Romania, a country rich in history and culture, is situated in southeastern Europe. Its capital city is Bucharest, a vibrant hub reflecting the nation’s dynamic character. Understanding Romania’s location provides a crucial backdrop to appreciating its unique blend of geographical features, historical influences, and modern developments.
Discovering Romania’s Geographical Position
Romania is strategically positioned in Southeastern Europe, bordering several countries that have shaped its history and continue to influence its regional role. To its north and east lies Ukraine, while Moldova shares its eastern border. Bulgaria marks its southern boundary, and Serbia is located to the southwest. Hungary completes the circle to the northwest. This location has placed Romania at the crossroads of various empires and cultural exchanges throughout history.
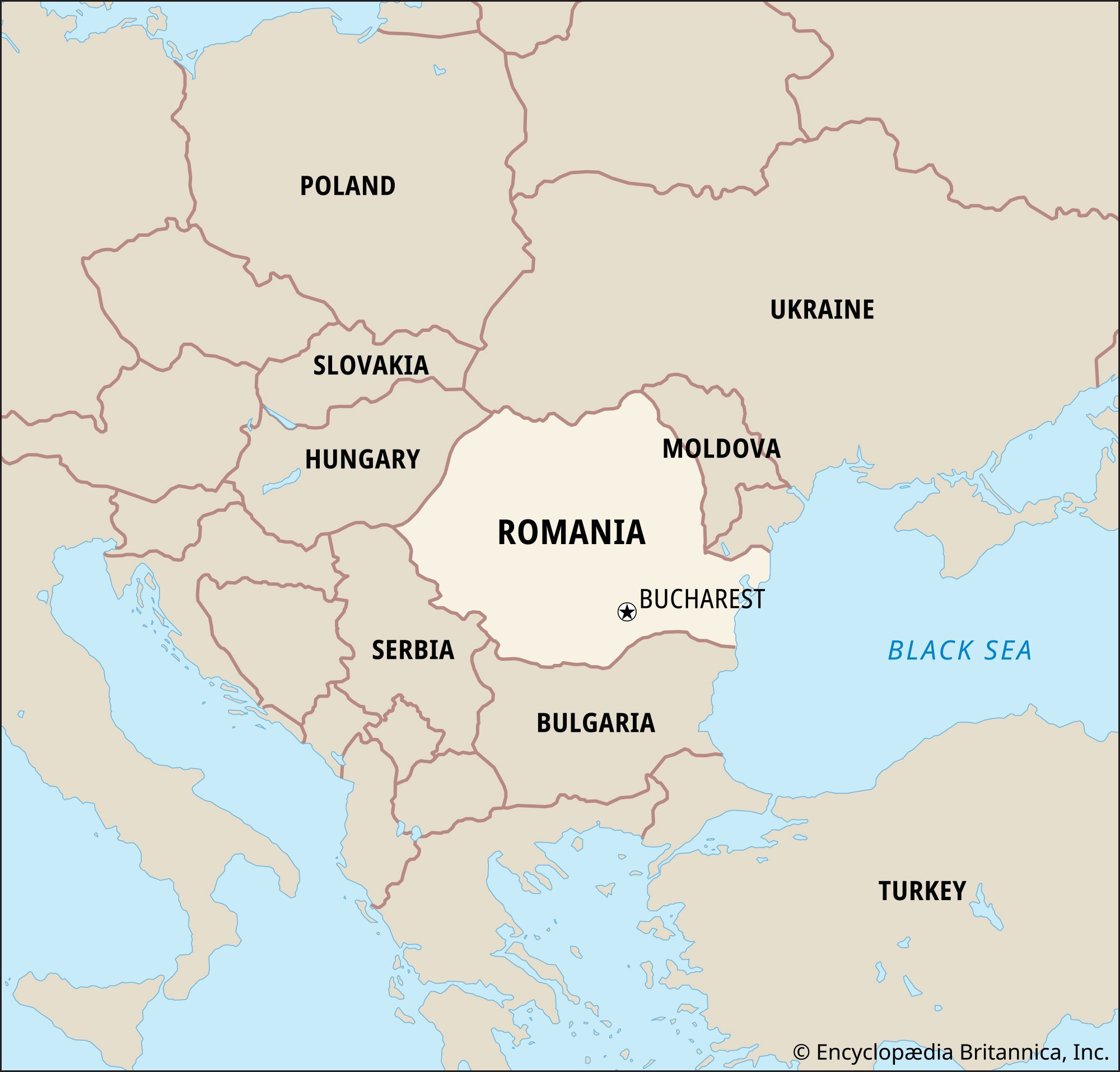 Location map of Romania in Europe
Location map of Romania in Europe
Geographically, Romania boasts a diverse landscape. Approximately one-third of the country is mountainous, dominated by the Carpathian range, offering stunning scenery and natural resources. Another third is covered by forests, contributing to its rich biodiversity and timber industry. The remaining terrain consists of hills and plains, providing fertile land for agriculture. Romania also has a coastline along the Black Sea, offering access to important ports and resort areas. The climate is temperate, with four distinct seasons, enhancing its agricultural potential and natural beauty.
A Brief Historical Journey of Romania
Romania’s history is marked by significant periods of influence and transformation. In 1944, towards the end of World War II, Romania came under Soviet occupation, and by 1948, it became a satellite state of the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.). This communist era lasted until 1989, when the regime of Nicolae Ceaușescu was overthrown through a revolution. The year 1990 marked a new beginning with free elections, paving the way for democratic governance. Romania further integrated into Western structures by joining the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 2004 and becoming a member of the European Union (EU) in 2007, solidifying its place in modern Europe.
Key Aspects of Romania: People, Culture, and Resources
The Romanian identity is deeply rooted in its Roman heritage. Romanians consider themselves descendants of the ancient Romans and the Dacians, who inhabited the region before Roman conquest. This blend is evident in the Romanian language, which has Latin roots, and the Eastern Orthodox faith, embraced by the majority of the population. Culturally, Romania is a vibrant mix of traditions, shaped by its unique history and geographical location.
Romania is also rich in natural resources. It possesses fertile land suitable for extensive agriculture, and pastures that support livestock farming. Its forests are a source of both hardwood and softwood. The country also has petroleum reserves and various metals, including gold and silver, particularly in the Apuseni Mountains. Numerous rivers provide hydroelectric power, and the Black Sea coast is crucial for trade and tourism. These resources have historically played and continue to play a significant role in Romania’s economy and development.
 Flag of Romania
Flag of Romania
In summary, Romania is located in southeastern Europe, a region of historical and geographical significance. It’s a country with a diverse landscape, a rich past shaped by Roman, Ottoman, and Soviet influences, and a promising future as a member of the EU and NATO. Its cultural heritage and natural resources contribute to its unique identity and its role in the European landscape.