Guam, a name that often surfaces in discussions about geography, travel, or international affairs, may leave some wondering: just where exactly is Guam? This island, while not as prominently featured on world maps as larger nations, holds a unique and important position in the Pacific Ocean and within the United States’ sphere of influence. Let’s delve into the geographical coordinates and significance of Guam.
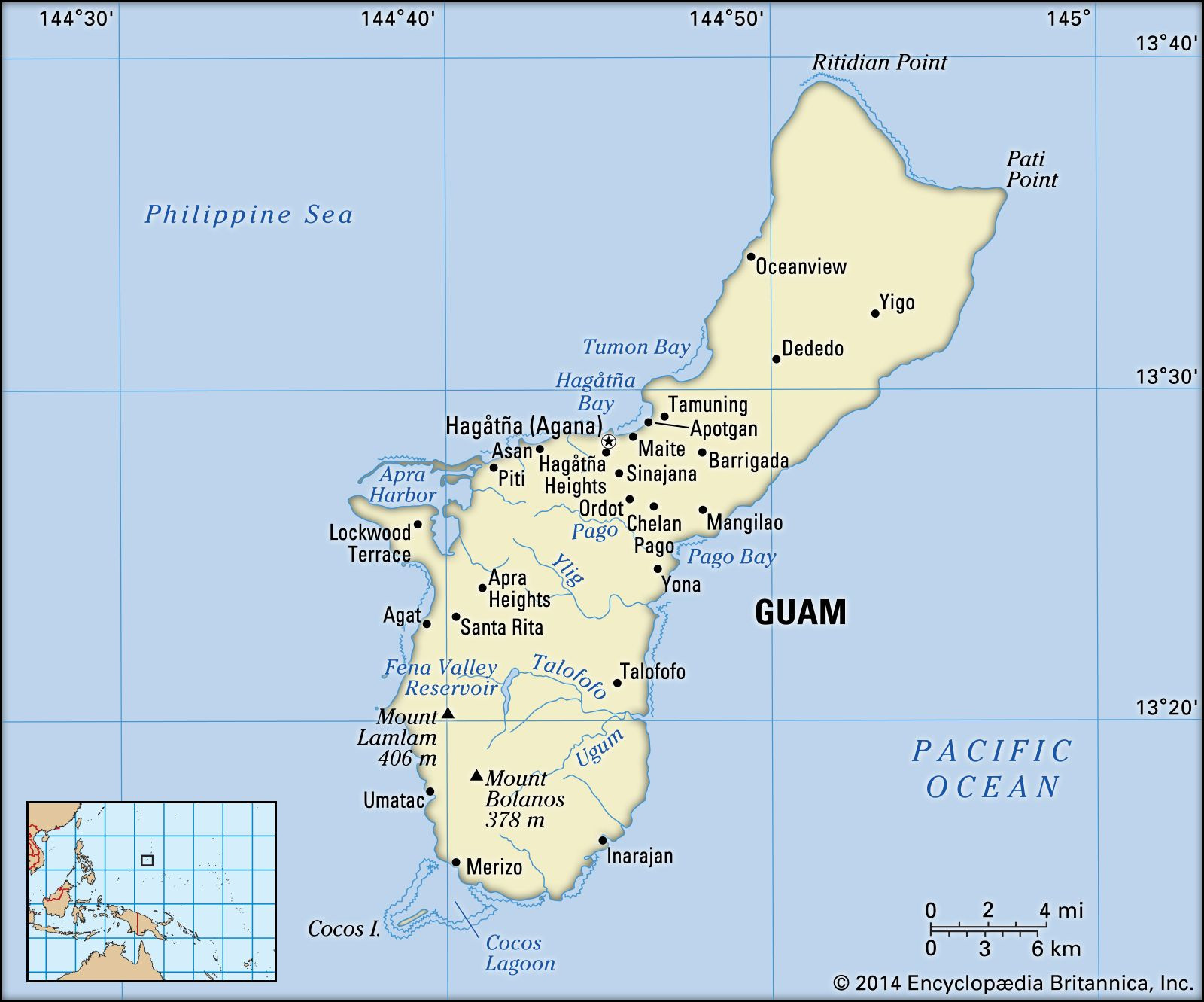
Guam is an island located in the North Pacific Ocean. To put it in perspective, it lies approximately 5,800 miles (9,300 km) west of San Francisco and about 1,600 miles (2,600 km) east of Manila, Philippines. Geographically, Guam is the largest, most populous, and southernmost island in the Mariana Islands archipelago. This places it in the westernmost reach of Micronesia, a region characterized by numerous small islands scattered across the vast Pacific.
