The COVID-19 pandemic spurred an unprecedented global health crisis, prompting a frantic search for effective treatments and preventative measures. Among the repurposed drugs that gained significant attention were hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin. While initial, often flawed, studies suggested potential benefits, these medications quickly became subjects of intense debate and misinformation. This analysis delves into the purchasing trends of ivermectin in the United States and Canada, exploring the factors that fueled a surge in demand, despite regulatory bodies advising against its use for COVID-19, and ultimately shedding light on the crucial role of accurate information in public health crises. Understanding where and why people sought to purchase ivermectin during this period offers valuable lessons for navigating future health emergencies and combating the spread of medical misinformation.
The Ivermectin Phenomenon: A Look at Purchasing Trends
To understand the ivermectin purchasing landscape during the pandemic, a retrospective analysis of outpatient pharmacy purchases in the U.S. and Canada was conducted, spanning from February 2016 to December 2021. This period encompasses the pre-pandemic baseline, the peak of misinformation surrounding ivermectin, and the subsequent decline following scientific retractions and clarifications.
Initial In Vitro Studies and Early Purchasing Reactions
Early in the pandemic, in April 2020, a study by Caly et al. suggested that ivermectin could inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Around the same time, Patel et al. released a pre-print suggesting reduced mortality based on a multinational registry analysis. However, as depicted in Figure 2, these initial reports did not trigger an immediate surge in ivermectin purchases in either the U.S. or Canada. Statistical analysis confirmed no significant pulse change in purchasing rates following these publications (p = 0.41 in the U.S. and p = 0.16 in Canada), indicating that the in vitro findings and preliminary registry data alone were not sufficient to significantly alter purchasing behavior at this stage.
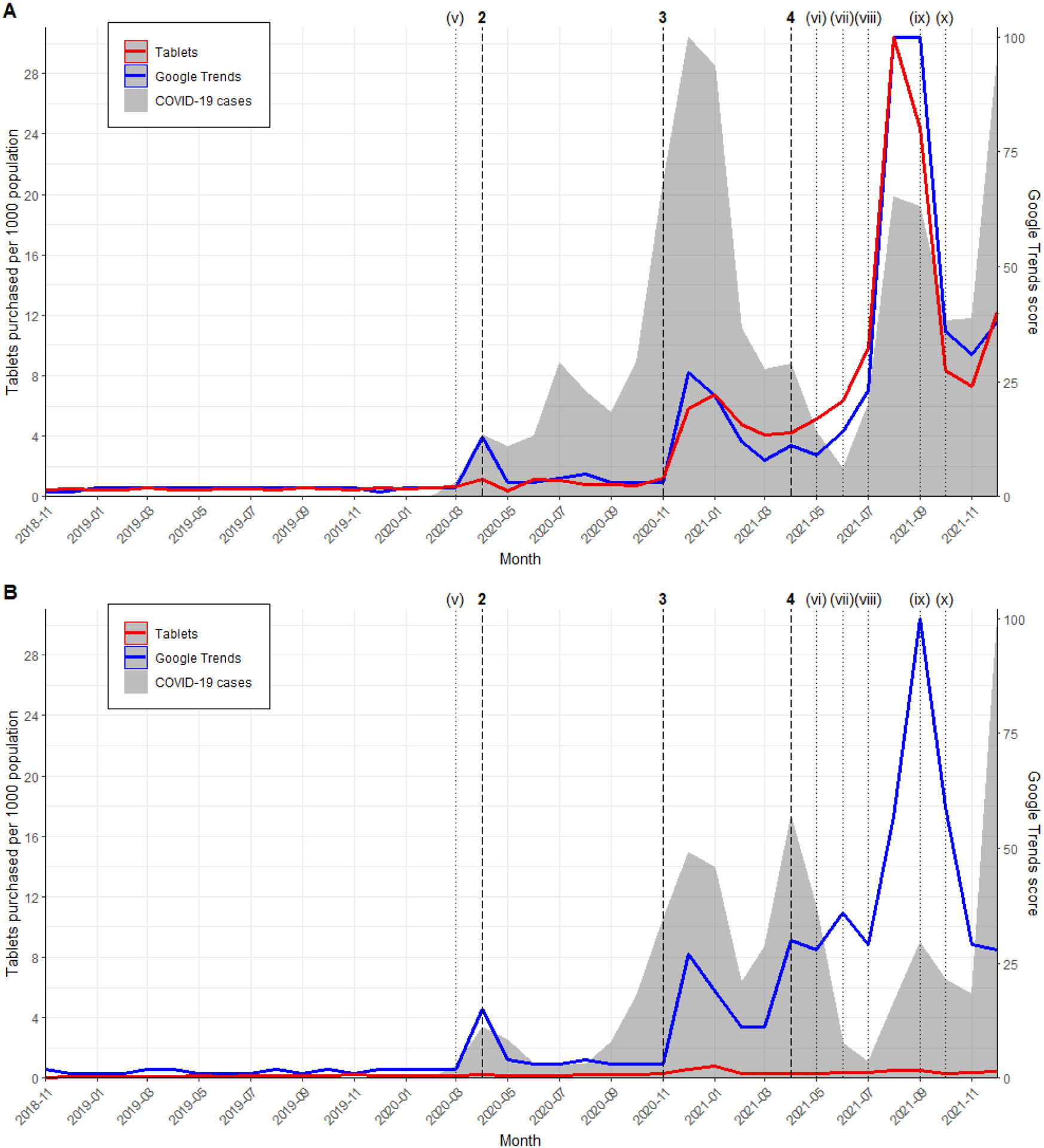 Figure 2. Population-adjusted ivermectin purchasing rates, Google Trends, and COVID-19 case rates in (A) the United States and (B) Canada.
