Choking is a frightening experience for both the baby and the caregiver, but knowing how to save a choking baby can make all the difference. At Savewhere.net, we are committed to providing you with clear, actionable guidance to handle such emergencies, ensuring you can act swiftly and confidently. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to respond effectively, including critical first aid techniques and preventive measures to safeguard your little one. Let’s delve into the life-saving information to keep your baby safe and sound with resources to handle infant choking hazards.
1. Understanding Infant Choking: Causes and Prevention
What are the common causes of choking in infants, and how can you prevent them?
Infant choking often occurs when a foreign object becomes lodged in their small airway. Common culprits include small toys, pieces of food, or even fluids. Prevention is key, and here’s how to reduce the risk:
- Keep Small Objects Away: Ensure toys and household items are too large for an infant to swallow.
- Supervise During Meals: Always watch your baby while they are eating.
- Cut Food Appropriately: Chop food into tiny, manageable pieces.
- Be Aware of Potential Hazards: Regularly inspect your home for potential choking hazards.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, hard, round foods like grapes, nuts, and hard candies are significant choking hazards for young children. A proactive approach can minimize these risks.
 Infant choking hazard
Infant choking hazard
2. Recognizing the Signs of Choking in Infants
How do you identify if an infant is choking?
Recognizing the signs of choking is crucial for a quick response. Here are key indicators to watch for:
- Inability to Cry or Cough: A choking infant may not be able to make any sound.
- Bluish Skin Color: Cyanosis, a bluish tint around the lips and face, indicates a lack of oxygen.
- Gagging or Wheezing: These sounds suggest the airway is partially blocked.
- Panicked or Distressed Look: The infant may appear frightened or agitated.
These signs require immediate action. Knowing them can save precious seconds in an emergency.
3. Immediate Steps: What to Do When an Infant Is Choking
What are the initial steps to take when you realize an infant is choking?
The first moments are critical. Follow these steps immediately:
- Call for Help: If you are not alone, have someone call 911 or your local emergency number.
- Assess the Situation: Quickly determine if the infant can cough forcefully. If not, intervention is needed.
- Prepare to Act: Position yourself to administer back blows and chest thrusts.
Acting swiftly and decisively can dislodge the obstruction and restore breathing.
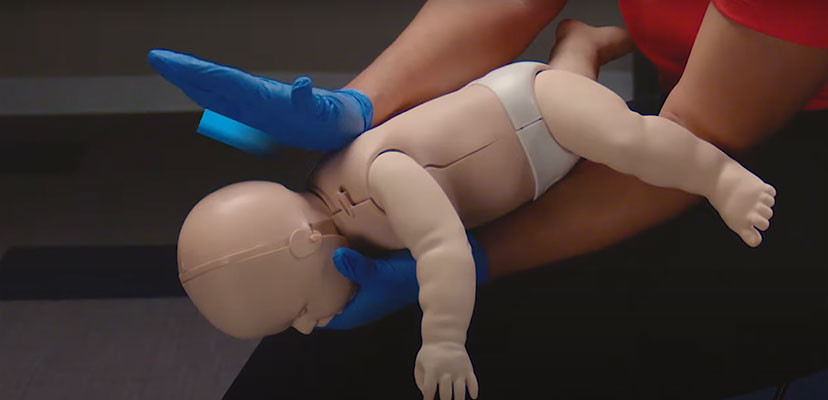
4. Administering Back Blows: A Step-by-Step Guide
How do you perform back blows on a choking infant?
Back blows are the first line of defense. Here’s how to do them correctly:
- Position the Infant: Hold the infant face down along your forearm, supporting their jaw and chest with your hand.
- Keep Head Lower: Ensure the infant’s head is lower than their body.
- Support Your Arm: Use your thigh for support.
- Deliver Back Blows: Use the heel of your other hand to deliver five firm back blows between the infant’s shoulder blades.
Each back blow should be forceful enough to dislodge the object but gentle enough to avoid injury.
According to the American Heart Association, back blows create pressure in the airway, which can help expel the object.
5. Performing Chest Thrusts: Technique and Precautions
How do you give chest thrusts to a choking infant?
If back blows are ineffective, proceed to chest thrusts:
- Turn the Infant: Turn the infant face up, supporting their head and neck.
- Position Your Fingers: Place two fingers in the center of the infant’s chest, just below the nipple line.
- Give Thrusts: Deliver five quick chest thrusts, compressing the chest about 1 ½ inches deep.
Chest thrusts mimic a cough and can help force the object out of the airway. Be cautious not to apply too much pressure, as this could cause injury.
6. Continuing the Cycle: Back Blows and Chest Thrusts
How long should you continue alternating between back blows and chest thrusts?