Administratively, Guam is an unincorporated territory of the United States. This means that while it is under US sovereignty, it is not fully integrated as a state. The capital of Guam is Hagåtña (formerly known as Agana), and other significant settlements include Dededo, Machanao, and Apotgan.
To further pinpoint its location, Guam can be found at roughly 13.4443° N latitude and 144.7937° E longitude. This tropical location gifts Guam with a consistently warm climate, influenced by northeast trade winds and the north equatorial ocean current. Temperatures typically fluctuate between 70 and 90 °F (20 and 30 °C) throughout the year. The island experiences a wet season, usually from May or June to November, receiving an average annual rainfall of about 95 inches (2,400 mm).
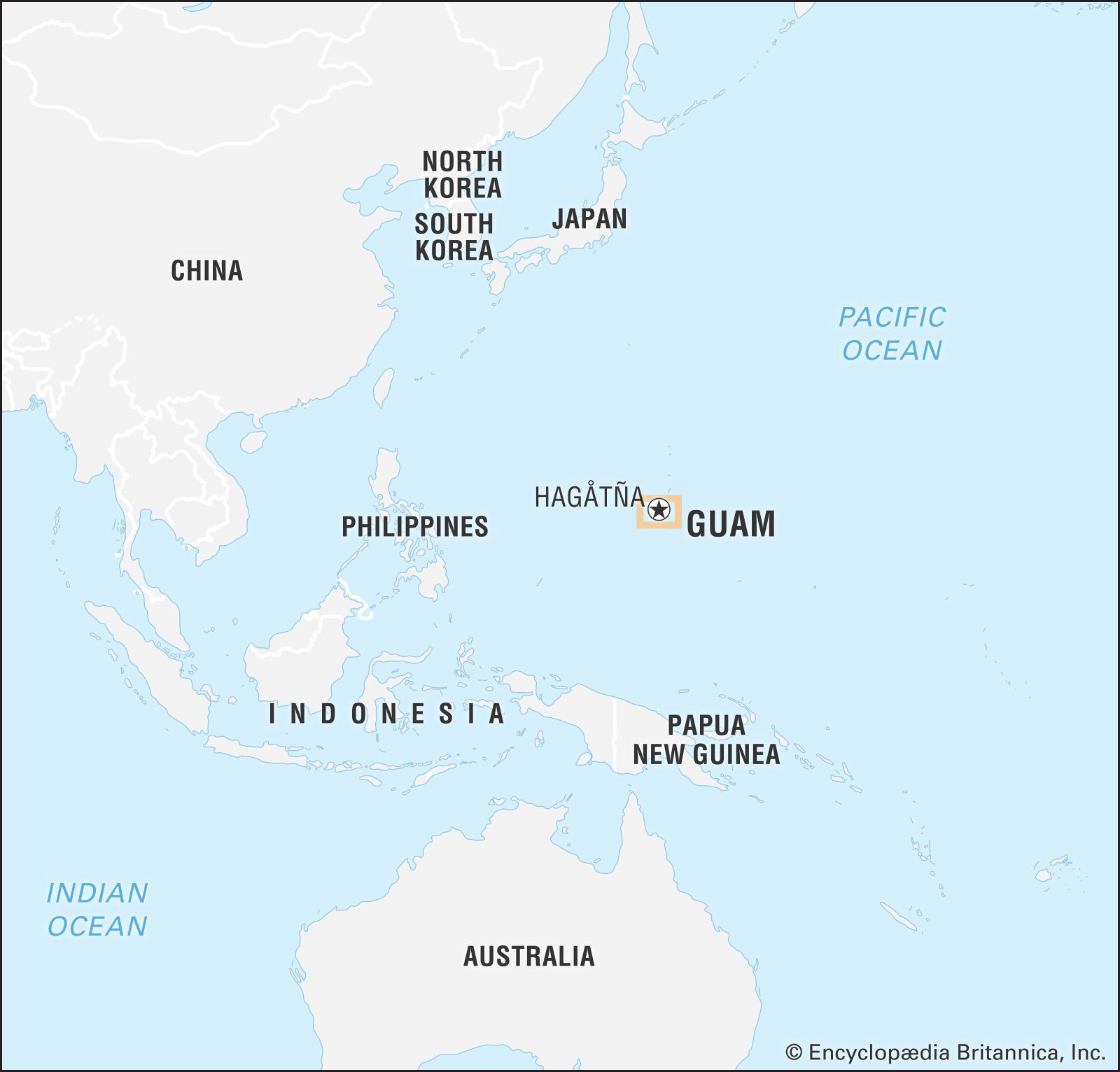 Guam Locator Map in World Data
Guam Locator Map in World Data
The landscape of Guam is geographically diverse. The northern part of the island is characterized by a relatively flat limestone plateau, averaging around 500 feet (150 metres) in elevation and covered in dense jungle vegetation. In contrast, the southern region is more mountainous, featuring volcanic hills that rise to over 1,000 feet (300 metres). Mount Lamlam, located in the southwest, is the highest point at 1,332 feet (406 metres). The terrain in the south supports primarily sword grass, with limestone slopes similar to the northern plateau found on the eastern and western sides of these hills.
