Ethiopia, officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a fascinating country located in the northeastern part of Africa, in a region famously known as the Horn of Africa. For those wondering Where Is Ethiopia exactly, it’s positioned in East Africa, sharing borders with several nations. Eritrea lies to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Notably, after Eritrea’s secession in 1993, Ethiopia became a landlocked country, adding a unique dimension to its geographical and political landscape.
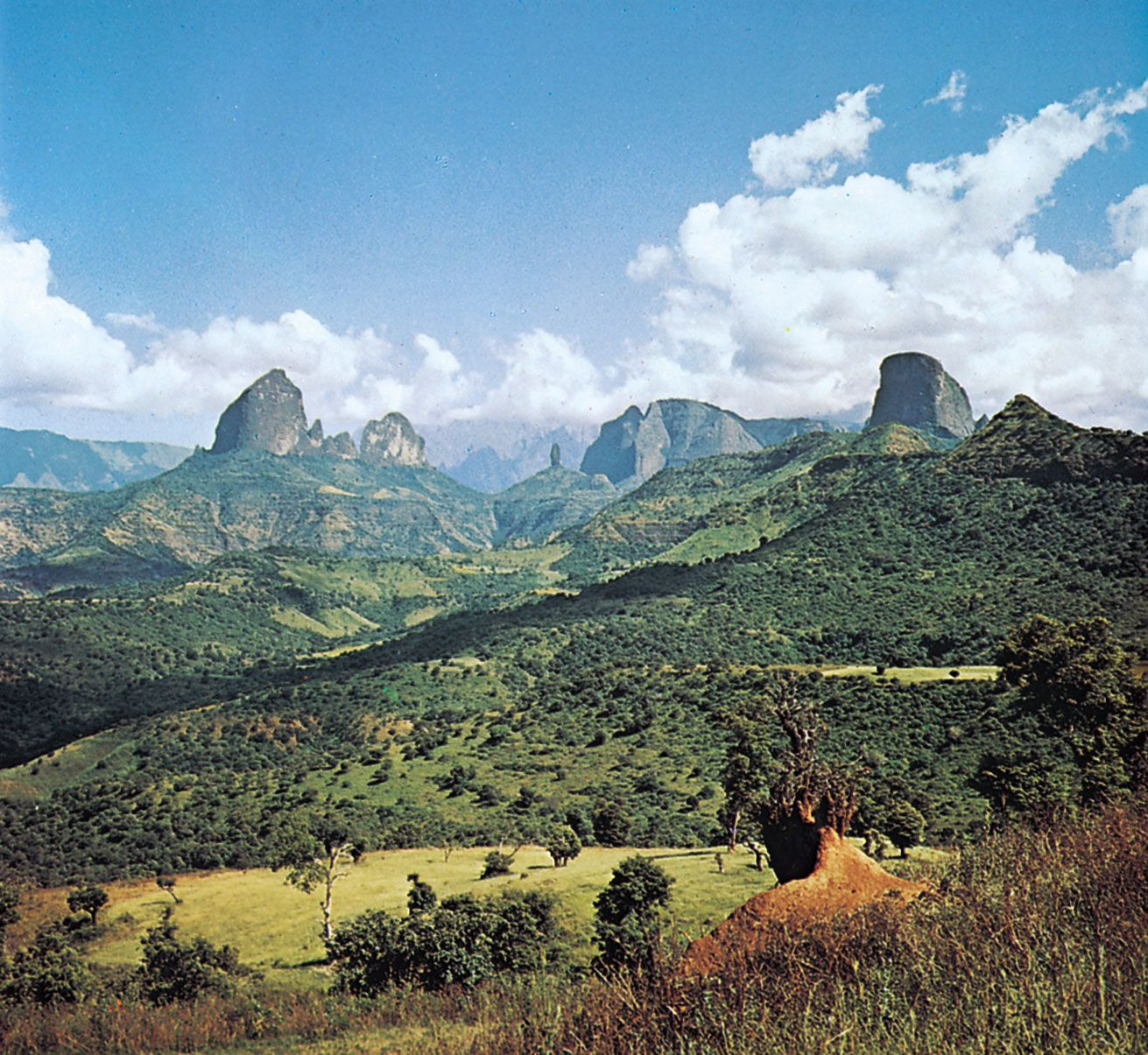 Simien Mountains National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Ethiopia, showcasing the dramatic landscapes of the Ethiopian Highlands.
Simien Mountains National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Ethiopia, showcasing the dramatic landscapes of the Ethiopian Highlands.
Geographically, Ethiopia is situated entirely within the tropical latitudes, giving it a diverse climate and landscape that ranges from arid lowlands to high mountainous plateaus. The Simien Mountains in the northwest offer breathtaking scenery and are home to unique wildlife. The country’s capital, Addis Ababa, meaning “New Flower” in Amharic, is located almost at the geographical heart of Ethiopia, serving as a major political and economic hub for the region and the seat of the African Union.