Continue alternating between five back blows and five chest thrusts until one of two things happens:
- The Object Is Dislodged: The infant can cough, cry, or breathe normally.
- The Infant Becomes Unresponsive: If the infant loses consciousness, begin CPR immediately.
Persistence is key in a choking emergency. Keep trying until help arrives or the airway is cleared.
7. Infant CPR: What to Do If the Baby Becomes Unresponsive
What steps should you take if a choking infant becomes unresponsive?
If the infant becomes unresponsive, CPR is essential:
- Call for Help: Ensure someone has called 911.
- Position the Infant: Place the infant on a firm, flat surface.
- Begin Chest Compressions: Use two fingers to deliver chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute, compressing about 1 ½ inches deep.
- Give Rescue Breaths: After 30 compressions, give two rescue breaths. Ensure the chest rises visibly with each breath.
- Continue CPR: Continue cycles of 30 compressions and two breaths until help arrives.
CPR can maintain circulation and oxygen delivery until emergency services take over.
According to the American Red Cross, CPR can double or triple an infant’s chance of survival after cardiac arrest.
8. Removing the Object: The Pinky Sweep Technique
When and how should you attempt to remove the foreign object from the infant’s mouth?
Only attempt to remove the object if you can see it:
- Open the Mouth: Gently open the infant’s mouth.
- Check for Object: Look for the foreign object in the back of the throat.
- Pinky Sweep: If visible, use your pinky finger to gently sweep the object out of the mouth.
Never perform a blind finger sweep, as this could push the object further down the airway.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid During an Infant Choking Emergency
What are some common errors people make during infant choking incidents, and how can you avoid them?
Avoiding these common mistakes can improve outcomes:
- Delaying Action: Hesitating can be fatal. Act quickly and confidently.
- Performing Blind Finger Sweeps: Never sweep blindly, as this can push the object further down.
- Using Abdominal Thrusts: These are not appropriate for infants and can cause injury.
- Panicking: Stay calm to perform the necessary steps effectively.
Preparation and knowledge are your best defenses against these mistakes.
 Back blows for choking infant
Back blows for choking infant
10. Prevention Tips: Creating a Safe Environment for Your Baby
What are some proactive steps you can take to create a safer environment for your infant and minimize choking risks?
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips:
- Safe Feeding Practices: Cut food into small, manageable pieces. Avoid giving infants hard, round foods.
- Toy Safety: Ensure toys are age-appropriate and do not have small, detachable parts.
- Regular Inspections: Routinely check your home for potential choking hazards.
- Supervision: Always supervise infants during meals and playtime.
By implementing these measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of choking incidents.
11. Advanced Training: Taking a First Aid and CPR Class
Why is it beneficial to take a certified first aid and CPR class, and what does it entail?
A certified class provides hands-on training and expertise:
- Hands-On Practice: Learn and practice techniques under the guidance of certified instructors.
- Up-to-Date Information: Receive the latest guidelines and best practices.
- Confidence Building: Gain the confidence to act effectively in an emergency.
- Certification: Obtain a certification that validates your knowledge and skills.
The American Red Cross and American Heart Association offer comprehensive courses that can equip you with life-saving skills.
12. The Role of Savewhere.net in Providing Safety Resources
How does Savewhere.net support parents and caregivers in accessing critical safety information and resources?
Savewhere.net is committed to providing accessible and reliable safety information:
- Informative Articles: Access articles, guides, and tips on infant safety and emergency response.
- Resource Directory: Find links to certified training courses and safety organizations.
- Community Support: Connect with other parents and caregivers to share experiences and advice.
Savewhere.net serves as a valuable resource for families seeking to enhance their knowledge and preparedness. Our address is 100 Peachtree St NW, Atlanta, GA 30303, United States. Phone: +1 (404) 656-2000.
13. Understanding the Heimlich Maneuver: Is It Safe for Infants?
Why is the Heimlich maneuver not recommended for infants, and what alternative techniques should be used instead?
The Heimlich maneuver, or abdominal thrusts, is not safe for infants because it can cause internal injuries. Instead, use back blows and chest thrusts:
- Back Blows: Gentle but firm strikes between the shoulder blades.
- Chest Thrusts: Compressions on the chest, similar to CPR, but with the intent to dislodge the object.
These techniques are specifically designed for the infant’s anatomy and are safer and more effective.
14. Addressing Parental Fears: Staying Calm in a Crisis
How can parents manage their fear and anxiety during a choking emergency to ensure they can provide effective assistance to their infant?
Staying calm is essential:
- Preparation: Knowing what to do can reduce anxiety.
- Deep Breathing: Take slow, deep breaths to calm your nerves.
- Focus: Concentrate on the steps you need to take.
- Remember Training: Trust in your training and knowledge.