Guam’s strategic location has made it a significant hub, particularly for the United States military. Its position in the Pacific Ocean makes it a crucial link between the US mainland and Asia. Andersen Air Force Base in northern Guam, along with numerous US Navy facilities scattered across the island, underscore its military importance. These installations have profoundly shaped Guam’s economy and demographics over the years.
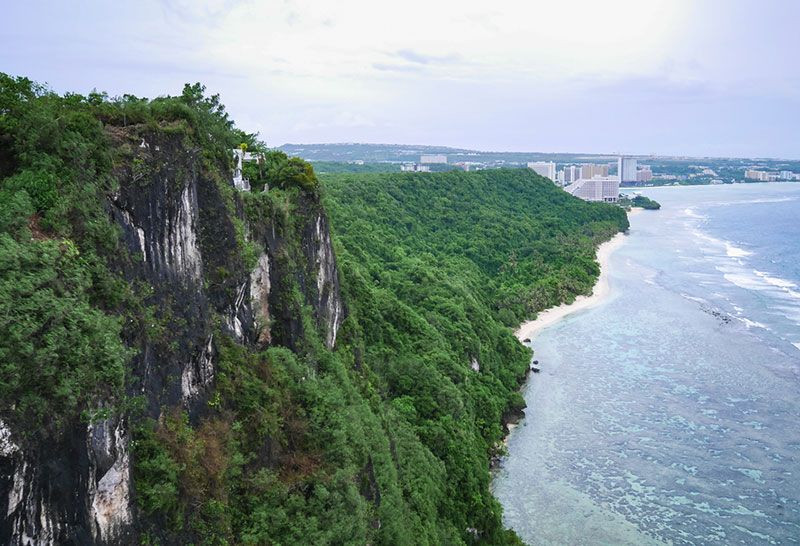 Tumon Bay Guam with Slopes of Two Lovers Leap
Tumon Bay Guam with Slopes of Two Lovers Leap
The native inhabitants of Guam are the Chamorro people, who have Malayo-Indonesian roots mixed with Spanish, Filipino, and other ancestries. They, along with other Micronesians, constitute about half of the island’s population. A significant portion of Guam’s residents are Asian, primarily Filipinos and Koreans, with a smaller European minority. English and Chamorro are the official languages, reflecting the island’s blended cultural heritage.
Economically, beyond its military significance, tourism is a major driver for Guam. The beautiful Tumon Bay area is lined with luxury hotels, attracting over a million visitors annually. Guam’s international airport facilitates connections with other Pacific islands, Asia, Hawaii, and the continental United States, further cementing its role as a Pacific crossroads.