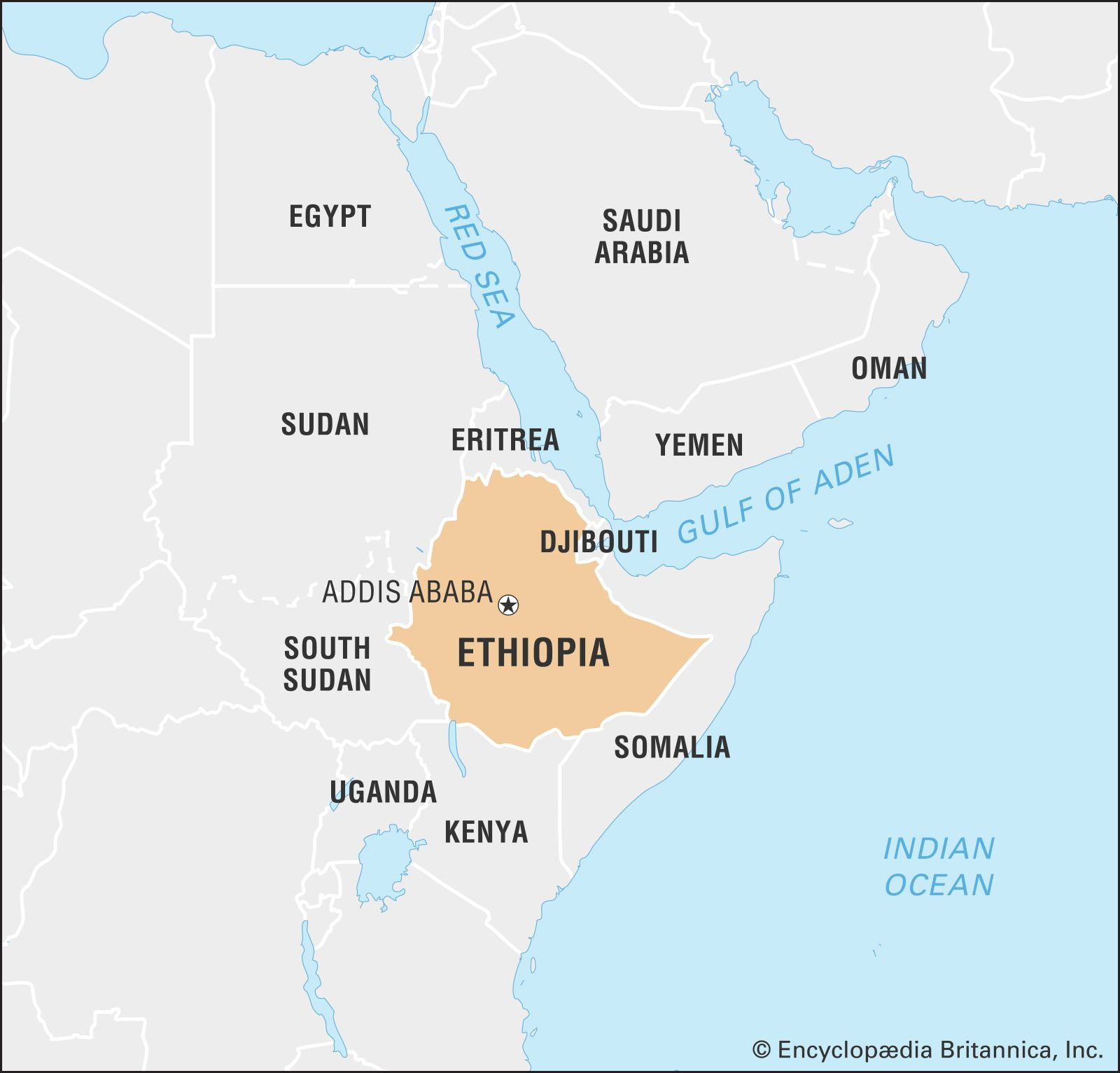 Location of Ethiopia in East Africa, highlighted on a world map, illustrating its position in the Horn of Africa region.
Location of Ethiopia in East Africa, highlighted on a world map, illustrating its position in the Horn of Africa region.
Ethiopia is not only geographically significant but also historically rich. It is considered one of the oldest countries in the world, with a history stretching back millennia. Ancient Aksum, located in northern Ethiopia, was a powerful kingdom and a major center of civilization. Ethiopia’s historical significance is further highlighted by its successful resistance against European colonization in the late 19th century, remaining independent during the Scramble for Africa, except for a brief Italian occupation from 1936-1941. This victory at the Battle of Adwa in 1896 became a symbol of African resilience and pride.
In modern times, Ethiopia continues to play a vital role in African and global affairs. It was among the founding members of the United Nations and a key advocate for Pan-African cooperation. The presence of the African Union headquarters and the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa in Addis Ababa underscores Ethiopia’s contemporary importance on the continent. With a large and growing population, Ethiopia stands as a major player in East Africa, bridging its ancient past with a dynamic present and future.