A calm parent can provide more effective and life-saving assistance.
15. The Importance of Post-Choking Evaluation: When to Seek Medical Attention
When and why should you seek medical attention for an infant who has experienced a choking incident, even if they appear to have recovered fully?
Always seek medical attention after a choking incident, even if the infant seems fine:
- Possible Injuries: Choking can cause internal injuries that may not be immediately apparent.
- Residual Obstruction: A small piece of the object may still be lodged in the airway.
- Emotional Trauma: The incident can be traumatic for the infant and caregiver.
A medical professional can assess the infant and provide any necessary treatment or support.
16. Adapting Techniques for Infants with Special Needs
How should choking first aid techniques be adjusted for infants with special needs, such as those with physical disabilities or respiratory conditions?
Adapt techniques based on the infant’s specific needs:
- Physical Disabilities: Adjust positioning to accommodate physical limitations.
- Respiratory Conditions: Be extra cautious with rescue breaths and monitor for any respiratory distress.
- Consult Professionals: Seek guidance from healthcare providers familiar with the infant’s condition.
Customizing the approach can ensure the safest and most effective intervention.
17. The Legal Aspects of Providing First Aid: Understanding Good Samaritan Laws
What are Good Samaritan laws, and how do they protect individuals who provide first aid in emergency situations?
Good Samaritan laws offer legal protection:
- Protection from Liability: Protect individuals who provide assistance in good faith.
- Encourages Action: Encourages people to help without fear of legal repercussions.
- Varies by State: Laws vary by state, so familiarize yourself with local regulations.
These laws provide peace of mind, knowing you are protected when helping in an emergency.
18. Recognizing Different Types of Airway Obstructions: Partial vs. Complete
How do you differentiate between a partial and complete airway obstruction in an infant, and how does this influence your response?
Distinguish between partial and complete obstructions:
- Partial Obstruction: The infant can cough or make sounds. Encourage them to keep coughing.
- Complete Obstruction: The infant cannot cough, cry, or breathe. Immediate intervention is needed.
Knowing the difference ensures you take the appropriate action.
19. Debunking Myths About Infant Choking First Aid
What are some common misconceptions about infant choking first aid, and what is the accurate information?
Separate fact from fiction:
- Myth: Use abdominal thrusts on infants. Fact: Use back blows and chest thrusts.
- Myth: Perform blind finger sweeps. Fact: Only remove the object if you can see it.
- Myth: It’s okay to wait and see if the infant can dislodge the object on their own. Fact: Act immediately if the infant cannot cough or breathe.
Accurate information is crucial for effective intervention.
20. The Emotional Impact of Choking Incidents: Supporting Caregivers
How can caregivers cope with the emotional aftermath of a choking incident involving an infant, and what resources are available to support them?
Choking incidents can be emotionally distressing:
- Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a therapist.
- Join Support Groups: Connect with others who have experienced similar situations.
- Self-Care: Practice self-care activities to manage stress and anxiety.
- Professional Counseling: Consider professional counseling if needed.
Remember, it’s okay to seek help and support after a traumatic event.
21. The Importance of Continuous Learning: Staying Updated on First Aid Techniques
Why is it essential to stay updated on the latest first aid and CPR techniques, and how can you ensure your knowledge remains current?
Stay current with the latest techniques:
- Evolving Guidelines: First aid and CPR guidelines are updated regularly.
- Refresher Courses: Take refresher courses to reinforce your knowledge.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources from reputable organizations like the American Red Cross.
- Practice: Practice techniques regularly to maintain proficiency.
Continuous learning ensures you are prepared to provide the best possible care.
22. The Role of Technology: Using Apps and Devices for Choking Assistance
What technological tools, such as mobile apps and anti-choking devices, are available to assist in infant choking emergencies, and how effective are they?
Explore technological aids:
- First Aid Apps: Provide step-by-step instructions and emergency information.
- Anti-Choking Devices: Devices designed to help dislodge objects from the airway.
- Research Effectiveness: Research the effectiveness and reliability of any device before use.
While technology can be helpful, it should not replace proper training and knowledge.
23. Creating a Choking Emergency Plan: Preparing for the Unexpected
How can families create a comprehensive choking emergency plan to ensure everyone knows what to do in the event of an incident?
Develop a comprehensive plan:
- Identify Roles: Assign specific roles to family members.
- Emergency Numbers: Keep emergency numbers readily accessible.
- Practice Drills: Conduct regular practice drills.
- First Aid Kit: Ensure you have a well-stocked first aid kit.
A well-prepared plan can improve response times and outcomes.
24. Understanding the Differences Between Infant and Child Choking First Aid
What are the key differences between providing choking first aid to an infant versus a child, and why is it important to use the correct techniques for each age group?
