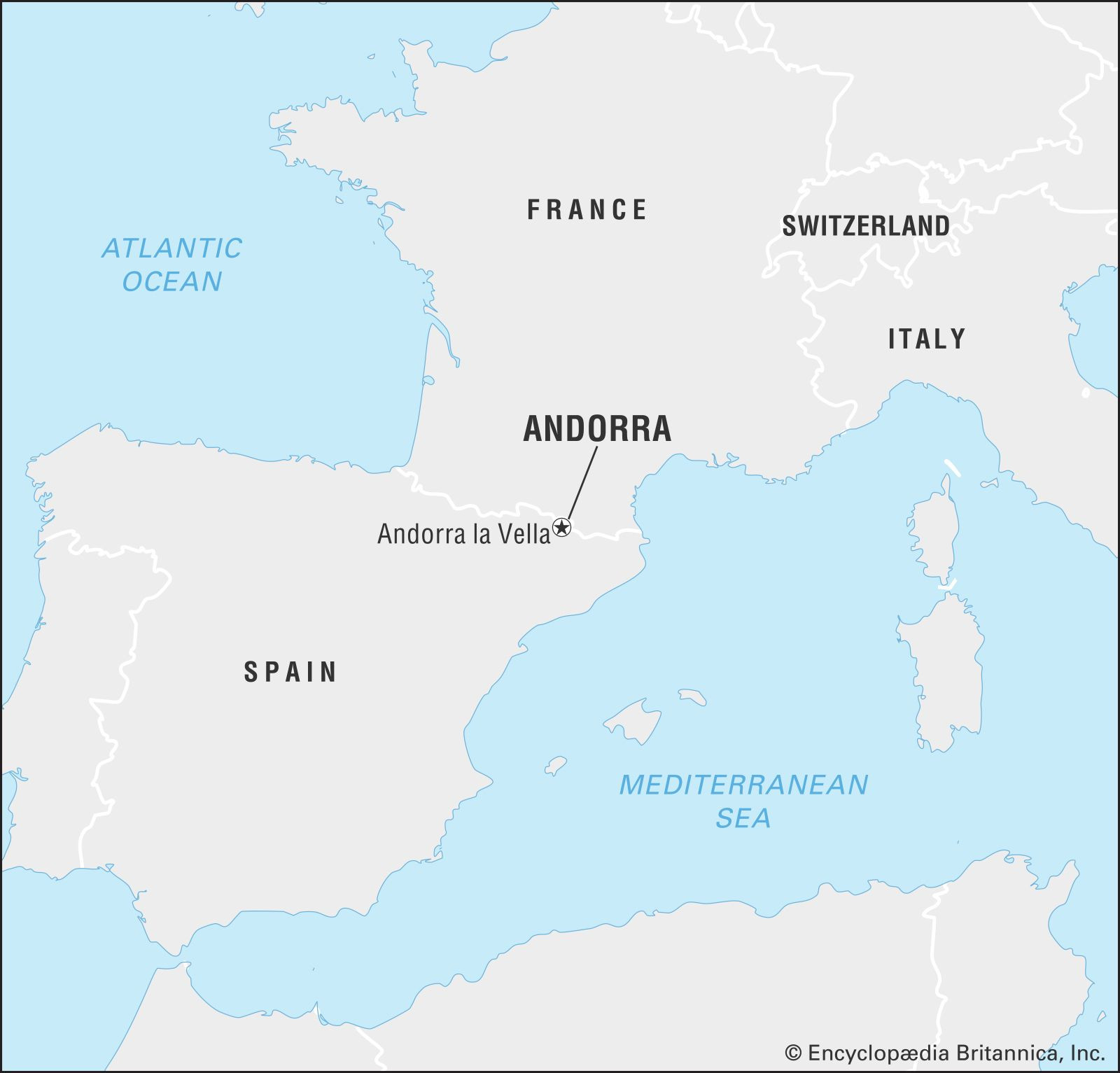
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a captivating microstate nestled high in the Pyrenees Mountains. Often overlooked on the map of Europe, this independent co-principality holds a unique geographical position and a rich history. So, Where Is Andorra exactly?
