage.
Adjusting antenna direction is a simple yet often overlooked step that can significantly impact your WiFi extender’s effectiveness. Make sure to physically orient the antennas straight up for the best results.
Obstacle Avoidance: Clear the Path for WiFi
Obstacles are the enemy of WiFi signals. Certain materials can significantly impede or disrupt wireless signals, hindering your extender’s performance. When selecting a location for your extender, be mindful of objects that can either reflect or absorb WiFi signals.
Mirrors and large metal objects can reflect signals, potentially creating dead spots or signal distortion. More commonly, dense materials like walls, especially those made of concrete or brick, cabinets, and masonry supports, can absorb WiFi signals, dramatically weakening them. Ideally, a direct line of sight between your router and extender, and between the extender and your devices, is best.
Furthermore, be aware of electronic devices that emit radio-frequency interference. Common culprits include microwave ovens, cordless phones, refrigerators, and even baby monitors. These devices can generate strong interference that disrupts WiFi signals. Keeping your extender away from these sources of interference is essential for maintaining a clean and strong wireless connection.
Directional Placement: Facing the Router
The direction in which you place your extender can also influence its performance. Positioning the extender facing towards the main router as much as possible is generally recommended.
The front of the extender, where the antennas are typically located, should ideally be directed toward the main router. This directional placement allows the extender’s antennas to effectively receive the signal from the router and then broadcast it outwards to extend your network’s reach. Clients located behind the extender, in relation to the router, are also likely to experience improved speeds in this configuration.
Using a Power Strip for Flexibility
A practical tip for optimizing extender placement is to plug it into a power strip. Using a power strip offers flexibility in adjusting the extender’s position without being restricted by wall outlet locations.
With a power strip, you can easily experiment with different heights, antenna angles, directions, and distances, as previously discussed. This adjustability allows you to fine-tune the extender’s location to find the absolute best spot for optimal signal extension and coverage in your specific environment.
Considering AP Mode for Wired Connections
In situations where obstacles are unavoidable, or the distance between the router and desired coverage area is too extensive for a reliable wireless backhaul, consider utilizing your extender in Access Point (AP) mode.
In AP mode, instead of wirelessly extending the signal, you connect the extender to your main router via an Ethernet cable. This creates a wired backhaul, eliminating signal degradation due to distance or obstructions. You can then place the extender closer to the area requiring better WiFi, ensuring a strong and stable signal for devices in that location. Consult your extender’s manual or online resources, such as FAQ1401, for instructions on configuring AP mode.
Visualizing Optimal Placement
The images below illustrate recommended and incorrect placement scenarios for WiFi extenders, helping to visualize the principles discussed.
 Recommended placement of WiFi extender facing the router with minimal obstacles at desktop height
Recommended placement of WiFi extender facing the router with minimal obstacles at desktop height
 Correct vertical antenna orientation for optimal signal transmission using a power strip
Correct vertical antenna orientation for optimal signal transmission using a power strip
 Example of incorrect WiFi extender placement, likely obstructed or poorly positioned
Example of incorrect WiFi extender placement, likely obstructed or poorly positioned
Position Examples:
Main Router Only: Notice the significant signal degradation in a room blocked by a wall and distance, resulting in only 40Mbps download speed.
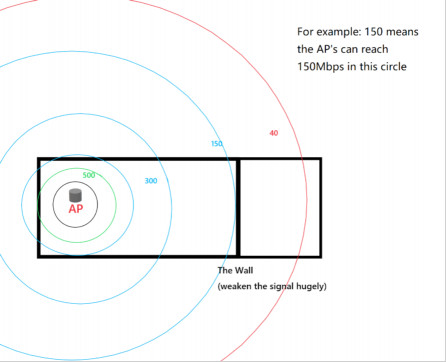 Reduced WiFi speed in a room due to wall and distance from main router alone
Reduced WiFi speed in a room due to wall and distance from main router alone
Router + RE: Observe the improved signal strength and speed (150Mbps) achieved in the same location by strategically placing a WiFi extender to relay the signal.
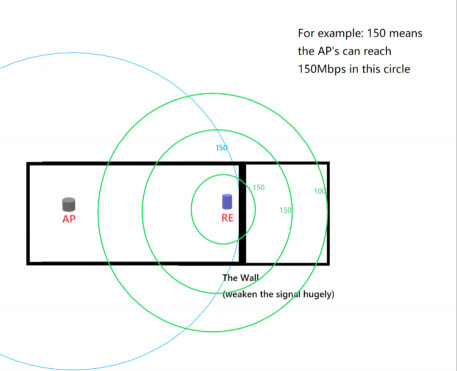 Improved WiFi speed with strategically placed range extender relaying signal
Improved WiFi speed with strategically placed range extender relaying signal
By carefully considering these placement factors and experimenting to find the ideal location, you can maximize the effectiveness of your WiFi extender and enjoy a robust and reliable wireless network throughout your space.
Related Articles:
What should I do if my range extender does not extend the Wi-Fi coverage?