Figure 2. Population-adjusted ivermectin purchasing rates, Google Trends, and COVID-19 case rates in (A) the United States and (B) Canada.
The Influence of Discredited Studies and Social Media
A more pronounced shift in ivermectin purchasing occurred towards the end of 2020 and into early 2021. In November 2020, Elgazzar et al. released a pre-print claiming significant mortality reduction with ivermectin treatment. Although later retracted due to data concerns, this study, particularly its subsequent versions, coincided with a notable increase in Google search interest for ivermectin. This period, from December 2020 to January 2021, witnessed a significant pulse increase in ivermectin purchasing in both the U.S. (p = 0.0006) and Canada (p = 0.02). This suggests that the Elgazzar pre-print, despite its eventual retraction, played a role in driving initial purchasing increases, possibly amplified by social media discussions and online information sharing.
Meta-Analyses and Peak Demand
The most substantial surge in ivermectin purchasing, particularly in the United States, followed the publication of several meta-analyses in 2021. Kory et al.’s meta-analysis in April 2021, followed by Bryant et al. and Hill et al.’s meta-analyses, all suggested significant benefits of ivermectin for COVID-19. Crucially, these meta-analyses incorporated data from the flawed Elgazzar study and other trials with questionable methodologies. As illustrated in Figure 2A, the U.S. experienced a dramatic ramp-up in ivermectin purchases starting in April 2021, peaking in August 2021 at 30 tablets per 1000 population. In contrast, while Canada also saw an increase, the peak was much lower and earlier, reaching 0.8 tablets per 1000 population in January 2021 (Figure 2B). This disparity highlights a significant divergence in purchasing behavior between the two countries, potentially influenced by differing public health messaging and regulatory actions.
Decline After Debunking and Retractions
The peak in ivermectin purchasing was ultimately unsustainable. Lawrence et al.’s publication in September 2021 raised serious concerns about the quality and potential fraud in key ivermectin studies, including Elgazzar and Niaee et al. This was followed by retractions of the Elgazzar and Samaha et al. studies. Concurrently, a Cochrane systematic review by Popp et al. in July 2021 did not support ivermectin’s use outside of clinical trials. Following these critical analyses and retractions, ivermectin purchasing began to decline, reflecting a shift in public perception and potentially a greater awareness of the lack of credible evidence supporting its use against COVID-19.
Factors Driving Ivermectin Purchases: Misinformation and Public Perception
The purchasing trends clearly indicate that scientific publications and public discourse significantly influenced the demand for ivermectin. However, the nature of these publications and the surrounding information ecosystem played a crucial role in shaping public perception and driving purchasing decisions.
The Role of Scientific Misinformation and Retracted Studies
The initial surge in ivermectin interest was significantly fueled by pre-prints and publications that were later retracted or discredited. The Elgazzar et al. pre-print, despite its flaws, coincided with an initial purchasing increase. The subsequent meta-analyses, which aggregated data including these flawed studies, further amplified the perception of ivermectin’s efficacy and contributed to the peak purchasing period. This highlights a critical issue: the rapid dissemination of preliminary or non-peer-reviewed research, especially during a crisis, can have a significant impact on public behavior, even when the scientific basis is weak or ultimately proven false.
Social Media and Public Discourse Influence
Beyond scientific publications, social media and public discourse played a powerful role in shaping ivermectin’s narrative. While not directly measured in this study, Google Trends data serves as a proxy for public interest and online discussions. The peaks in Google Trends for ivermectin closely mirrored the purchasing trends, suggesting that online information seeking and sharing were important drivers of demand. Anecdotal evidence and reports from the time also indicate that social media platforms became echo chambers for pro-ivermectin narratives, often amplifying weak or misrepresented scientific claims and contributing to a widespread belief in its efficacy against COVID-19.
