Laos, officially known as the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, is a captivating nation nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia. Often referred to as a hidden gem, this landlocked country boasts a rich tapestry of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and historical significance. But Where Is Laos exactly? Let’s delve into the geographical details to pinpoint its location and understand its unique landscape.
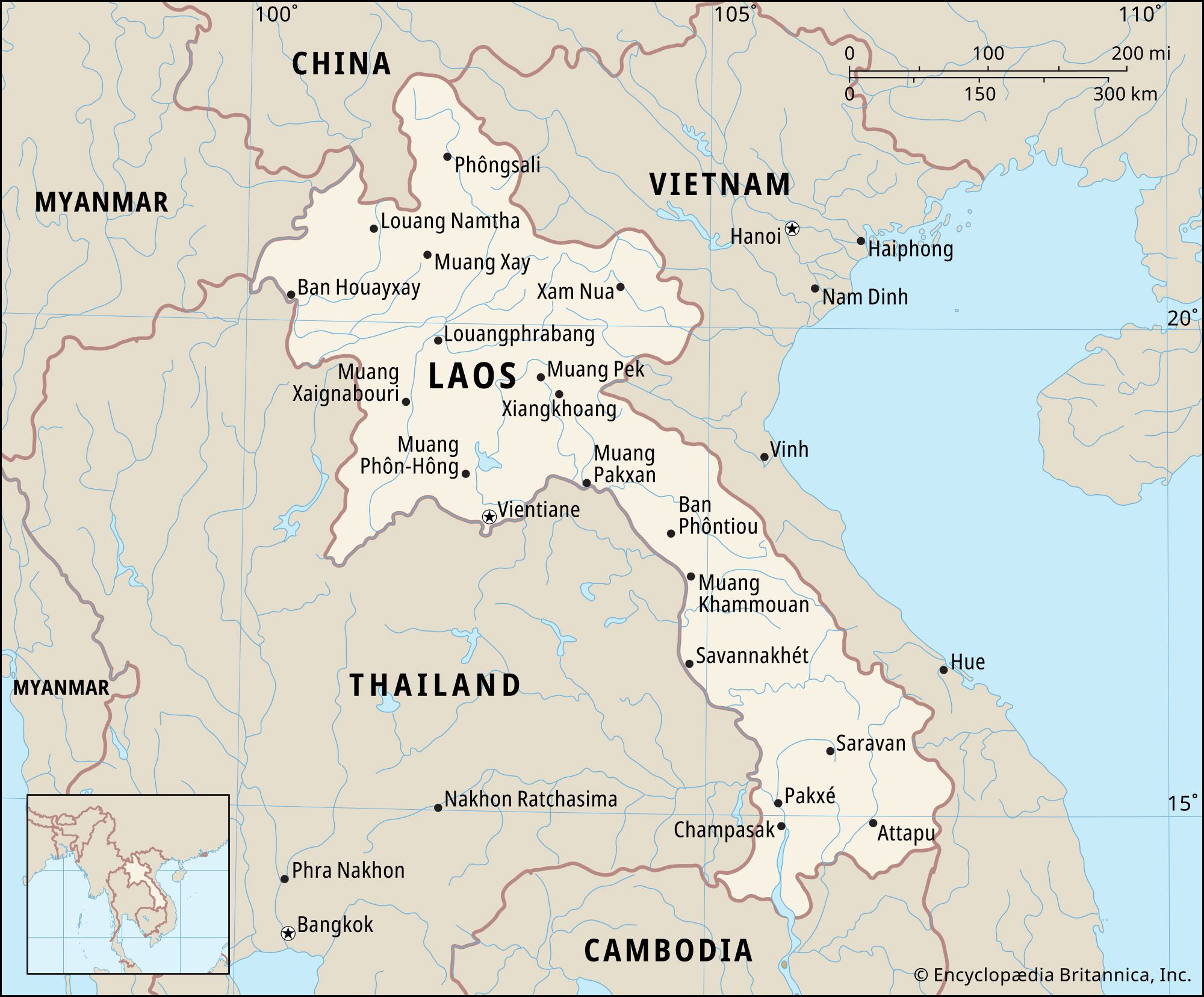 Laos map highlighting its location in Southeast Asia
Laos map highlighting its location in Southeast Asia
Laos occupies a strategic position in northeast-central mainland Southeast Asia. Imagine a country shaped like an irregular round portion in the north gracefully tapering into a peninsula-like region in the southeast. This elongated shape stretches approximately 650 miles (1,050 kilometers) from the northwest to the southeast. Vientiane (Viangchan), the vibrant capital city, is strategically situated on the banks of the majestic Mekong River, in the northern part of the country.