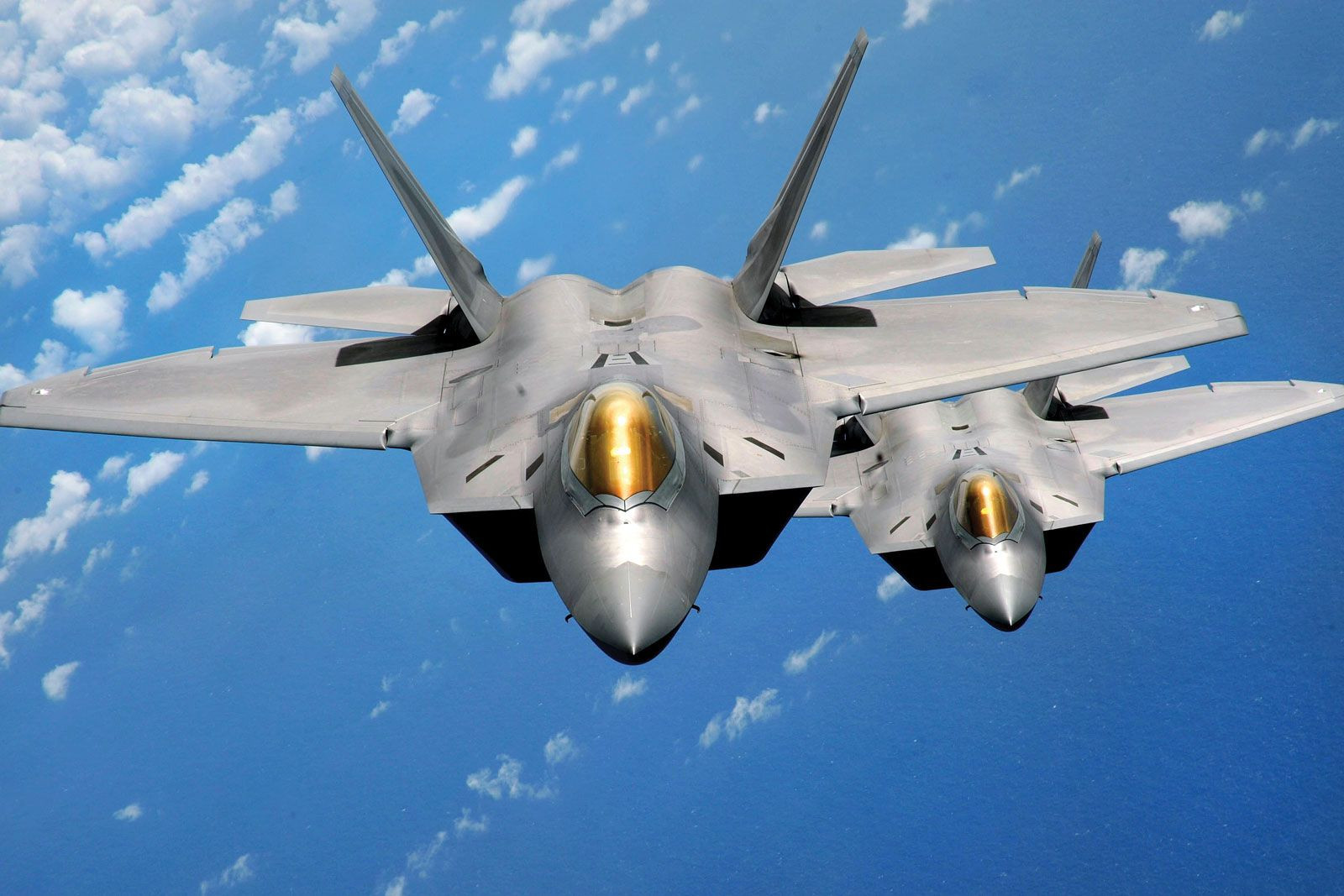 F-22 Raptors at Andersen Air Force Base Guam
F-22 Raptors at Andersen Air Force Base Guam
In conclusion, Guam is located in the western Pacific Ocean, part of the Mariana Islands and a US territory. Its geographical coordinates place it strategically between Asia and the US, contributing to its military and economic importance. Beyond its location, Guam offers a rich blend of cultures, a diverse landscape, and a significant role in the Pacific region. Understanding where Guam is situated is just the first step in appreciating its multifaceted identity and significance in the world.