US vs. Canada: Contrasting Regulatory and Government Responses
The marked difference in peak ivermectin purchasing rates between the U.S. and Canada points to the influence of regulatory and governmental responses. While both countries’ national health bodies advised against ivermectin use for COVID-19, the Canadian response appears to have been more impactful in curbing widespread purchasing. Health Canada actively cautioned against ivermectin use and took action against misleading advertising. Furthermore, Canadian medical licensing bodies took a strong stance, with some instances of license restrictions for inappropriate ivermectin prescribing. In contrast, the U.S. response was more varied, with some state legislatures even attempting to protect physicians prescribing ivermectin for COVID-19. This difference in regulatory environments and public health messaging likely contributed to the significantly higher and more sustained purchasing rates observed in the U.S.
Implications of Increased Ivermectin Purchasing
The surge in ivermectin purchasing, driven by misinformation and misinterpretations of scientific data, had several negative implications, extending beyond individual health choices to broader public health concerns.
Drug Shortages for Legitimate Uses
Increased demand for ivermectin, driven by off-label use for COVID-19, led to supply chain strains and shortages. This had a direct impact on individuals who rely on ivermectin for its approved uses, such as treating parasitic infections. Reduced availability of ivermectin for legitimate medical needs poses a significant health risk to vulnerable populations who depend on this medication.
Safety Concerns and Poisoning Cases
The widespread use of ivermectin outside of medical supervision and for unapproved indications raised serious safety concerns. Reports of ivermectin poisoning increased during the pandemic, as individuals, sometimes relying on veterinary formulations, self-medicated with the drug. These adverse events underscored the dangers of using medications without proper medical guidance and highlighted the potential for harm when public health information is distorted or misrepresented.
Substitution of Standard Care and Vaccination
Perhaps the most concerning implication is the potential for ivermectin use to substitute for evidence-based preventive measures and treatments for COVID-19. Individuals who believed in ivermectin’s efficacy might have been less likely to get vaccinated or seek timely medical care when infected with COVID-19. This substitution effect could have contributed to poorer health outcomes and prolonged the pandemic, as effective public health strategies were undermined by misinformation and the allure of unproven remedies.
Lessons Learned and the Importance of Accurate Information
The ivermectin purchasing episode during the COVID-19 pandemic offers crucial lessons for navigating future public health crises and combating medical misinformation.
Need for Scientific Integrity and Rigorous Research
The rapid dissemination of flawed or preliminary research had a tangible and negative impact on public behavior. This underscores the paramount importance of scientific integrity, rigorous peer review, and cautious communication of research findings, especially during public health emergencies. Efforts to enhance data transparency, improve peer-review processes, and ensure robust methodologies are critical to maintaining public trust in science and preventing the spread of misinformation.
Responsible Media Reporting and Peer Review
Media outlets play a vital role in shaping public understanding of scientific issues. Responsible reporting requires prudence when covering pre-prints and non-peer-reviewed studies, emphasizing the uncertainty inherent in preliminary findings. Highlighting the peer-review process and the importance of evaluating evidence critically can help the public distinguish between robust scientific findings and preliminary or flawed research.
Public Health Messaging and Evidence-Based Decisions
Clear, consistent, and evidence-based public health messaging is essential for guiding public behavior during health crises. The contrasting experiences of the U.S. and Canada with ivermectin purchasing suggest that proactive and decisive communication from regulatory bodies and healthcare organizations can effectively mitigate the impact of misinformation. Emphasizing evidence-based decision-making and promoting critical evaluation of health information are crucial components of effective public health strategies.
Conclusion
The surge in ivermectin purchases during the COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark reminder of the potent influence of misinformation and the critical importance of evidence-based decision-making in public health. While initial hopes for repurposed drugs were understandable, the ivermectin story highlights how quickly weak or flawed scientific claims, amplified by social media and public discourse, can lead to widespread adoption of unproven remedies. The differences observed between the U.S. and Canada underscore the impact of regulatory environments and public health messaging in shaping public behavior. Moving forward, strengthening scientific integrity, promoting responsible media reporting, and fostering critical health literacy are essential to ensure that public health decisions are guided by evidence, not misinformation, particularly in times of crisis. Individuals seeking health information should prioritize consulting healthcare professionals and reputable sources, exercising caution when encountering health claims online, and remembering that purchasing medications should always be guided by evidence-based medical advice.
References
(References would be included here as in the original article, maintaining their original numbering and links for accuracy, but are omitted here for brevity in this example.)
Associated Data
(Associated data section would be included if applicable, as per the original article.)