Andorra is landlocked and strategically situated in southwestern Europe, perched in the eastern Pyrenees mountains. To pinpoint its location more precisely, Andorra is bordered by two much larger European nations: France to the north and east, and Spain to the south and west. This places Andorra in a fascinating cultural and geographical crossroads, blending influences from both Iberian and Gallic traditions. Its capital city, Andorra la Vella, is one of the highest capitals in Europe, reflecting the mountainous terrain that defines the country.
Geographical Location and Landscape
Andorra’s geography is overwhelmingly mountainous, characterized by a stunning network of valleys carved by streams that converge to form the Valira River. The landscape is dominated by the towering peaks of the Pyrenees, creating dramatic vistas and offering breathtaking natural beauty. Within this mountainous terrain lies the Madriu-Perafita-Claror valley, a particularly significant area recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site since 2004. This valley, encompassing about a tenth of Andorra’s territory, showcases remarkable glacial landscapes, steep, rugged valleys, and picturesque open pastures, highlighting the pristine natural environment of Andorra.
Borders and Accessibility
Andorra’s borders are shared with France and Spain, two major European countries. While landlocked, its location amidst the Pyrenees provides both a sense of isolation and a unique accessibility. There is no railway system within Andorra itself, but well-maintained roads connect it to both France and Spain, facilitating travel by car and bus. For air travel, Andorra is served by a nearby small airport located in Seo de Urgel, Spain, providing connections to wider European and international destinations. This accessibility, despite its mountainous location, has been crucial for Andorra’s development, particularly in tourism and trade.
Key Facts and Figures
To further understand Andorra’s place in the world, here are some quick facts:
- Head of Government: Xavier Espot Zamora
- Capital: Andorra la Vella
- Population: Approximately 88,800 (2025 est.)
- Heads of State: Co-Princes – President of France (Emmanuel Macron) and Bishop of Urgell, Spain (Joan Enric Vives Sicília)
- Form of Government: Parliamentary co-principality
- Official Language: Catalan
- Official Religion: None (Roman Catholicism has special recognition)
- Official Name: Principat d’Andorra (Principality of Andorra)
- Total Area: 468 sq km (181 sq mi)
- Currency: Euro (€)
Historical Context
Andorra’s independence is steeped in history, traditionally linked to Charlemagne in 803 AD, who is said to have liberated the region from the Muslims. His son, Louis I, further solidified Andorra’s status by granting a charter of liberties to its inhabitants. Over time, control passed to the Counts of Urgel and subsequently to the Bishops of Urgel. This historical trajectory laid the foundation for Andorra’s unique dual governance system. By the late 13th century, a proprietary dispute led to the establishment of the co-principality, with governance shared between the Spanish Bishop of Urgel and the French heirs to the Countship of Urgel. This feudal system endured until 1993, marking Andorra as one of Europe’s oldest surviving microstates with a distinctive political heritage.
Modern Andorra
In modern times, Andorra has evolved into a thriving nation. While not a member of the European Union, it adopted the euro as its official currency in 2002 and formalized this with a monetary agreement with the EU in 2011. The 1993 constitution was a pivotal moment, modernizing the government by establishing separate executive, legislative, and judicial branches and significantly reducing the powers of the co-princes. Andorra joined the United Nations in 1993 and the Council of Europe in 1994, asserting its place on the international stage.
Economically, Andorra has transitioned from a traditional agricultural base to an economy largely driven by tourism, retail trade, and banking. Its duty-free status has made it a popular shopping destination, attracting visitors from across Europe. The stunning Pyrenean landscape and excellent winter sports facilities further bolster its tourism industry.
In conclusion, Andorra’s location in the heart of the Pyrenees Mountains, nestled between France and Spain, is central to its identity. This unique geographical position has shaped its history, culture, and economy, making Andorra a fascinating and distinctive European nation, a hidden gem waiting to be discovered.