Geographic Location and Borders of Laos
To answer definitively “where is Laos”, we need to look at its neighboring countries. Laos is uniquely landlocked, bordered by five nations, each contributing to its diverse cultural and geographical landscape.
Bordering Countries
Laos shares its borders with:
- China to the north: This border connects Laos to the vast landscapes of East Asia.
- Vietnam to the northeast and east: Sharing a significant eastern border, Vietnam has been a long-term neighbor and influencer.
- Cambodia to the south: Laos’s southern border links it to the historical and cultural richness of Cambodia.
- Thailand to the west: The western border, largely defined by the Mekong River, connects Laos to Thailand, a major Southeast Asian hub.
- Myanmar (Burma) to the northwest: In the northwest, Laos meets Myanmar, further contributing to its diverse regional context.
This central location in Southeast Asia has positioned Laos as a crossroads of cultures and trade routes throughout history.
Mekong River’s Role
The Mekong River is not just a geographical feature; it’s the lifeline of Laos. Flowing along and through western Laos, it dramatically shapes the country’s geography and serves as a natural boundary with Myanmar and a significant portion of the border with Thailand. While the Mekong’s course is constricted by dramatic gorges in northern Laos, as it approaches Vientiane, the valley broadens, creating fertile floodplains. These plains, while vital for agriculture, are also prone to flooding, as famously witnessed in 1966.
Topography and Landscape
The landscape of Laos is remarkably diverse, moving from towering mountains to fertile plateaus and lowland plains. This varied topography is a defining characteristic when considering “where is Laos” geographically.
Mountainous Terrain
Mountains dominate the Laotian landscape, particularly in the north. These forest-covered mountains, part of the Annamese Cordillera (Chaîne Annamitique), create a natural barrier and have historically made travel challenging. Mount Bia, the highest peak, reaches an elevation of 9,245 feet (2,818 meters) above sea level. Secondary mountain ranges branch out, adding to the rugged terrain.
Plateaus and Plains
Amidst the mountains, plateaus and plains offer contrasting landscapes. The Xiangkhoang Plateau in north-central Laos is home to the intriguing Plain of Jars (Thông Haihin). Despite its name, it’s more of a rolling grassland than a flat plain, serving as a crucial communication hub. In central Laos, the karst landscapes of Bolikhamxay and Khammouan provinces feature striking caverns and eroded limestone pinnacles. Southern Laos is characterized by the Bolovens Plateau, elevated at about 3,600 feet (1,100 meters), known for its open woodland and fertile soils. The only extensive lowlands are found along the eastern banks of the Mekong River, providing crucial agricultural land.
Climate and Environment
Understanding the climate and environment further contextualizes “where is Laos” within Southeast Asia.
Tropical Monsoon Climate
Laos experiences a typical tropical monsoon climate, characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The southwest monsoon brings the rainy season from May to October, depositing substantial rainfall, averaging 50 to 90 inches (1,300 to 2,300 mm), and reaching up to 160 inches (4,100 mm) on the Bolovens Plateau. The northeast monsoon dominates the dry season, from November to April. Temperatures fluctuate throughout the year, with cooler months from December to February averaging 60 to 70 °F (16 to 21 °C) and hotter temperatures exceeding 90 °F (32 °C) in March and April before the rains begin. The average temperature during the wet season is around 80 °F (27 °C).
Biodiversity
This climate supports diverse ecosystems. Northern Laos is covered in tropical rainforests with broad-leaved evergreens, while southern Laos features monsoon forests of mixed evergreens and deciduous trees. Monsoon forest areas are characterized by tall tranh grass and secondary growth forests rich in bamboo, scrub, and wild banana. Laos is also a haven for orchids and palms. The rich flora supports a wealth of fauna, including a wide array of mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and birds. While Laos boasts incredible biodiversity, including elephants, tigers, and various primates, many species are endangered, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.
Cultural and Historical Context
Beyond its physical location, “where is Laos” also encompasses its cultural and historical placement. Influenced by neighboring Khmer, Siamese, and Myanmar kingdoms, Laos has absorbed elements of Indian culture, particularly Buddhism, which is practiced by the majority of the population. French colonization in the 19th and 20th centuries added a European layer to its cultural identity. Emerging as a communist country in 1975 after periods of war and upheaval, Laos is now focusing on economic reforms and tourism, gradually integrating more into the global landscape.
Conclusion
So, to answer the question “where is Laos?”: Laos is a landlocked nation located in the heart of Southeast Asia, bordered by China, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and Myanmar. Its geography is defined by mountainous terrain, plateaus, and the life-giving Mekong River. Understanding its location reveals not just its physical coordinates but also its crucial position in regional dynamics, biodiversity, and cultural exchange. Exploring where Laos is is the first step to appreciating the multifaceted beauty and significance of this Southeast Asian country.