Recognize the differences:
- Infant Techniques: Use back blows and chest thrusts.
- Child Techniques: Use abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver).
- Anatomical Differences: Infants have different anatomies than children, requiring different techniques.
Using the correct techniques is crucial for safety and effectiveness.
25. The Global Perspective: Infant Choking Prevention and Awareness Initiatives
What are some global initiatives aimed at preventing infant choking and raising awareness about choking hazards and first aid techniques?
Global initiatives are essential:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Campaigns to educate parents and caregivers about choking hazards.
- Training Programs: Programs to train individuals in infant choking first aid.
- Product Safety Standards: Regulations to ensure products are safe for infants and children.
Global efforts can help reduce the incidence of choking and improve outcomes worldwide.
26. The Importance of Community Involvement: Supporting Local Safety Programs
How can individuals get involved in supporting local safety programs and initiatives aimed at preventing infant choking and promoting first aid education in their communities?
Get involved in your community:
- Volunteer: Volunteer with local safety organizations.
- Donate: Donate to support safety programs.
- Advocate: Advocate for policies that promote infant safety.
- Educate: Educate others about choking prevention and first aid.
Community involvement can make a significant impact on infant safety.
27. The Impact of Choking on Long-Term Health: Monitoring for Complications
What are some potential long-term health complications that can arise from a choking incident in an infant, and how should these be monitored and managed?
Monitor for long-term complications:
- Respiratory Issues: Choking can lead to respiratory problems.
- Swallowing Difficulties: Some infants may experience difficulty swallowing.
- Emotional Trauma: Monitor for signs of emotional distress.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups are essential.
Early detection and management can minimize the impact of long-term complications.
28. The Role of Government Agencies: Regulations and Safety Standards
How do government agencies contribute to infant choking prevention through regulations and safety standards for products and food?
Government agencies play a critical role:
- Product Safety Regulations: Regulations to ensure products meet safety standards.
- Food Safety Standards: Standards for food preparation and packaging.
- Public Education Campaigns: Campaigns to educate the public about choking hazards.
Government oversight helps protect infants from potential choking hazards.
29. Addressing Cultural Differences: Adapting First Aid Techniques to Different Cultures
How can first aid techniques be adapted to accommodate cultural differences and beliefs to ensure they are culturally sensitive and effective in diverse communities?
Adapt techniques to cultural contexts:
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware of cultural beliefs and practices.
- Language Accessibility: Provide information in multiple languages.
- Community Input: Seek input from community leaders.
Cultural sensitivity can improve the effectiveness and acceptance of first aid interventions.
30. Staying Informed: Resources for Continuous Learning and Support
What are some reliable resources for continuous learning and support related to infant choking prevention and first aid, including websites, organizations, and support groups?
Utilize these resources:
- American Red Cross: Offers training courses and resources.
- American Heart Association: Provides guidelines and information on CPR.
- Safe Kids Worldwide: Focuses on preventing injuries to children.
- Local Hospitals and Clinics: Offer classes and support groups.
Staying informed and connected can help you provide the best possible care for your infant.
Savewhere.net is here to assist you on your journey to saving.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About Infant Choking
1. What are the most common foods that cause choking in infants?
Common culprits include grapes, nuts, hot dogs, and hard candies. Always cut food into small, manageable pieces.
2. Can I use an anti-choking device on an infant?
Consult with a healthcare provider before using any anti-choking device. Ensure you are properly trained in its use.
3. How often should I take a first aid and CPR class?
It’s recommended to renew your certification every two years to stay updated on the latest guidelines.
4. What should I do if I am alone when my infant is choking?
Call 911 immediately and then begin administering back blows and chest thrusts.
5. Is it safe to give water to a choking infant?
No, giving water can worsen the situation. Focus on back blows and chest thrusts.
6. How can I tell if my infant has a partial or complete airway obstruction?
A partial obstruction allows the infant to cough or make sounds. A complete obstruction prevents the infant from coughing, crying, or breathing.
7. What are the signs of a silent choking incident?
Signs include bluish skin, inability to cry or cough, and a panicked expression.
8. How deep should chest thrusts be on an infant?
Chest thrusts should be about 1 ½ inches deep.
9. Should I check for a pulse during a choking emergency?
Focus on clearing the airway first. If the infant becomes unresponsive, then check for a pulse and begin CPR.
10. What is the best way to prevent choking when introducing solid foods?
Introduce one food at a time, cut food into small pieces, and supervise the infant during meals.
By understanding these key aspects of infant choking and how to respond effectively, you can protect your baby and provide the necessary care in an emergency. Remember to stay calm, act quickly, and seek professional help when needed.
Visit savewhere.net for more valuable tips and resources to keep your family safe.

